Magnetic resistance type magnetic suspension device
A suspension device and magnetoresistive technology, applied in the field of magnetic suspension, can solve the problems of high cost, low energy consumption and high energy consumption of the magnetic suspension device, and achieve the effect of large magnetic force and low energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
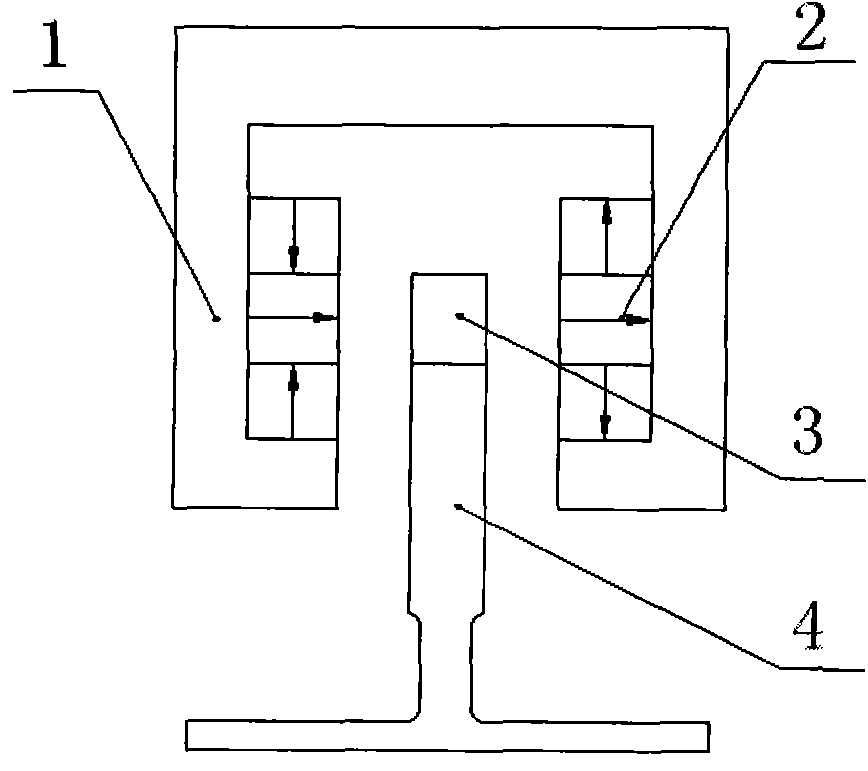
[0043] figure 1 Among them, the magnetoresistive magnetic levitation device includes a magnet frame 1, two rows of magnet arrays 2 arranged in the form of Halbach arrays are fixed on both sides of the non-magnetically conductive magnet frame 1, and the two rows of Halbach arrays 2 are arranged in parallel and at equal heights, and each row of Halbach arrays Array 2 contains three magnets, and the magnetization directions of the three magnets from top to bottom in one column are as follows: vertically upward, horizontally to the right, and vertically downward; corresponding to the magnetization of the other three magnets from top to bottom The directions are as follows: vertically downward, horizontally to the right, and vertically upward, a loop of magnetic force lines is formed between two rows of Halbach arrays 2; between the two rows of Halbach arrays 2 is a magnetically conductive yoke I3, and the yoke I3 and the Halbach arrays on both sides The air gaps of 2 are equal, an...
Embodiment 2
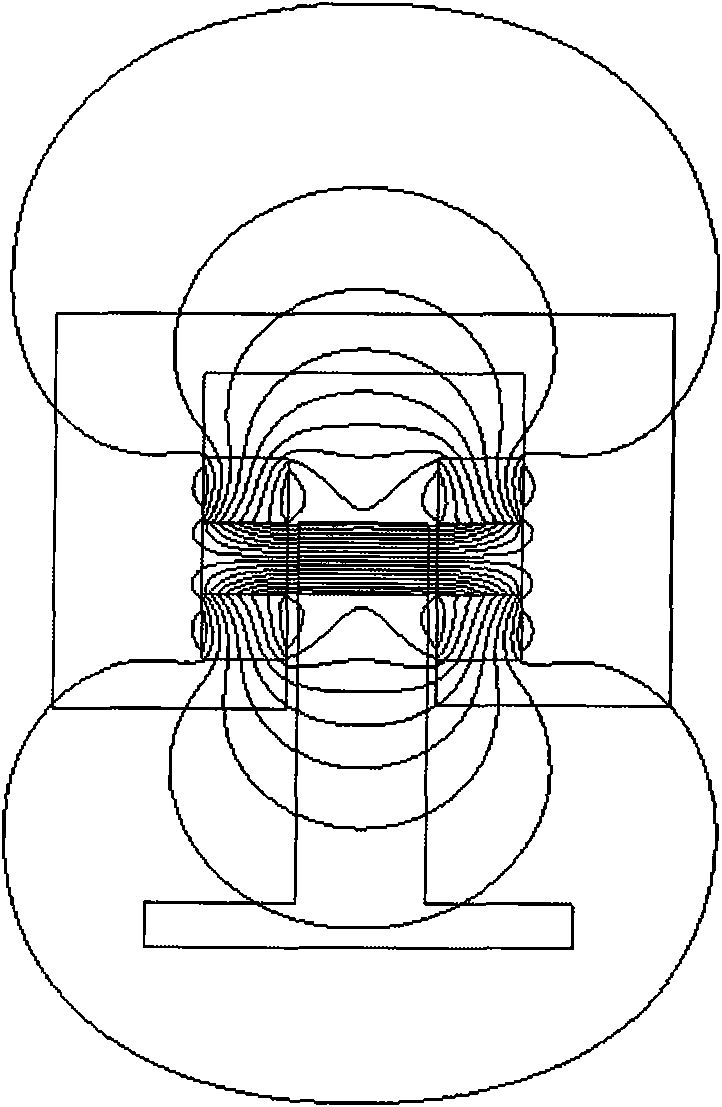
[0049] like Image 6 As shown, the yoke II 8 is fixed at the bottom of the Halbach array 2 , the yoke III 9 is fixed between the Halbach array 2 and the magnet frame 1 , and other structures are the same as in the first embodiment.
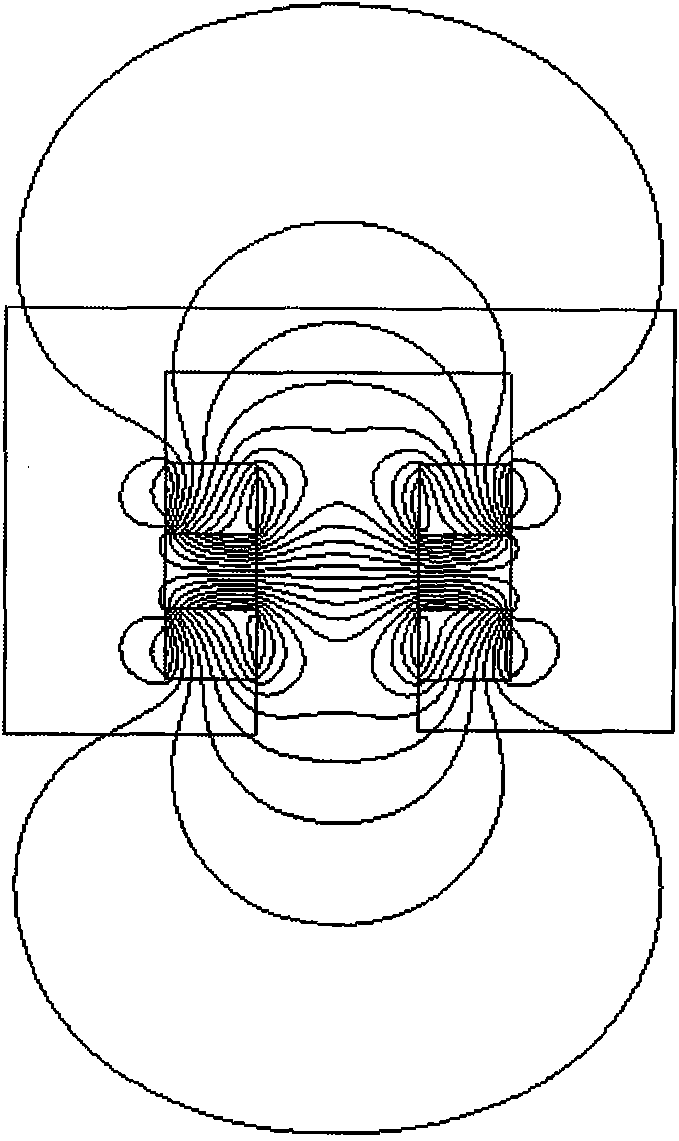
[0050] like Figure 7 As shown, after the upper and lower ends of the two Halbach arrays 2 are respectively fixed with yokes II8 and III9, the schematic diagram of the distribution of magnetic force lines between the two Halbach arrays 2 is shown. The magnetic field path at the center of the two Halbach arrays 2 is the shortest, and the magnetic field path at the upper and lower ends is the longest. From the principle of Embodiment 1, it can be seen that when the horizontal centerline of the yoke I3 coincides with the centerline of the middle magnet in the Halbach array 2, the vertical force on the yoke I3 is minimal. When the yoke I3 moves upward, the yoke I3 is subjected to the downward restoring force of the magnet; on the contrary, when the yo...
Embodiment 3
[0053] like Figure 11 As shown, two rows of magnet arrays 11 arranged at intervals are fixed on both sides of the magnet frame 1, and a magnetic field line loop is formed between the two rows of interval arrays 11. A magnet, a protruding iron 10 is set between the two magnets; the magnetization directions of the two magnets are vertical and the magnetization directions are opposite, and in the two spaced arrays 11, the magnetization directions of the two magnets in parallel positions are opposite; the two spaced arrays Between 11 is a magnetically conductive yoke I3, the air gap between the yoke I3 and the spaced arrays 11 on both sides is equal, and the yoke I3 is supported by a non-magnetically conductive yoke frame 4.
[0054] like Figure 12 Shown is a schematic diagram of the distribution of magnetic force lines between two spaced arrays 11 . The magnetic field path at the center of the two spacing arrays 11 is the shortest, and the magnetic field path at the upper and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com