Method and device for marking a surface using controlled periodic nanostructures
A technology of marking and equipment, applied in the field of nanostructure marking surface, which can solve the problems of slow speed and not allowed to write
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
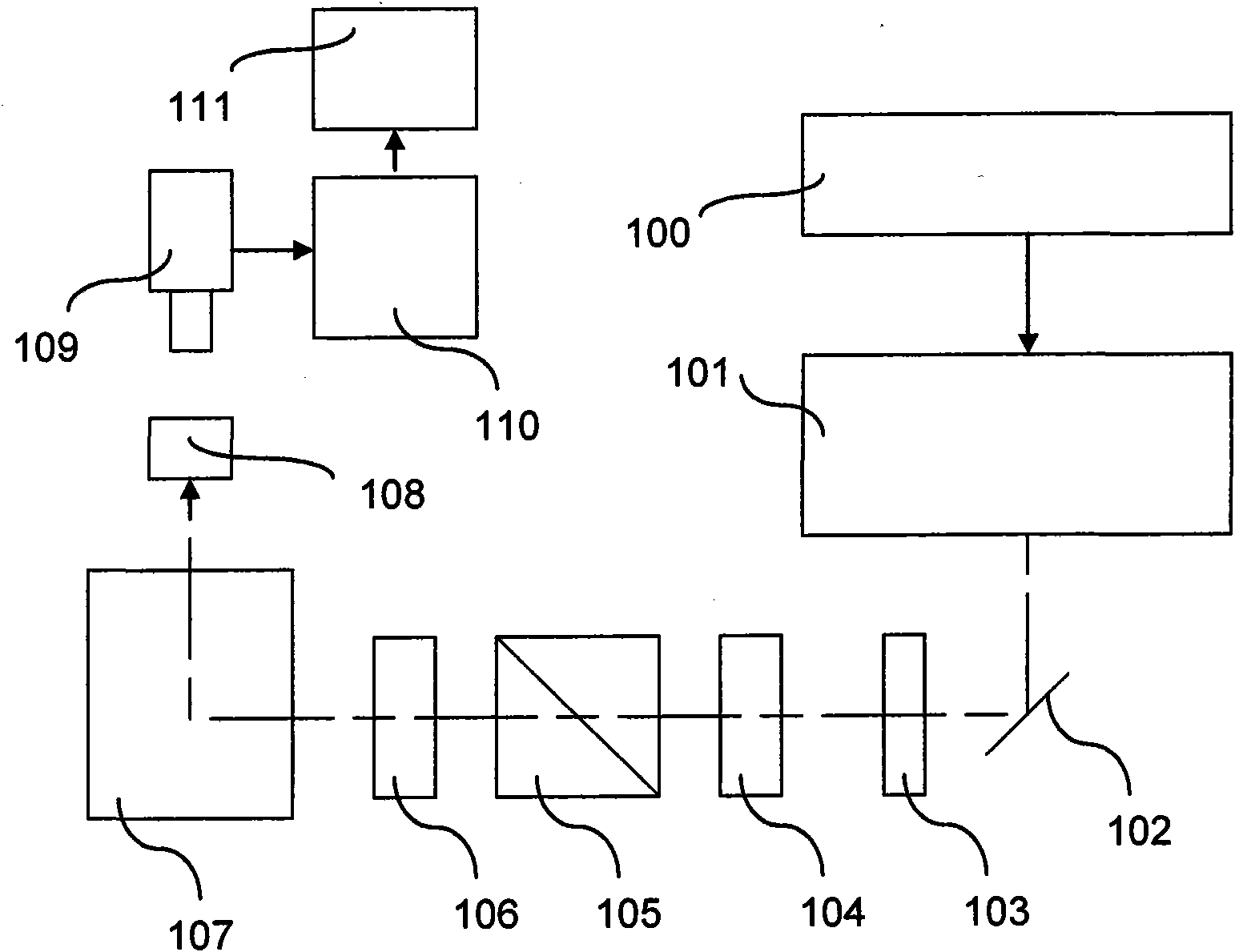
[0049] figure 1 Shown are a control device 100 , a laser 101 , a mirror 102 , an aperture 103 , a polarizer 104 , a separator cube 105 , a polarizer 106 , a scanner 107 and a surface 108 to be marked.
[0050] The control device 100 of the laser 101 is designed to be able to determine the image to be marked on the surface 108, an area table of coded items carrying information for each area forming the image.
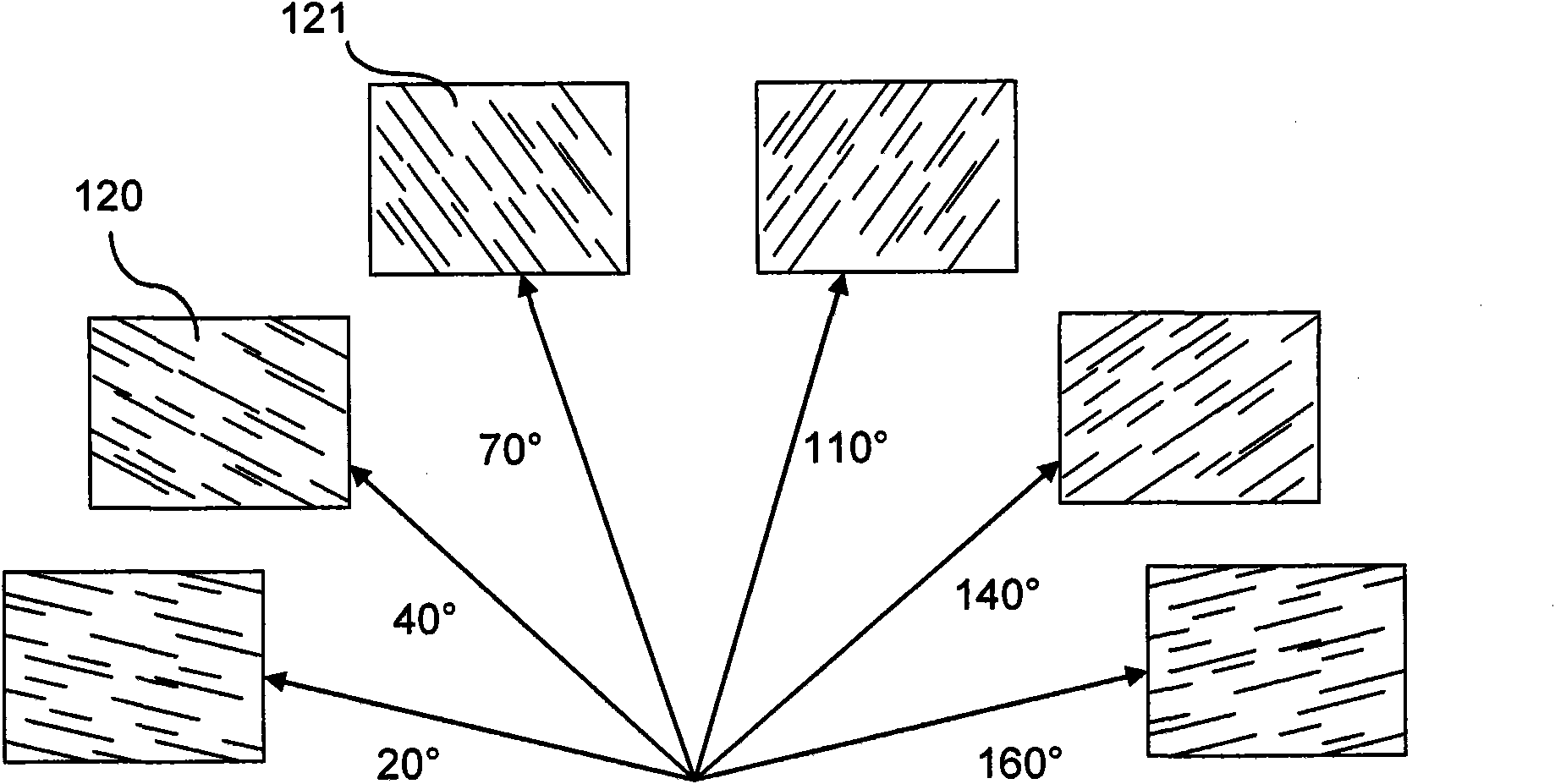
[0051] The information items carried by each field may or may not be binary. As described below, a region carries at least one information value (here each) corresponding to a particular polarization orientation and another information value corresponding to no label, no polarization or a different polarization orientation.
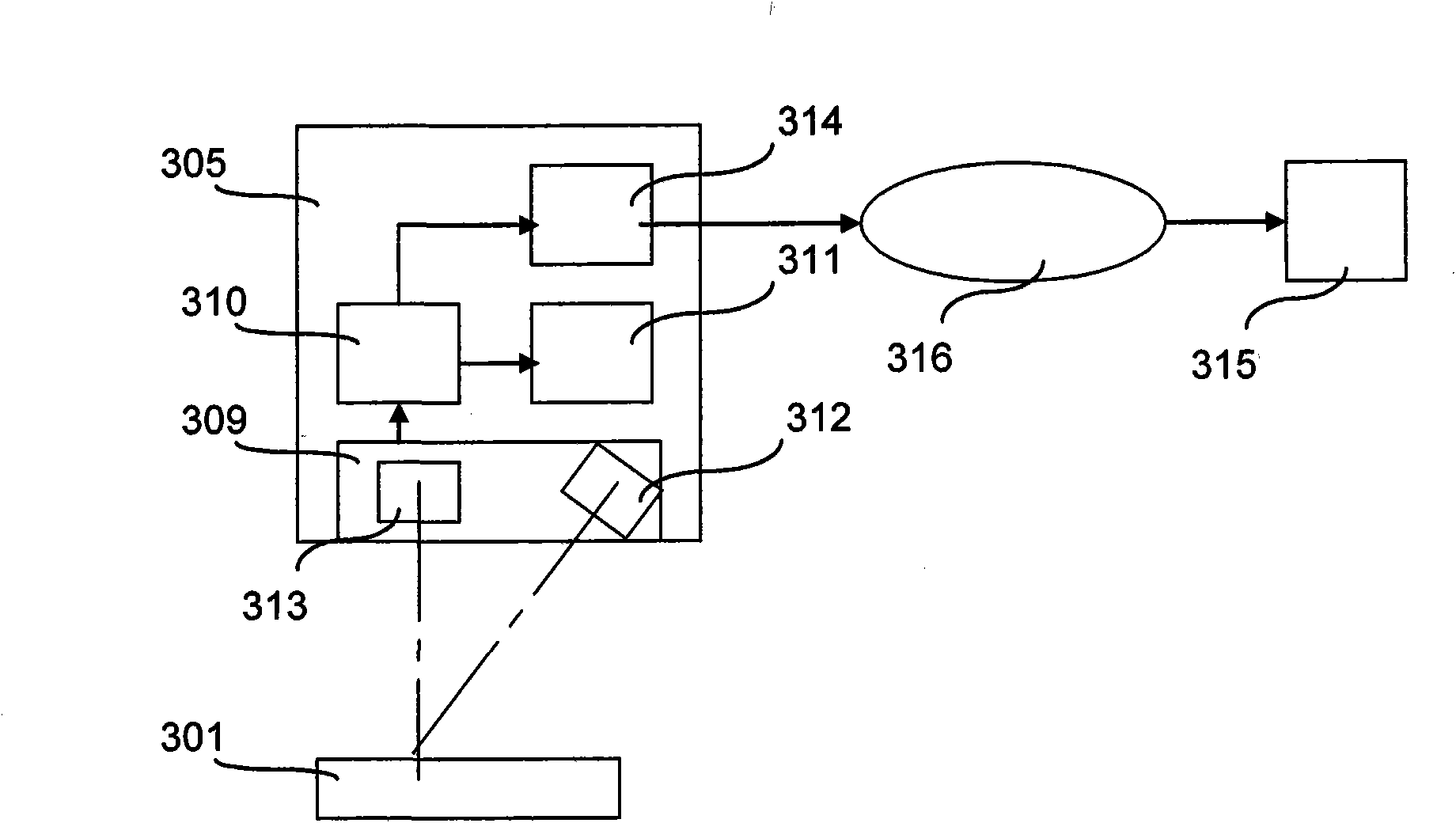
[0052] In an embodiment, the control device 100 receives encoded items of information from a computer system. In another embodiment, the control device 100 receives information to be encoded of an image and calculates the image after encoding the in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com