Distribution network fault location method utilizing natural frequency and artificial neural network
A technology of artificial neural network and fault location, which is applied in the direction of biological neural network model, fault location, etc., to achieve good robustness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
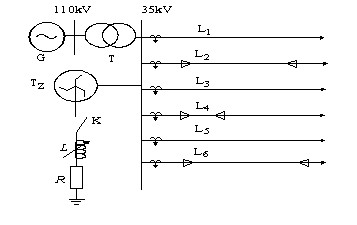
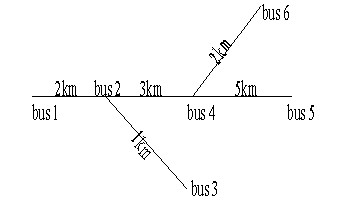
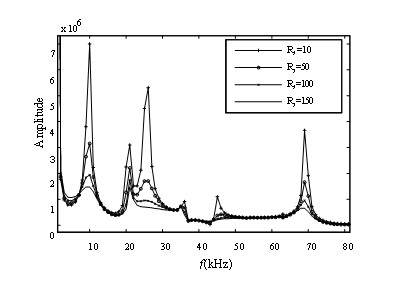
[0062] Specific simulation models such as figure 2 As shown, take a fault point every 50m on the line, that is, Δ l =50m, the fault resistance is 20Ω, and the fault closing angle θ=0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, 90°, the simulation is carried out.
[0063] (1) After a single-phase ground fault occurs in the distribution network, the starting element starts immediately, and the zero-sequence current fault component of the fault can be obtained according to the three-phase current measured at the protection installation for:
[0064] (1)
[0065] where, are the three-phase currents of fault lines A, B, and C respectively, k =1, 2, 3... N , N is the length of the sampling sequence;
[0066] (2) Perform FFT transformation on the transient zero-sequence current of the fault line. The sampling frequency is 1MHz and the sampling length is 2048. After FFT transformation, a 2048×2 matrix is obtained:
[0067] (2)
[0068] In the formul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com