A method of providing hip-based mobility services to hip nodes
A mobility and node technology, applied in transmission systems, electrical components, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] Abbreviations used in the discussion below include:
[0021] DNS - Domain Name System
[0022] HIP - Host Identification Protocol
[0023] IETF - Internet Engineering Task Force
[0024] RVS - Rendezvous Server
[0025] WG - Working Group
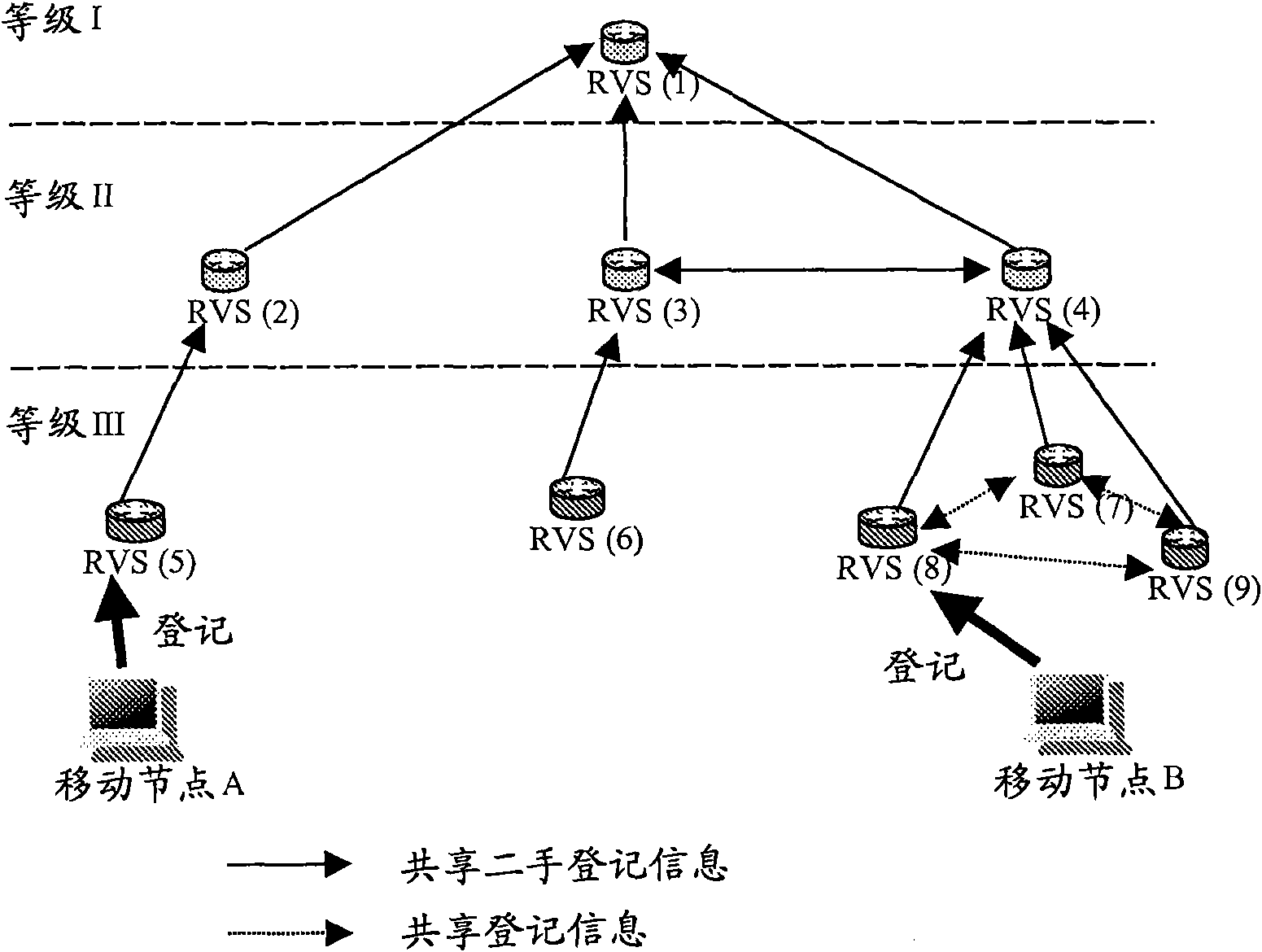
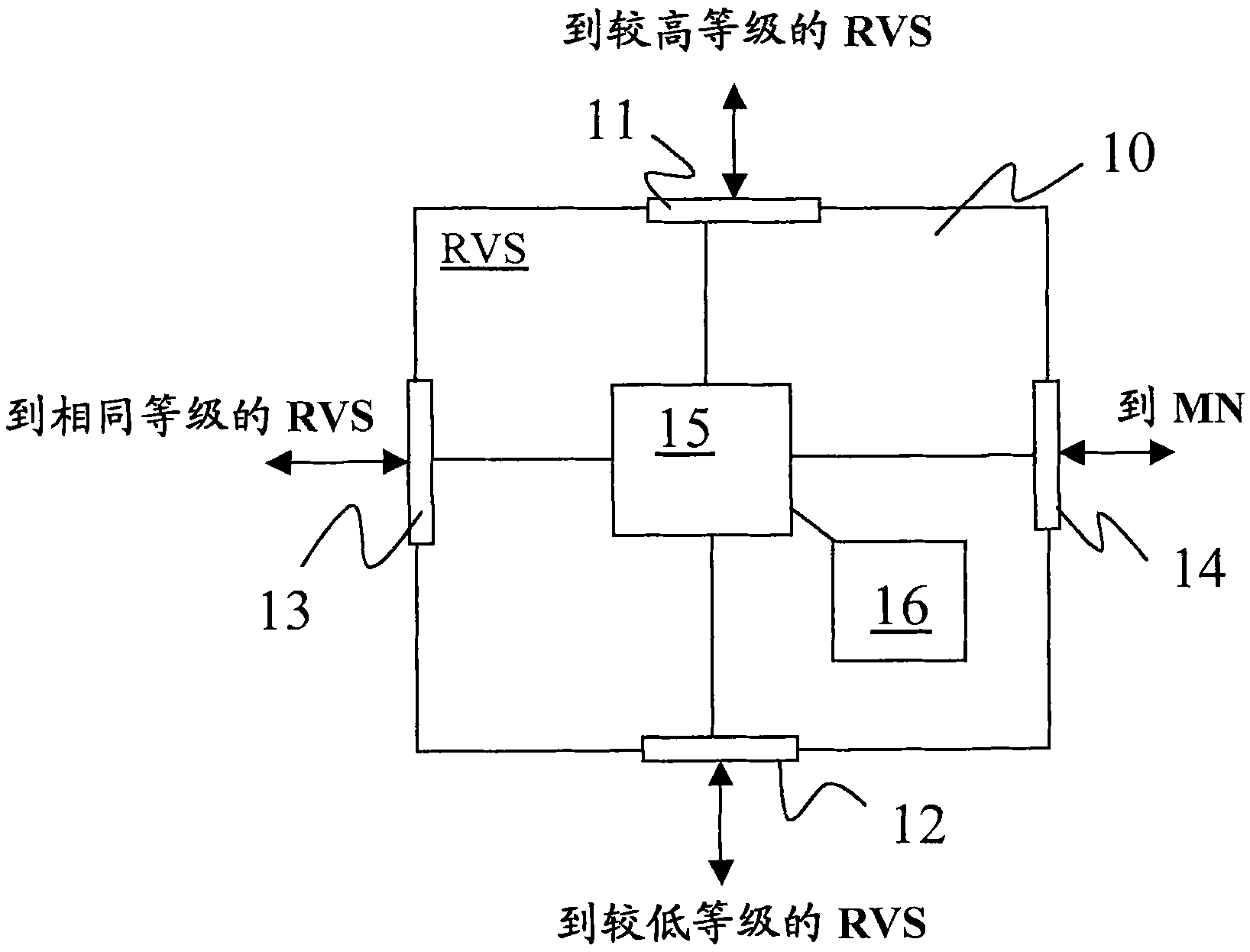
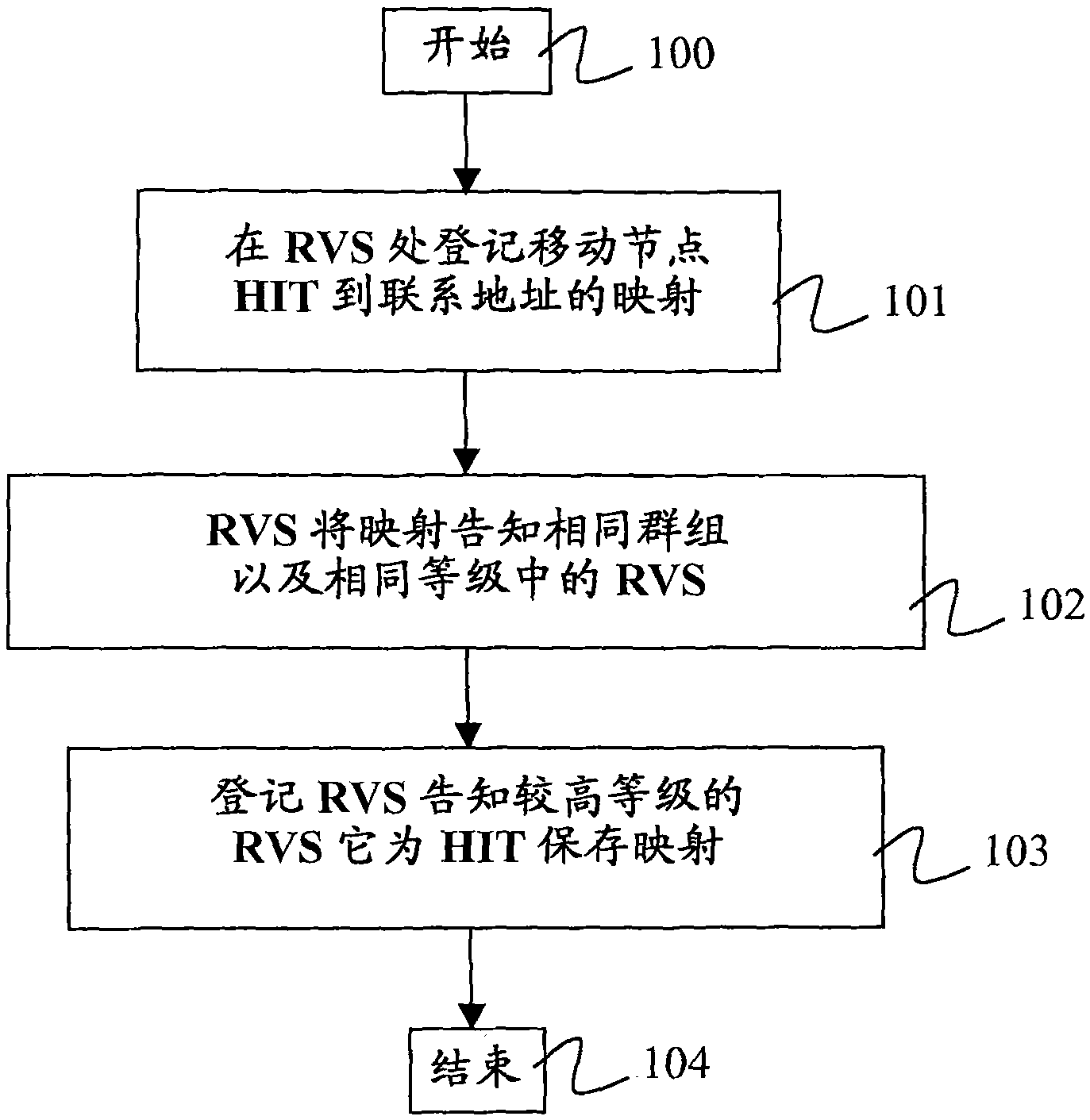
[0026] A hierarchical and robust RVS architecture is proposed here. Registration information is shared between RVSs that are close to each other from a network perspective. All of these RVSs can be used to locate a mobile HIP node, not just the one with which the HIP node is registered. In addition, information identifying the RVS that knows the location of the mobile HIP node is shared with one or more RVSs at higher levels in the RVS hierarchy. These higher level RVSs do not know the actual current location of the HIP node, ie its contact (IP) address, but are able to identify the RVS with this information. If the RVS does not know the target host for the I1 group (initiator 1's group), send the I1 group up the RVS hierarchy...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com