Method and device for measurement of nanometer resolution total reflection differential micrometric displacement
A total reflection and differential technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, optical devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of limited resolution, influence, expensive system, etc., and achieve the effect of improving sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
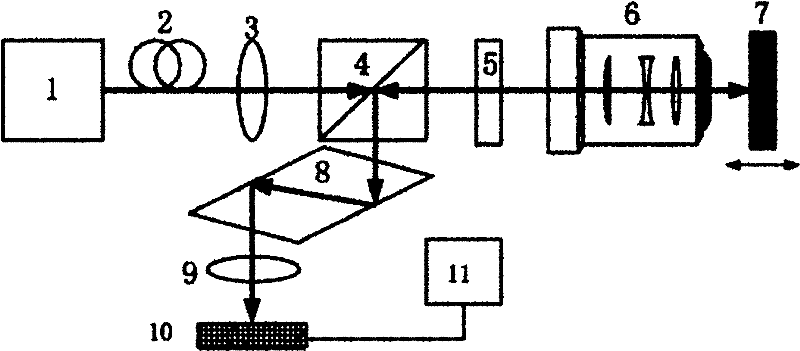
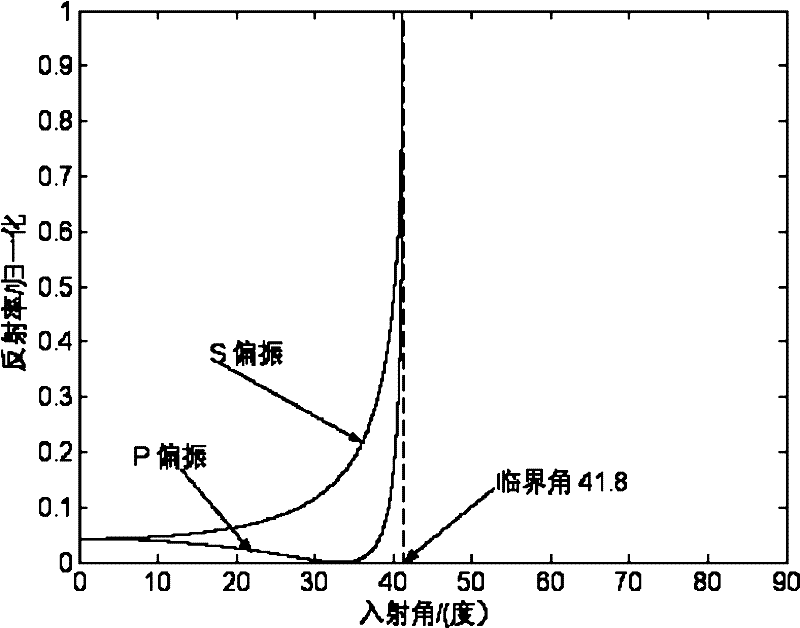
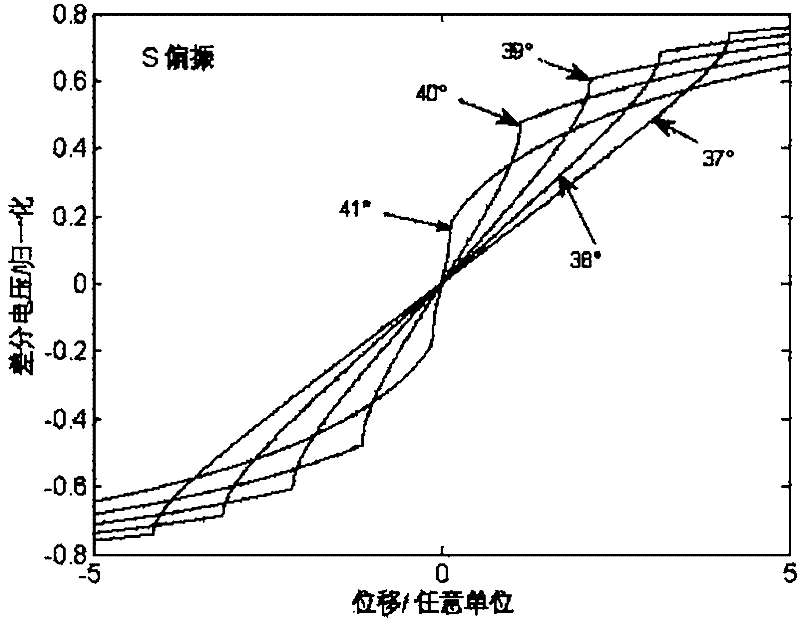
[0042] Such as figure 1 As shown, a device for measuring nanometer-resolution total reflection differential micro-displacement, including: laser 1, single-mode fiber 2, collimator lens 3, polarization beam splitter 4, λ / 4 wave plate 5, microscope objective lens 6, the measured A target mirror 7 , a rhombic prism 8 , a convex lens 9 , a differential detector 10 , and a drive and display unit 11 .
[0043] The laser 1, the single-mode optical fiber 2 and the collimating lens 3 constitute the first component group in sequence, the polarization beam splitter 4 is the second component group, and the first component group and the second component group are sequentially located on the optical path of the light emitted by the laser 1; The λ / 4 wave plate 5 and the microscopic objective lens 6 constitute the third component group, which are sequentially located on the first transmission light path of the polarization beam splitter 4 with the target lens 7 to be measured; the rhomboid pr...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Such as Figure 7 As shown, a device for measuring nanometer-resolution total reflection differential micro-displacement, including: laser 1, single-mode fiber 2, collimator lens 3, polarization beam splitter 4, λ / 4 wave plate 5, microscope objective lens 6, the measured A target mirror 7 , a rhombic prism 8 , a convex lens 9 , a differential detector 10 , and a drive and display unit 11 .
[0059] The laser 1, the single-mode optical fiber 2 and the collimating lens 3 constitute the first component group in sequence, the polarization beam splitter 4 is the second component group, and the first component group and the second component group are sequentially located on the optical path of the light emitted by the laser 1; The λ / 4 wave plate 5 and the microscopic objective lens 6 constitute the third component group, which are sequentially located on the first reflected light path of the polarizing beam splitter 4 with the measured target mirror 7; the rhomboid prism 8, c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com