A shift register circuit having threshold voltage compensation
A shift register and threshold voltage technology, applied in static memory, digital memory information, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as transistor performance degradation and limited circuit life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
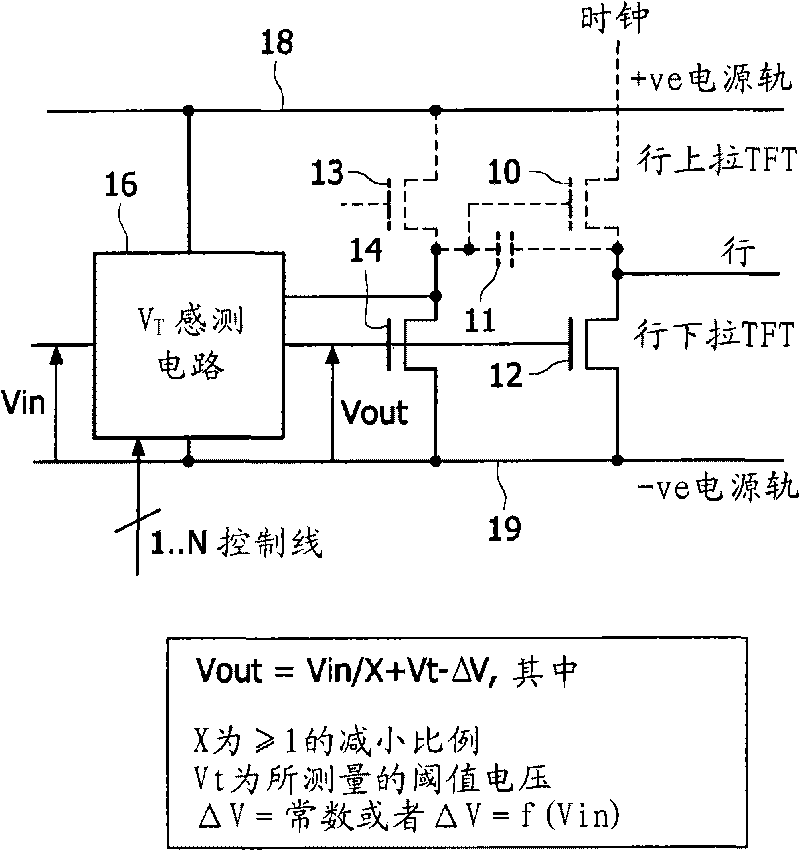
[0060] figure 1 A first simplified example of the inventive circuit is shown to illustrate the principles of the invention.
[0061] The present invention provides sensing of the threshold voltage of the most critical transistor or transistors in the circuit. The row driver circuit has: a row pull-up transistor 10, which is turned on to provide a row pulse on the row from the clocked power supply line "CLOCK"; and a row pull-down transistor 12, which is used on the remaining Time keeps the row at a low negative power rail voltage. Row pull-down transistor 12 operates at a high duty cycle and therefore suffers from the greatest drift.
[0062] In one example, the present invention provides threshold voltage sensing of the row pull-down transistor 12 . The sensing circuit may use thin film transistors (TFTs) of the row driver circuit, or it may use dedicated TFTs designed to match the characteristics of the TFT being compensated.
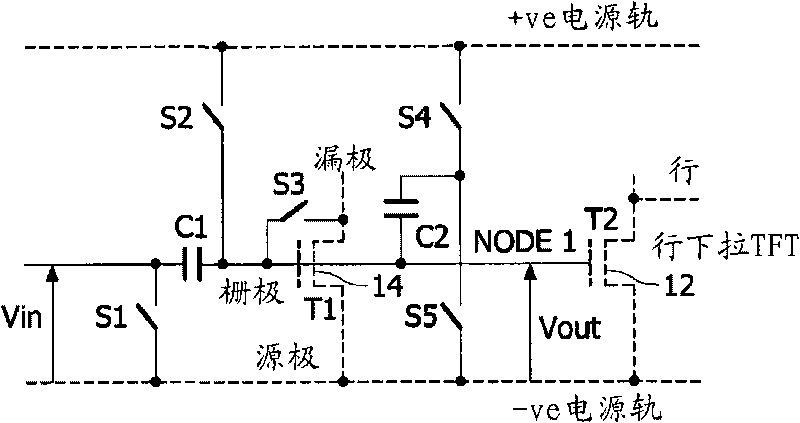
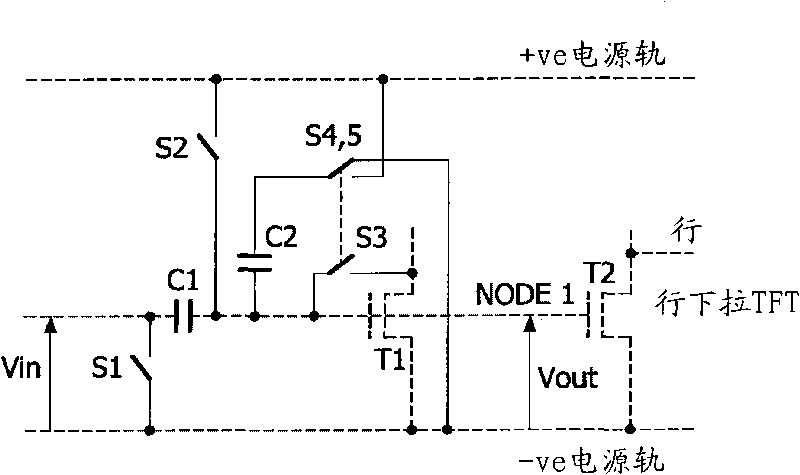
[0063] figure 1 Transistor 14 for replicat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com