Inversion of alternate instruction and/or data bits in a computer
A digital, even number technique used in the field of physical representation of binary numbers in computer circuits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
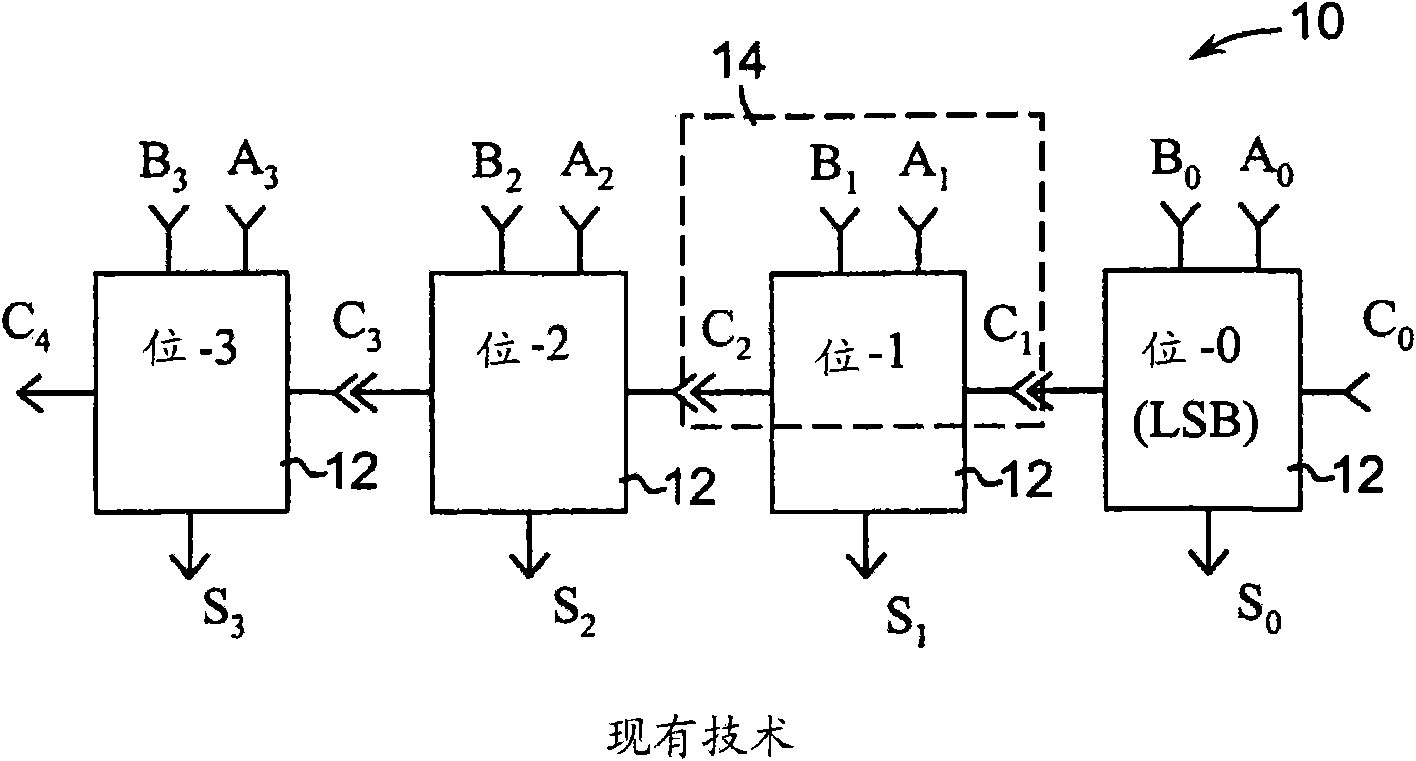
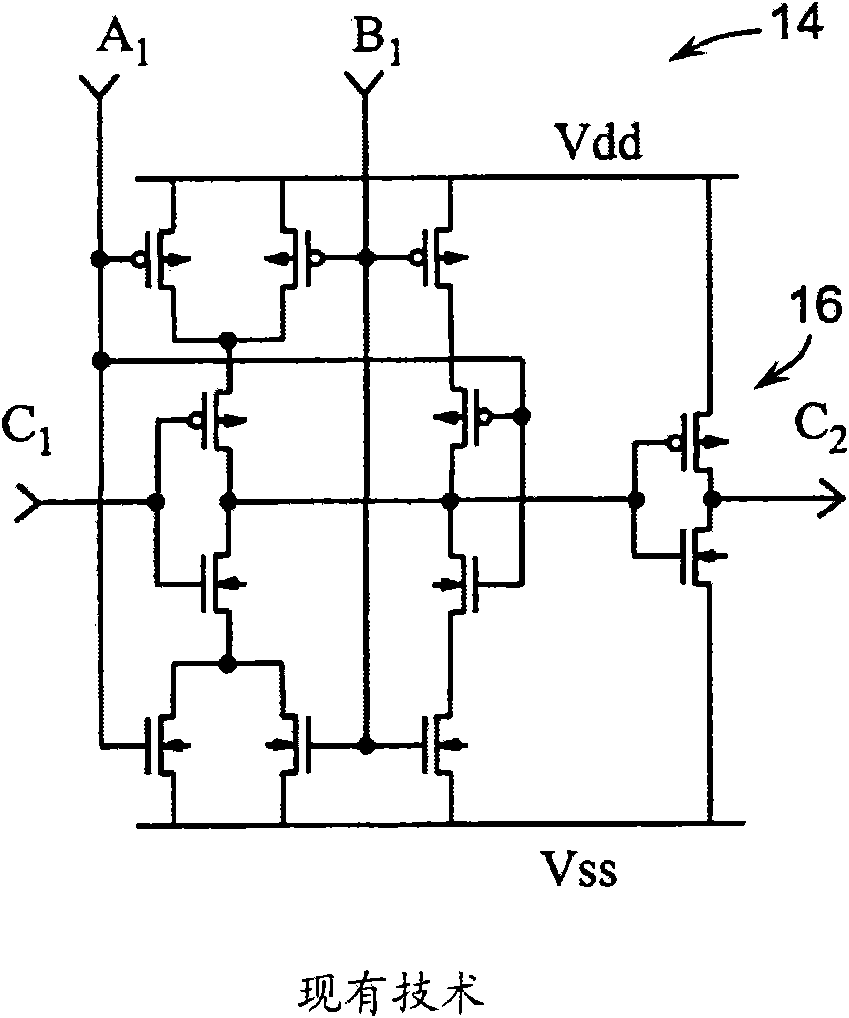
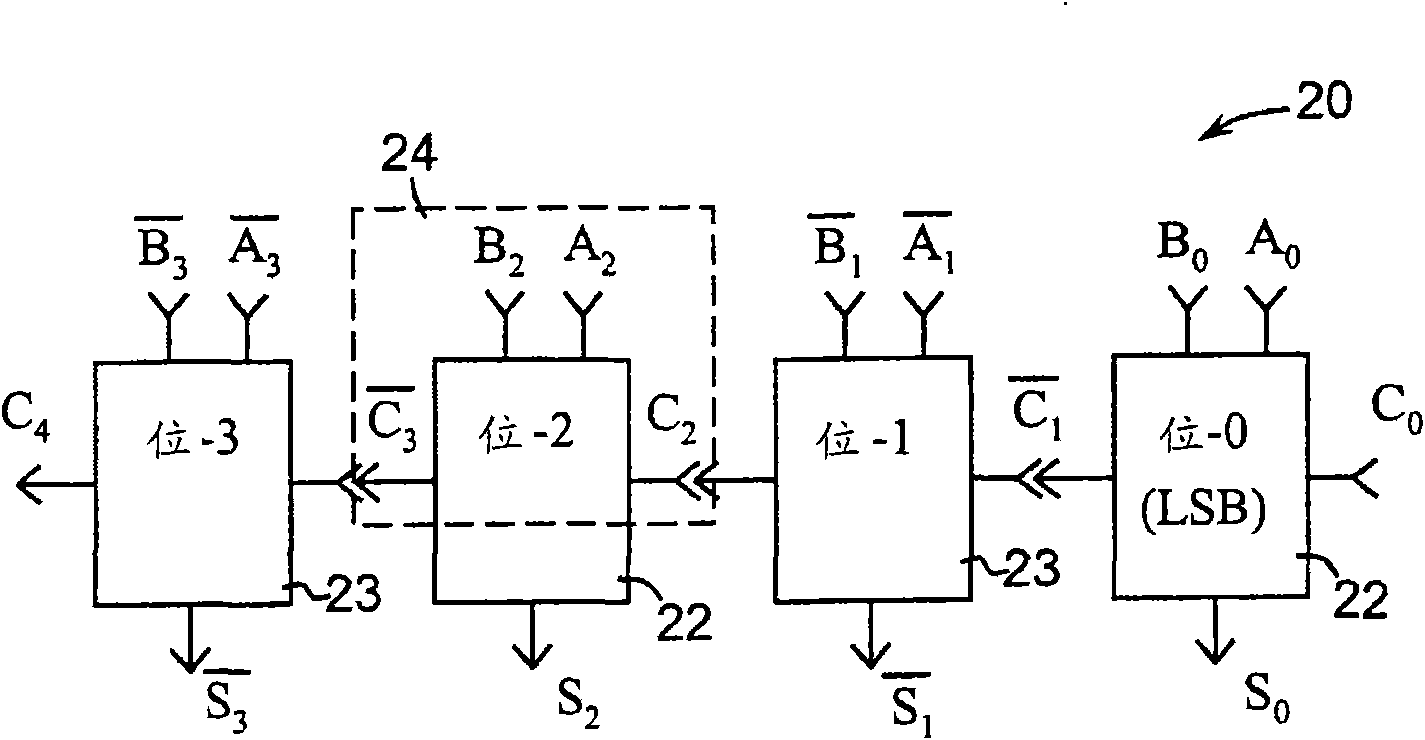
[0022] With reference to the accompanying drawings, the present invention is described in the following description, wherein the same numbers represent the same or similar elements. Although the present invention has been described in terms of a mode for achieving the purpose of the present invention, those skilled in the art will understand that modifications can be made in consideration of these teachings without departing from the spirit or scope of the present invention.
[0023] The embodiments and modifications of the present invention described here and / or shown in the drawings are given only for the sake of example, and they do not limit the scope of the present invention. Unless specifically stated otherwise, various aspects and components of the present invention can be omitted or modified, or, therefore, they can be replaced with known equivalents, or alternatives that are still unknown (such as those that can be developed in the future, or can be Future discoveries ar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com