Process for producing regenerated building waste autoclaved brick
A construction waste and production process technology, which is applied in the field of regenerated construction waste autoclaved brick production process, can solve the problems of no recycling, environmental impact, large quantity, etc., and achieves low processing cost, reduced waste, and simple process. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
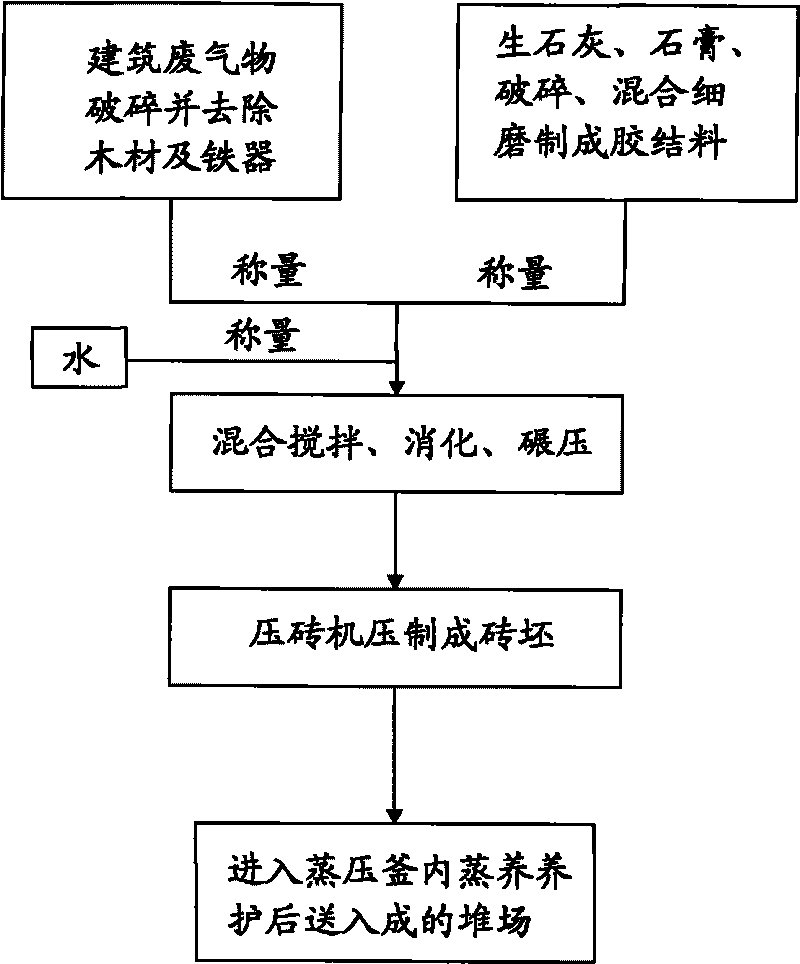
[0036] Embodiment one, such as figure 2 Shown:
[0037] 1. Raw material preparation
[0038] 1. Construction waste: The construction waste is transported by dump truck into the factory shed for storage, and after simple pre-homogenization, it is transported by belt to the jaw crusher for coarse crushing. The particle size of the coarse crushing is controlled below 20mm. After wood removal and iron removal with permanent magnetic suspension iron remover, the coarsely crushed products enter the hammer crusher by gravity to be finely crushed to less than 5mm, and then manually remove wood and iron removal with permanent magnetic suspension iron remover, and then store in the silo for use. The composition of the construction waste treated by this step satisfies the SiO 2 Not less than 40%, Al 2 o 3 15-35%, SO 3 Not more than 2%, loss on ignition not more than 12%.
[0039]2. Quicklime and gypsum: block quicklime is transported into the factory by dump truck, and poured into...
Embodiment 2
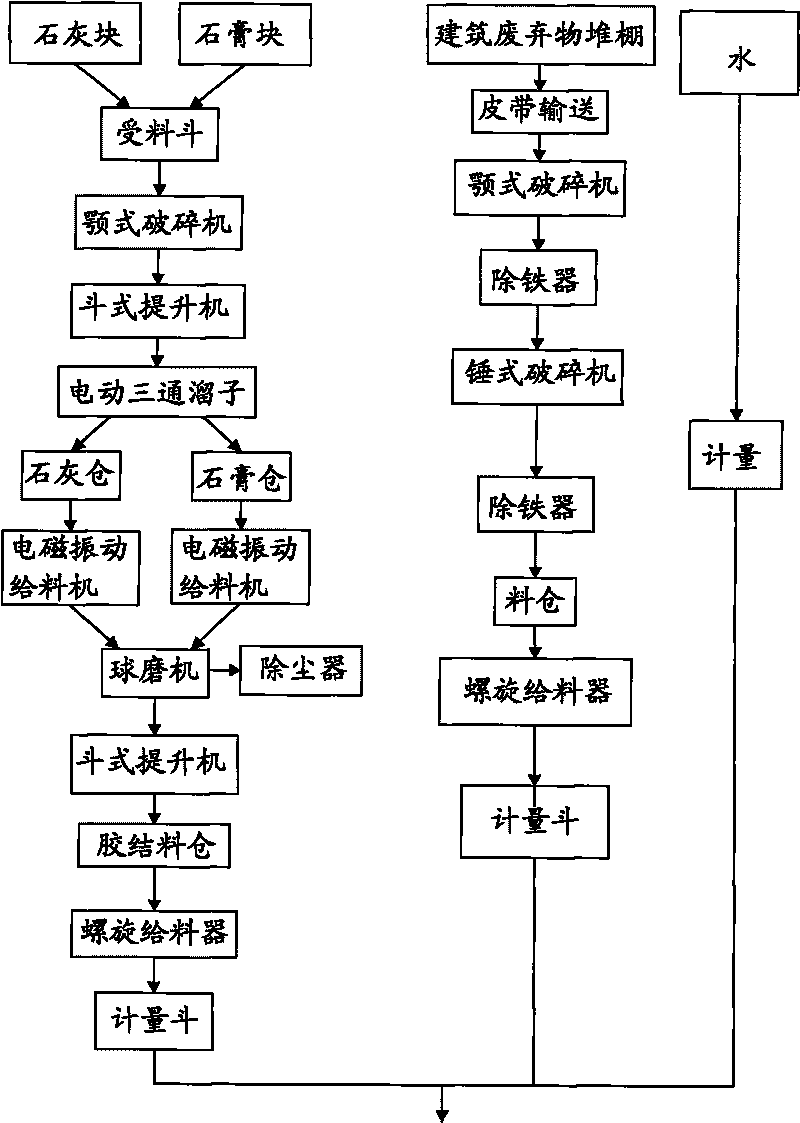
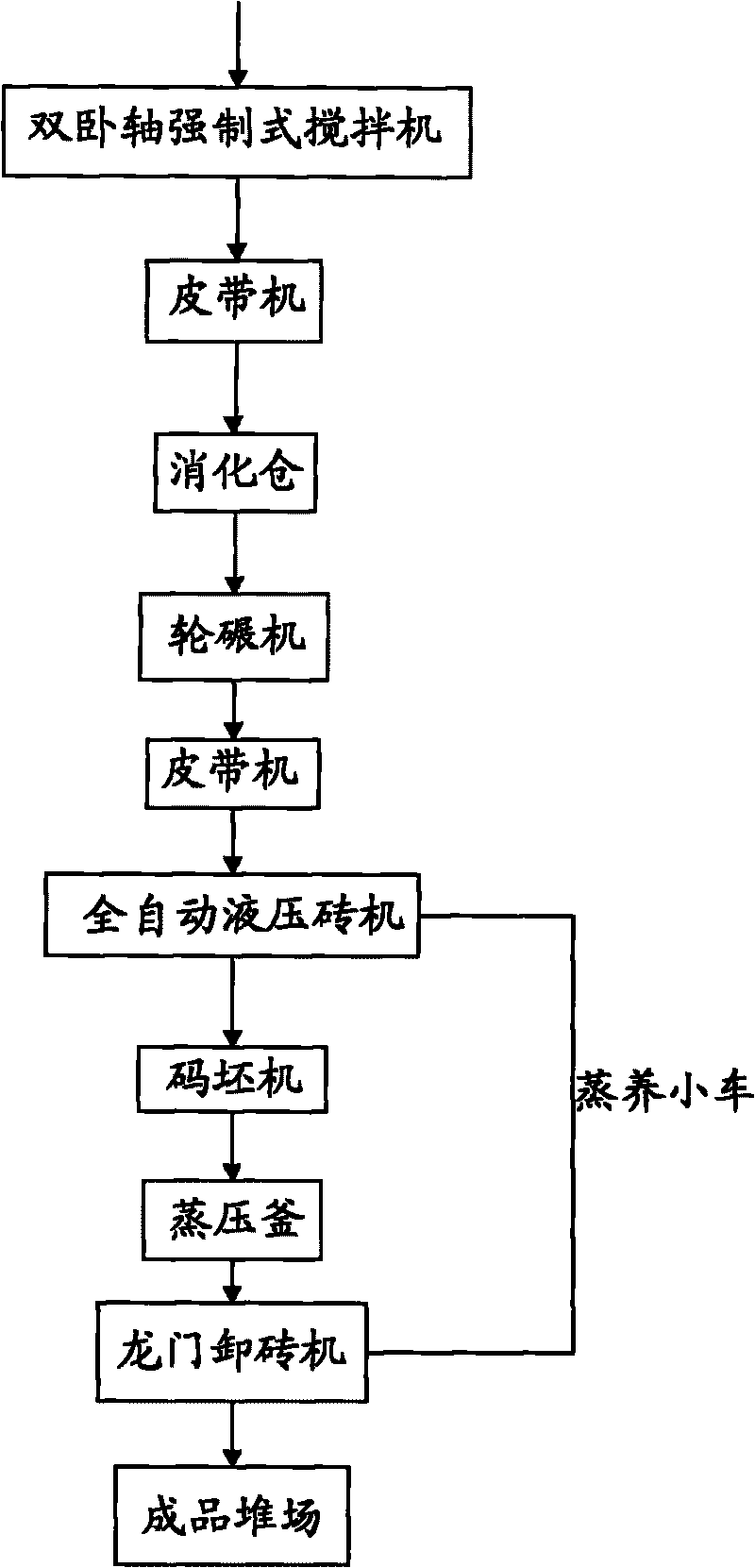
[0047] Embodiment two, such as image 3 Shown:
[0048] 1. Raw material preparation
[0049] 1. Construction waste
[0050] Coarsely crushed products enter the hammer crusher by gravity and finely crush to less than 2.5mm, and the rest are the same as the above-mentioned embodiments
[0051] 2. Quicklime, gypsum
[0052] Wherein, quicklime and gypsum are fed into a ball mill at a ratio of 9:2 for mixing and fine grinding, and the rest are the same as in the first embodiment above.
[0053] 3. Water and additives
[0054] The water is common tap water, and the admixture can be purchased from chemical raw materials or chemical waste. The admixture is a reinforcing agent such as JM-I type (super early strength) concrete high-efficiency reinforcing agent, a plasticizer such as a low-viscosity polycarboxylate superplasticizer, a coagulation regulator such as XPM coagulation regulator, and a diluent such as XHDB001 A mixture of thinners, the reinforcing agent, plasticizer, coa...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Embodiment three, still refer to image 3 Shown:
[0062] 1. Raw material preparation
[0063] 1. Construction waste
[0064] With the above-mentioned embodiment one.
[0065] 2. Quicklime, gypsum
[0066] Wherein, quicklime and gypsum are fed into a ball mill at a mass ratio of 3:1 for mixing and fine grinding, and the rest are the same as in the first embodiment above.
[0067] 3. Water and additives
[0068] The water is common tap water, and the admixture can be purchased from chemical raw materials or chemical waste. The admixture is a reinforcing agent such as a silicone concrete reinforcing agent, a plasticizer such as a construction mortar plasticizer, a coagulation regulator such as an XPM coagulation regulator, and a diluent such as a mixture of XHDB001 type diluents. The reinforcing agent, plasticizer, The amount of coagulation regulator and diluent accounts for 0.4-0.7% of the total weight of crushed construction waste, lime and gypsum, and the total a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com