High-pressure reducing valve
A pressure reducing valve, high pressure technology, applied in the field of high pressure pressure reducing valve, can solve the problems affecting the stability of the outlet pressure, the change of the outlet pressure, and the change of the throttle area of the orifice, so as to improve the accuracy of the pressure stabilization, reduce the area of the piston, The effect of reducing friction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
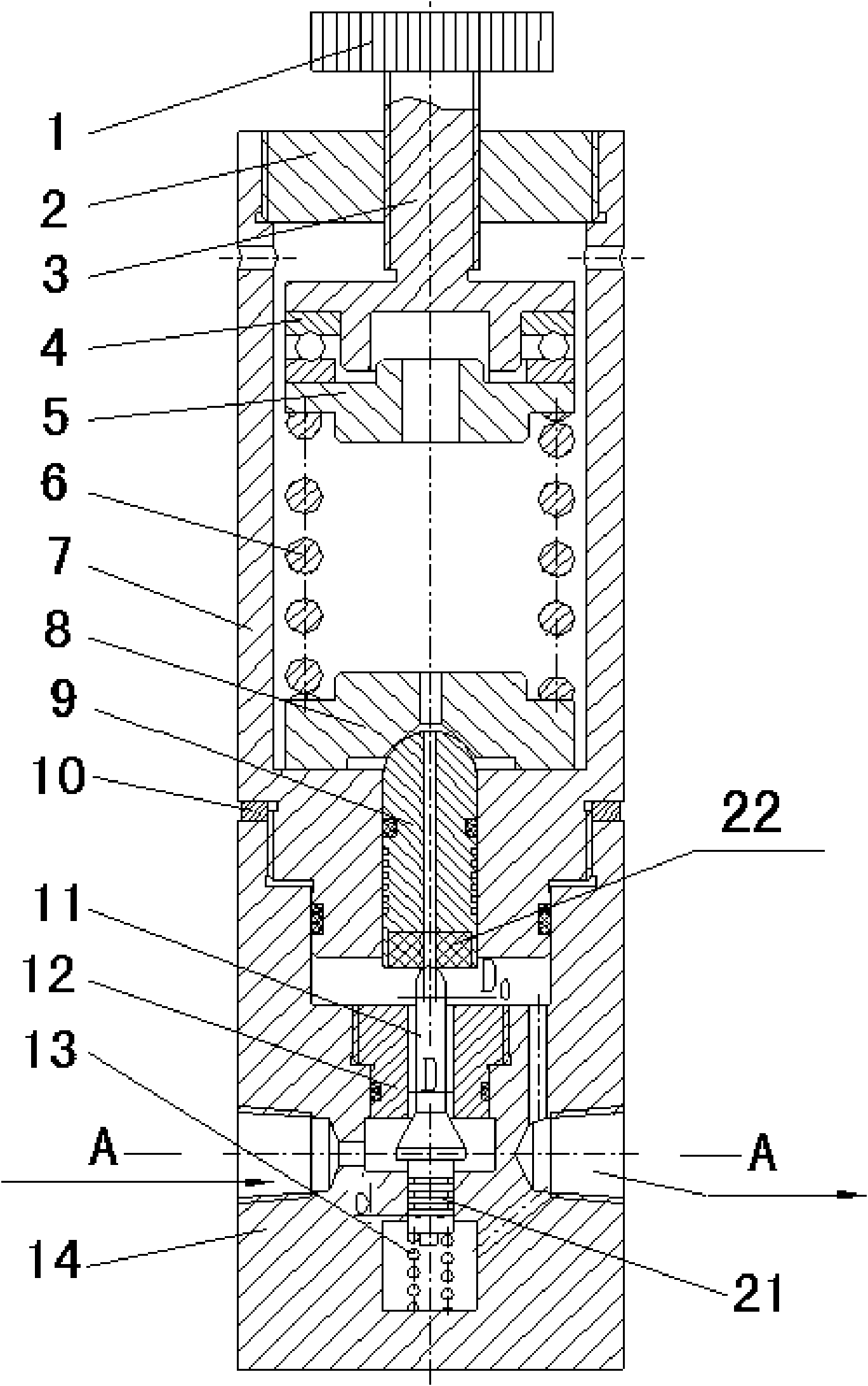
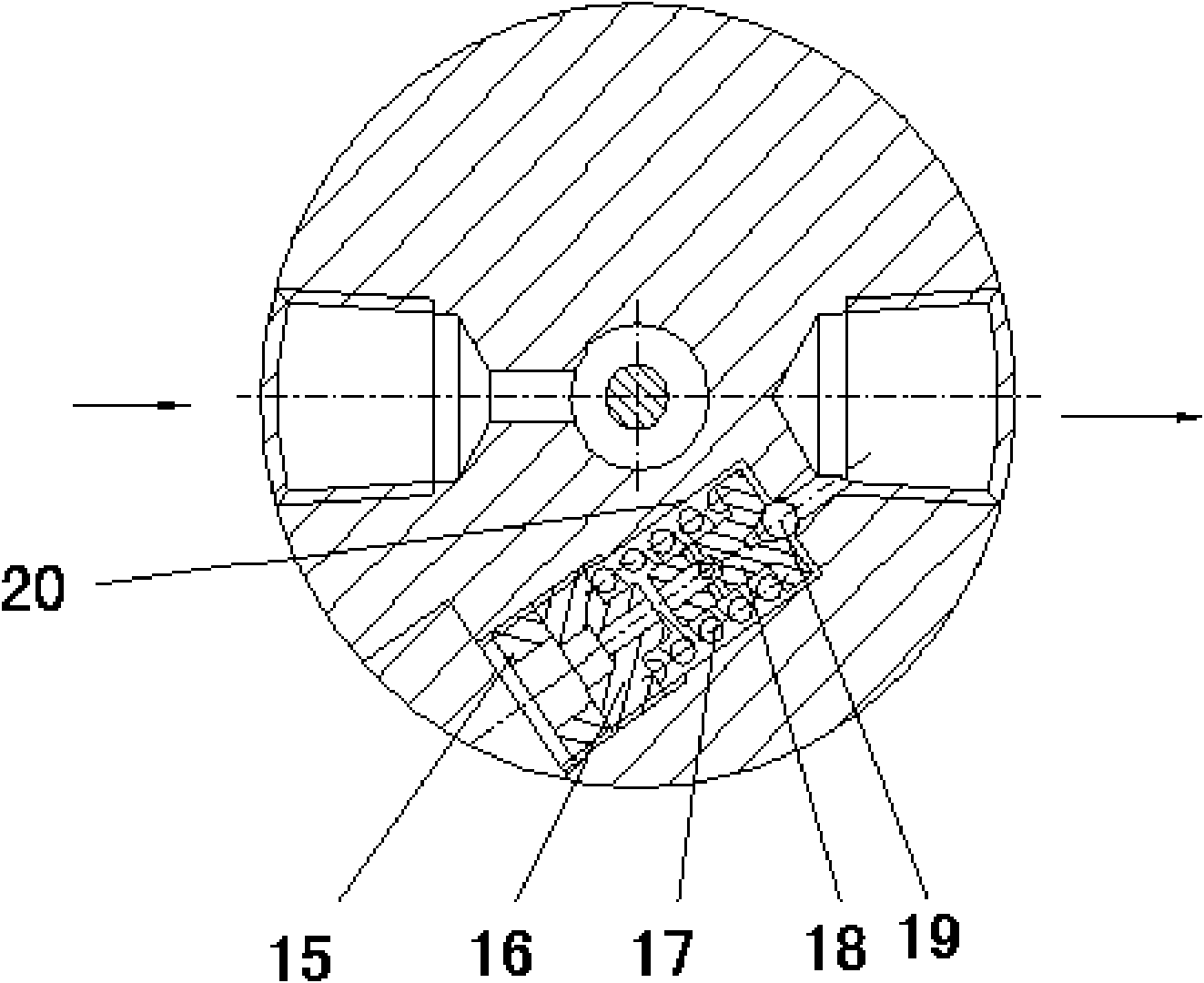
[0028] Such as figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, the arrow in the figure shows the direction of gas flow. The high-pressure pressure relief valve provided by the present invention includes upper and lower valve bodies 7 and 14 connected by threads. 9. There is a spring pressure regulating device on the top of the piston 9. The spring pressure regulating device includes a pressure regulating knob 1 screwed on the top of the upper valve body 7, a pressure regulating shaft 3 fixedly connected with the pressure regulating knob 1, and a rotating assembly on the lower end of the pressure regulating shaft 3. The pressure regulating spring seat 5, the piston seat 8 assembled on the top of the piston 9, the pressure regulating spring 6 installed between the pressure regulating spring seat 5 and the piston seat 8. A thrust ball bearing 4 is installed between the pressure regulating shaft 3 and the pressure regulating spring seat 5, and the pressure regulating spring 6 is connected between...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com