Service data dynamic adjustment server and system on basis of JAVA CLASS compilation
A dynamic adjustment and business data technology, applied in memory systems, electrical digital data processing, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in rule control and adjustment, inability to meet rules for rapid adjustment, difficulty in applying rule engine products, etc., to avoid complex technical difficulties Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
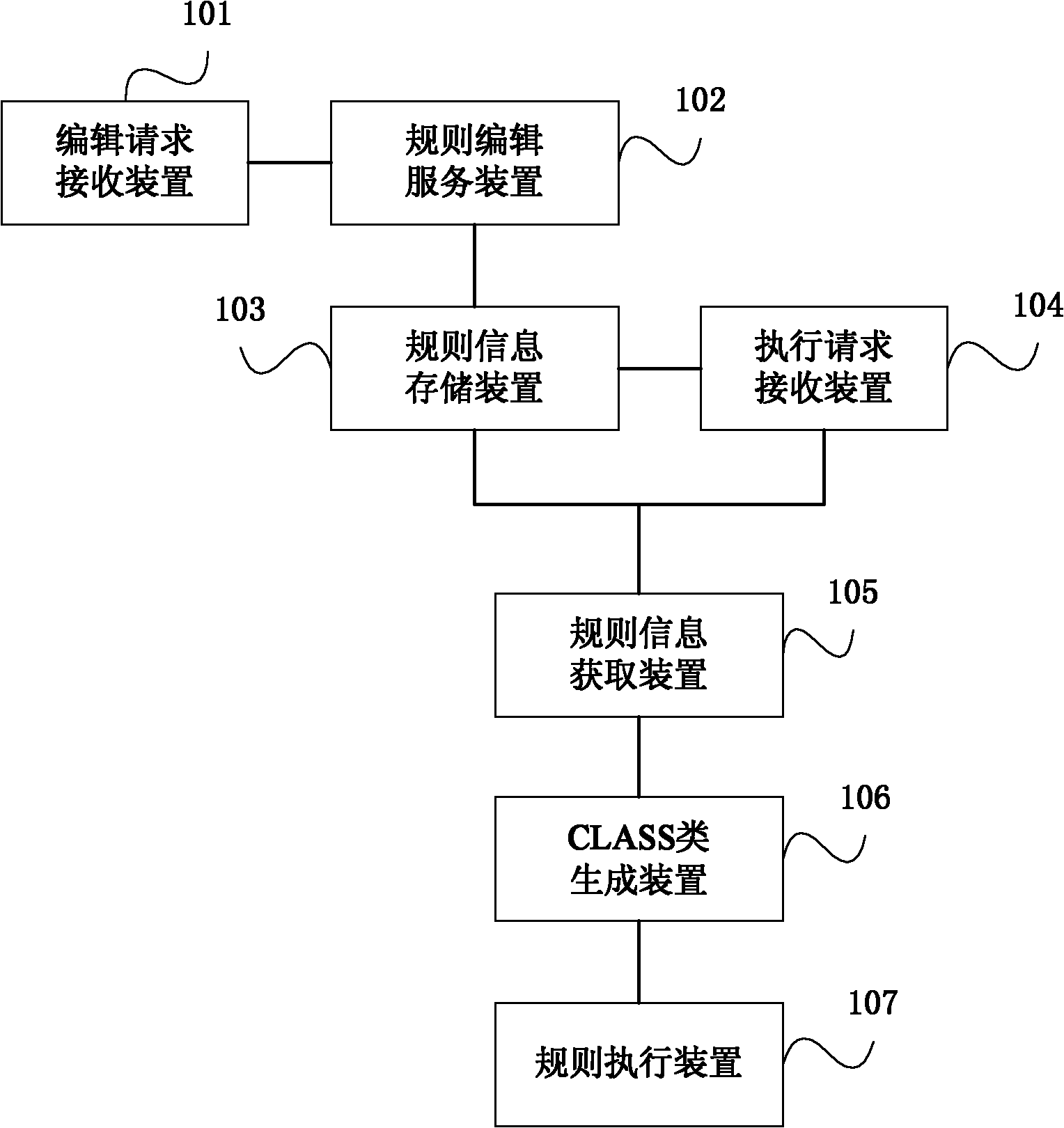
[0029] Image 6 The flow chart of the first embodiment of the method for dynamically adjusting the business data dynamic adjustment server compiled based on JAVA CLASS of the present invention, as shown in the figure, the dynamically adjustable rule processing method includes:
[0030] S601. Receive a business rule editing request from an external business application system;
[0031] S602, providing a corresponding rule editing service interface to the business application system according to the rule editing request;
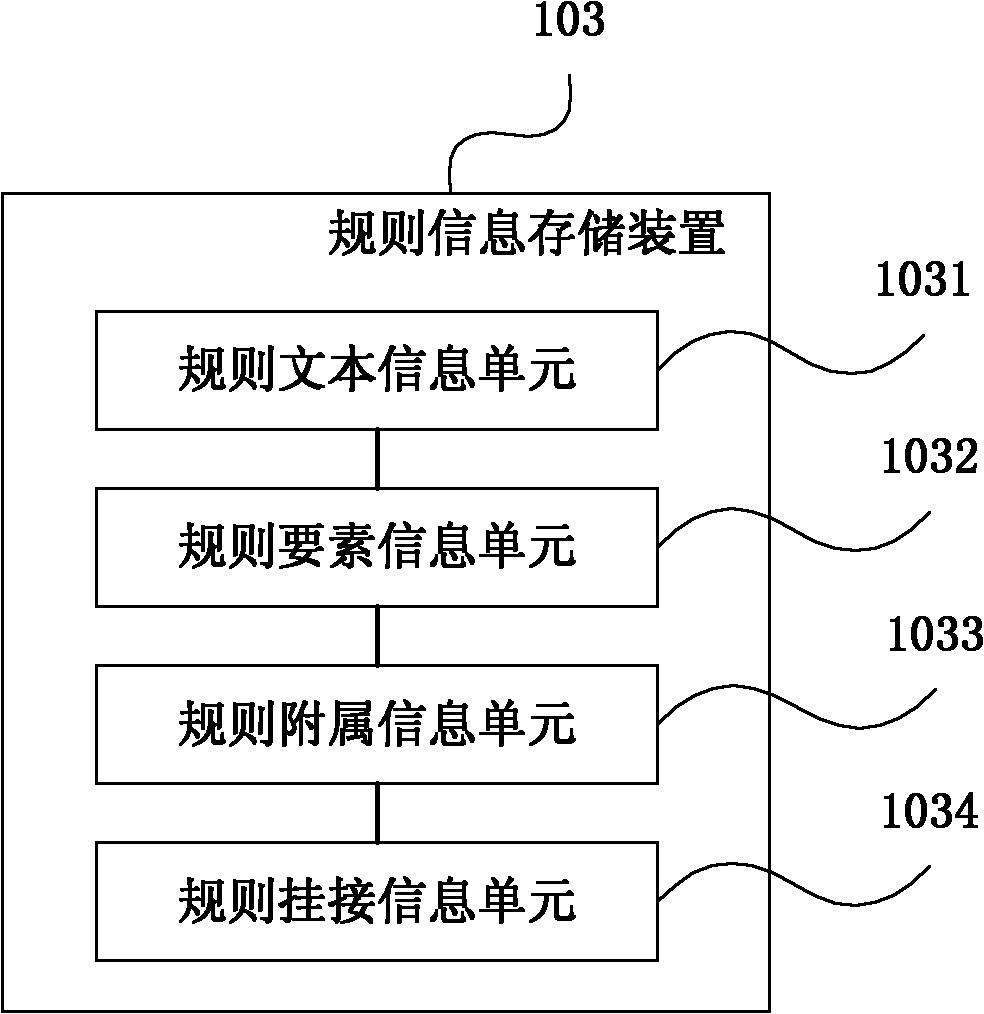
[0032] S603. Receive and store the business rule information generated by the business application system according to the rule editing service interface, including rule version number, rule text information and rule attachment information;
[0033] S604. Receive a rule execution request corresponding to the business process sent by the business application system;
[0034] S605. Obtain business rule information corresponding to the business process accordin...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Figure 7 The flow chart of the second embodiment of the method for dynamically adjusting the service data dynamic adjustment server compiled based on JAVA CLASS of the present invention.
[0040] Step S701: the business application system sends a rule creation and editing request to the business data dynamic adjustment server.
[0041] Step S702: The editing request receiving means 101 receives the request, calls the rule editing service means 102, and provides a rule editing service interface to the business application system.
[0042] Step S703: The application system edits the rule control required in its own business process through the rule editing service provided by the rule editing service device 102 . Rule control is essentially the processing of if-else. The rules edited by the business application system can contain multi-level nested if-else relationships, and the rules can refer to various elements or attributes involved in the business application syste...
specific example
[0050]
[0051]
[0052] Of course, for the convenience of front-end users editing rules, the rule input interface can be optimized and guided on this basis, and the results edited by users can be encapsulated in XML at the background program level to avoid direct input of JAVA language and XML format by users.
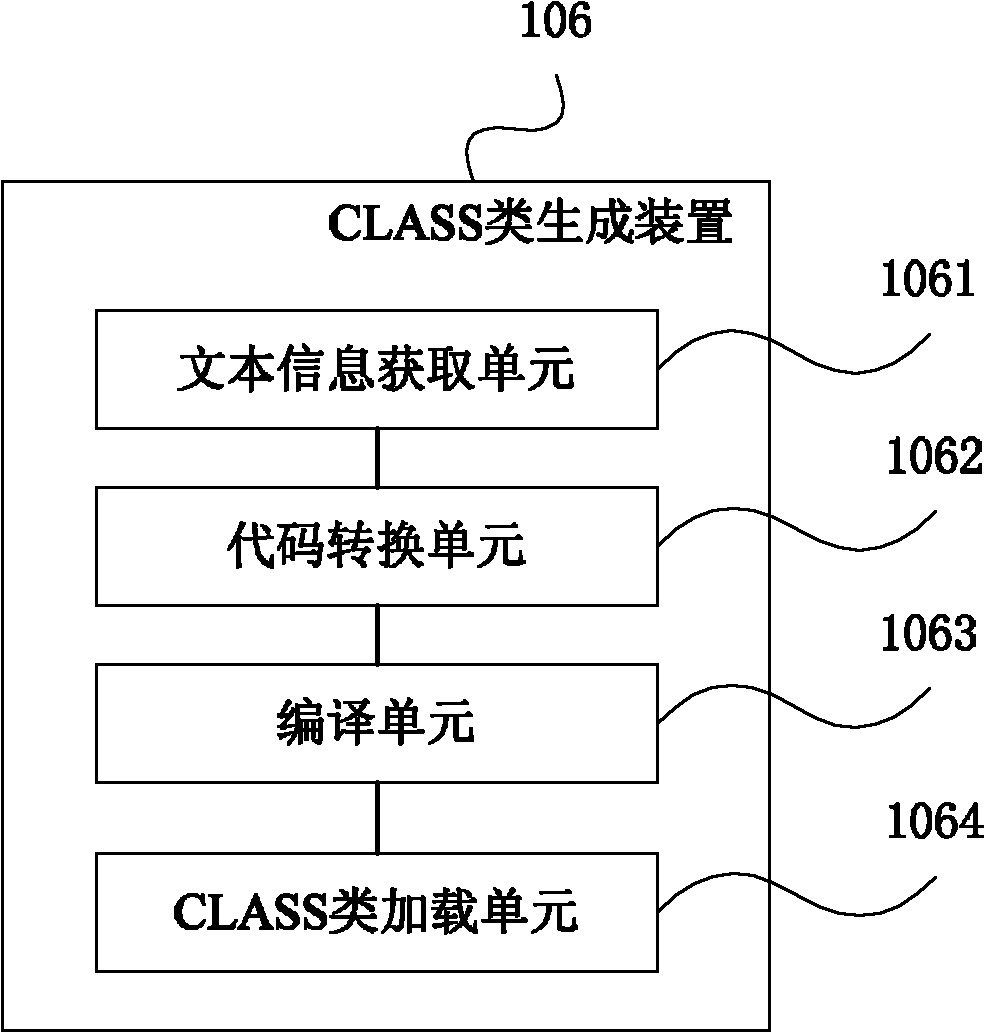
[0053] For the above rule language specification, it can be converted into JAVA language according to the following principles:
[0054] (1) For labels It is directly converted into a JAVA language function, and the function name is the name of the name tag.
[0055] (2) For each tag content, where the tag ... The content in the JAVA language is converted into "if(...)"; the label ... The content in the JAVA language is converted into "{...}"; the label ... The content in is converted into "else{...}" of the JAVA language.
[0056] (3) For tags ... The content in the JAVA language is converted into "..."; for the label ... For th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com