Controlling memory redundancy in a system
A technology of memory and memory nodes, the redundancy in hardware is used for data error detection, instrumentation, and response error generation, etc., which can solve problems such as uncorrectable master nodes and system crashes.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
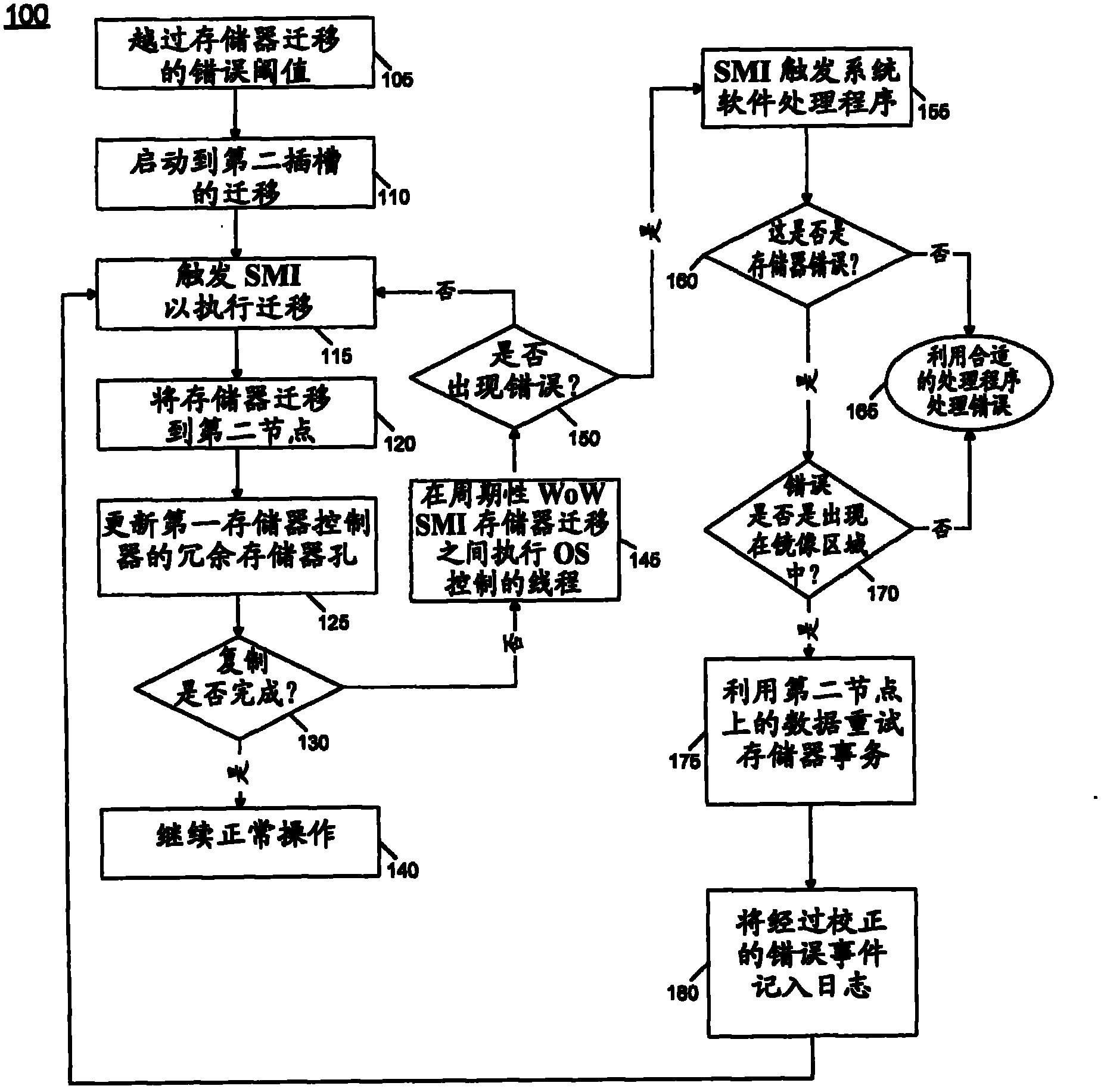
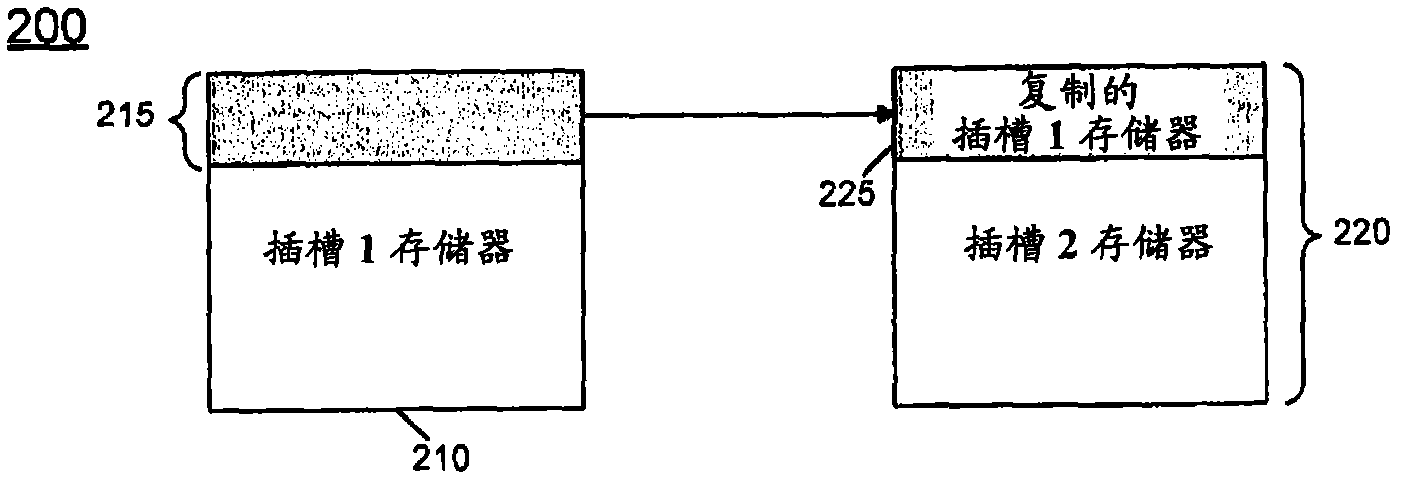
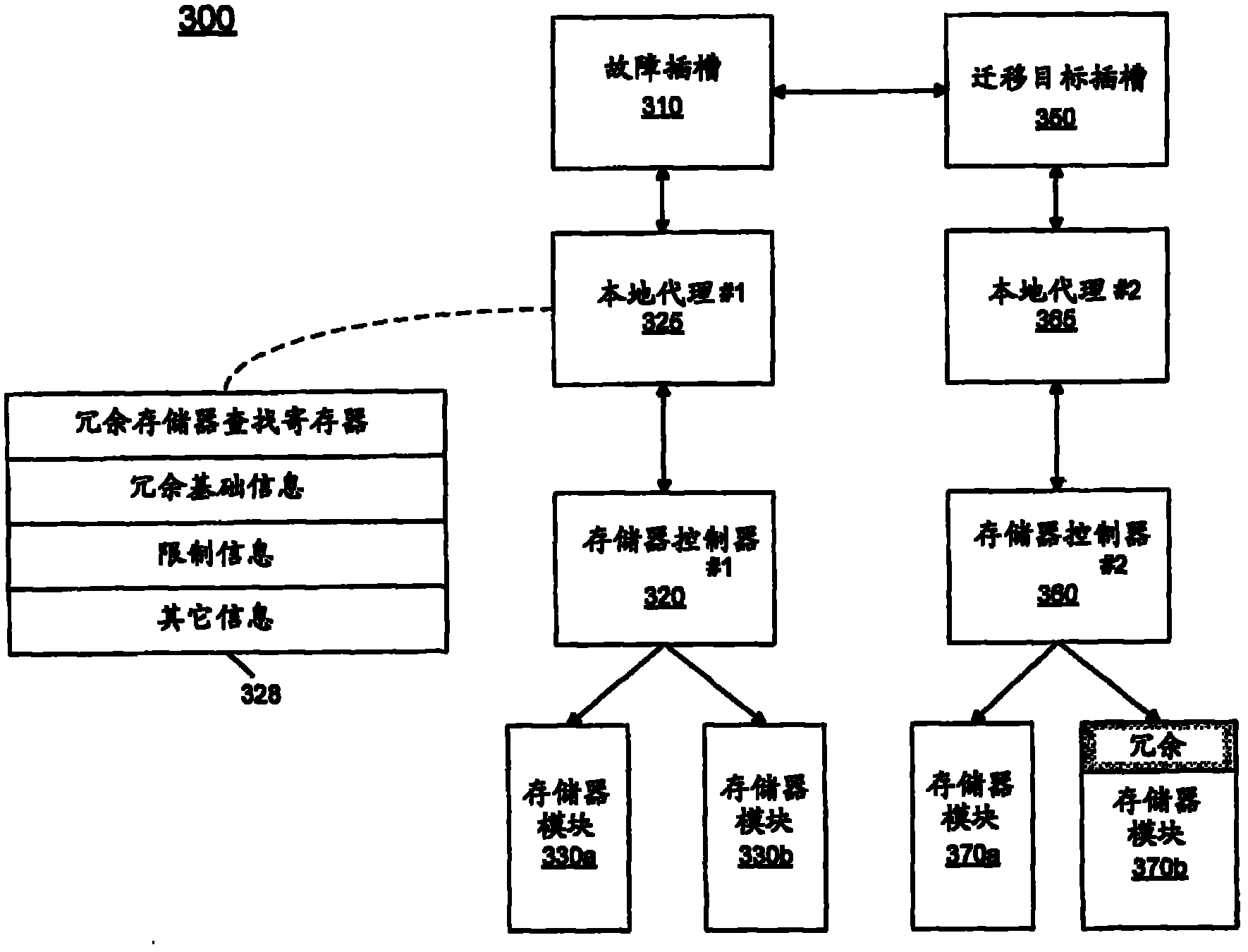
[0025] In various embodiments, during a migration operation, management software (e.g., Basic Input Output System (BIOS)) may interact with system hardware so that uncorrectable errors are encountered at the primary node during the memory migration process while in migration mode This enables the slave memory node to process the access request. During memory migration, the BIOS can read the cache line (filled by the master) and write it back (to the master and slave). In this way, the contents of the master node can eventually be copied to the slave nodes on a cache-line by cache-line basis. This is called write-on-write (WOW) replication. Note that write-on-read (WOR) is handled in a similar fashion, but these writes are done by the hardware itself after the BIOS reads the cache line. During migration, as the management software starts copying storage, it can disambiguate ranges of storage that have been copied (and are now redundant) from ranges that are yet to be copied (...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com