Water absorbing agent for paper and preparation method thereof
A technology for water-absorbing agent and paper, applied in the direction of papermaking, textile and papermaking, non-fiber pulp addition, etc., can solve the problems of reduced wet strength, reduced water absorption performance, unfavorable water absorption, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
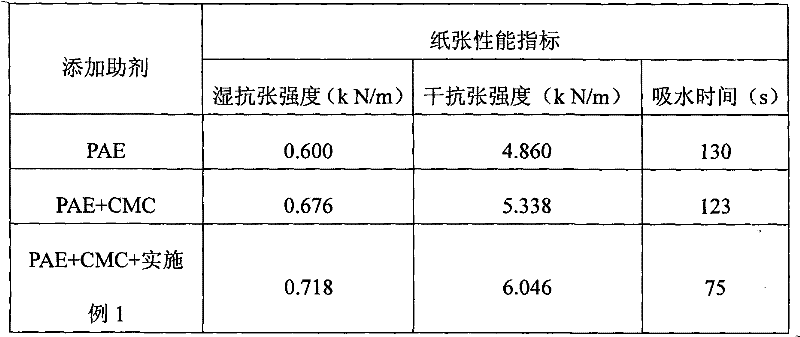
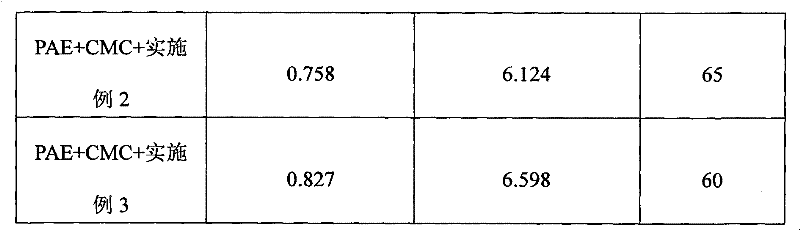
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Add 206 grams of diethylenetriamine to a 2L four-necked flask equipped with a condenser, a thermometer and agitation. While stirring, add 20.6 grams of hydrochloric acid with a concentration of 10% by weight. After stirring evenly, add hexane within one hour. 292 grams of diacid, reacted at 130°C for 30 minutes, continued to heat up to 190°C and reacted for 2 hours, and when cooled to 140°C, added 426 grams of hot water at 80°C to obtain a polycondensate solution with a solid content of 50%, and cooled to room temperature.
[0025] In the polycondensate solution, adjust the pH of the polycondensate solution to 5.0 with formic acid with a weight concentration of 10%, add 0.7 g of glyoxal with a weight of 30%, stir well, slowly heat up to boiling, and reflux for 1 hour, add 365 grams of deionized water to adjust the solid content of the solution to 35%, and then reduce the system temperature to 40°C;
[0026] Use 32% sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH value of the above s...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Add 292 grams of triethylenetetramine to a 2L four-necked flask equipped with a condenser, a thermometer and agitation. While stirring, add 87.6 grams of hydrochloric acid with a concentration of 10% by weight. After stirring evenly, add butyl 236 grams of diacid, reacted at 130°C for 40 minutes, continued to heat up to 180°C and reacted for 3 hours, and when cooled to 140°C, added 456 grams of hot water at 80°C to obtain a polycondensate solution with a weight concentration and a solid content of 50%. , cooled to room temperature.
[0029] In the polycondensate solution, adjust the pH of the polycondensate solution to 5.5 with formic acid with a weight concentration of 10%, add 2.92 grams of glyoxal with a weight concentration of 30%, after stirring evenly, slowly heat up to boiling, and reflux after 1.5 hours, Add 608 grams of deionized water to adjust the solid content of the solution to 30%, and then lower the system temperature to 40°C;
[0030] Use 32% potassium ...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Add 199 grams of tetraethylenepentamine to a 2L four-necked flask equipped with a condenser, a thermometer and stirring, and add 99.5 grams of sulfuric acid with a concentration of 10% by weight while stirring. 202 grams of diacid, react at 130°C for 60 minutes, continue to heat up to 155°C and react for 6 hours, when cooling to 140°C, add 329 grams of hot water at 80°C to obtain a polycondensate solution with a solid content of 50%, and cool down to room temperature.
[0033] In the polycondensate solution, use 10% hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH of the polycondensate solution to 6.0, add 33.1 grams of glutaraldehyde with a weight concentration of 30%, stir evenly, slowly heat up to boiling, reflux for 1 hour, and then add The weight concentration solid content of 517 grams of ionized water adjustment solution is 28%, then system temperature is down to 40 ℃;
[0034] Use 32% sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH value of the above solution to 8.5, slowly add 46 grams o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com