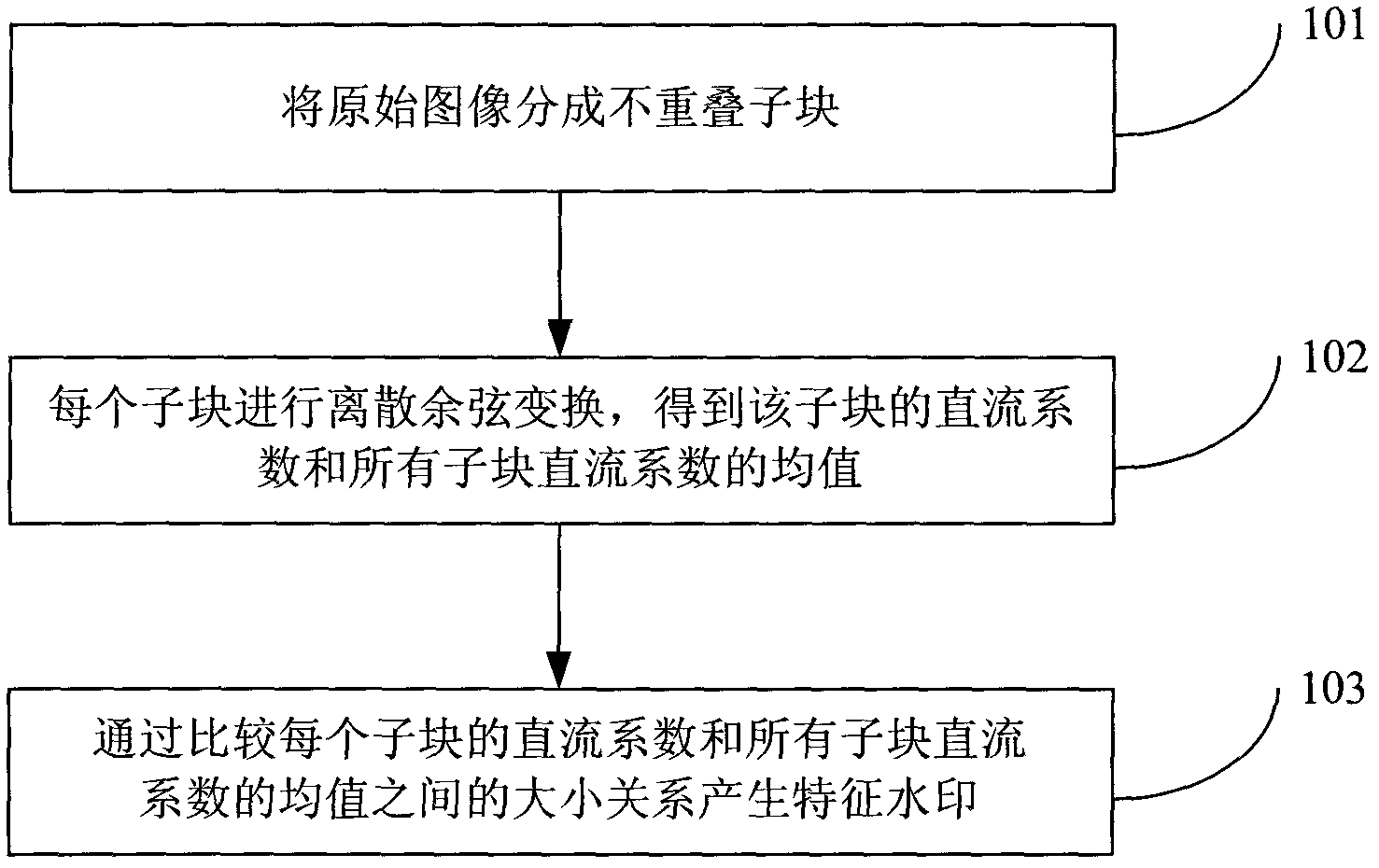
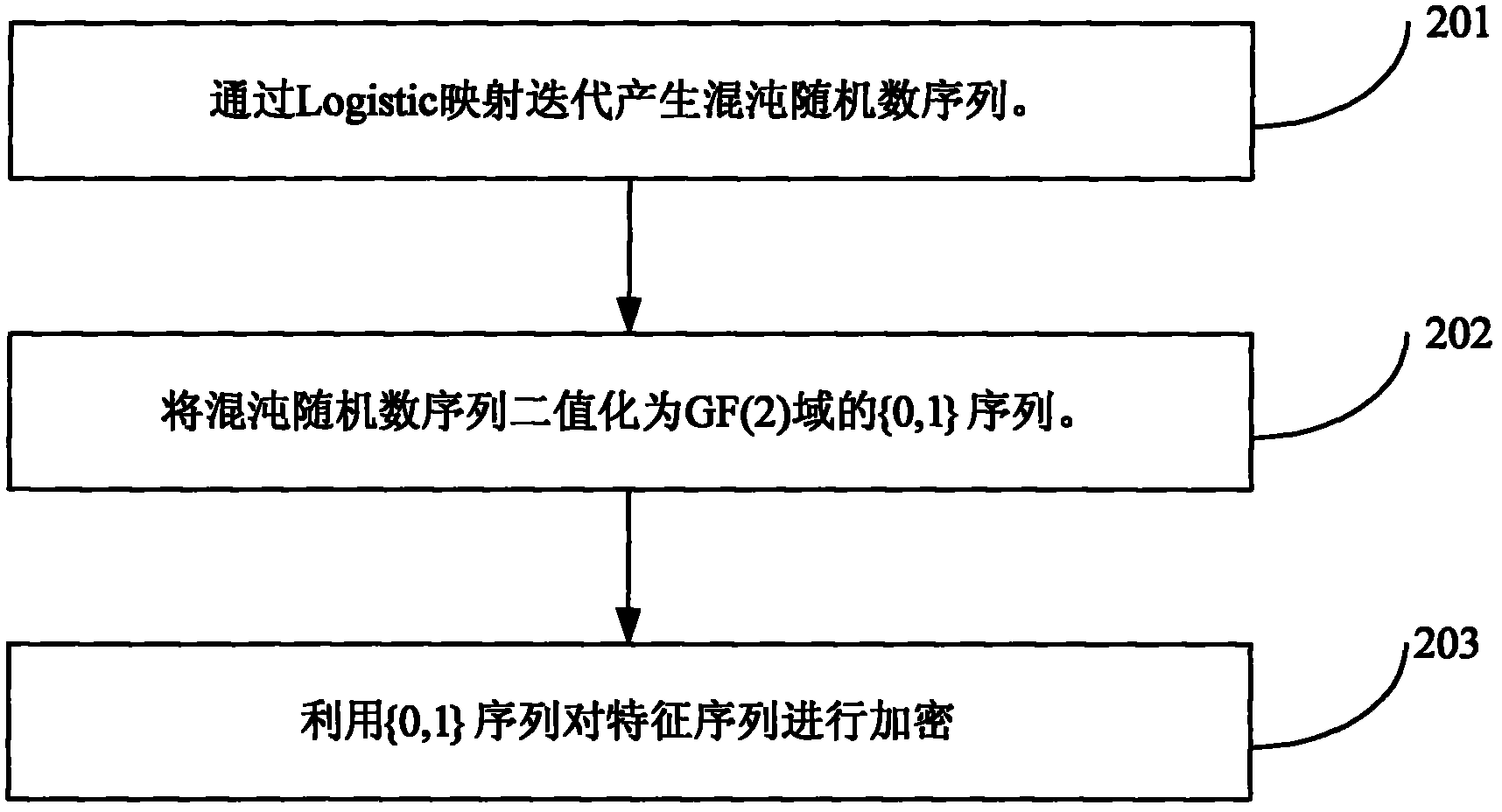
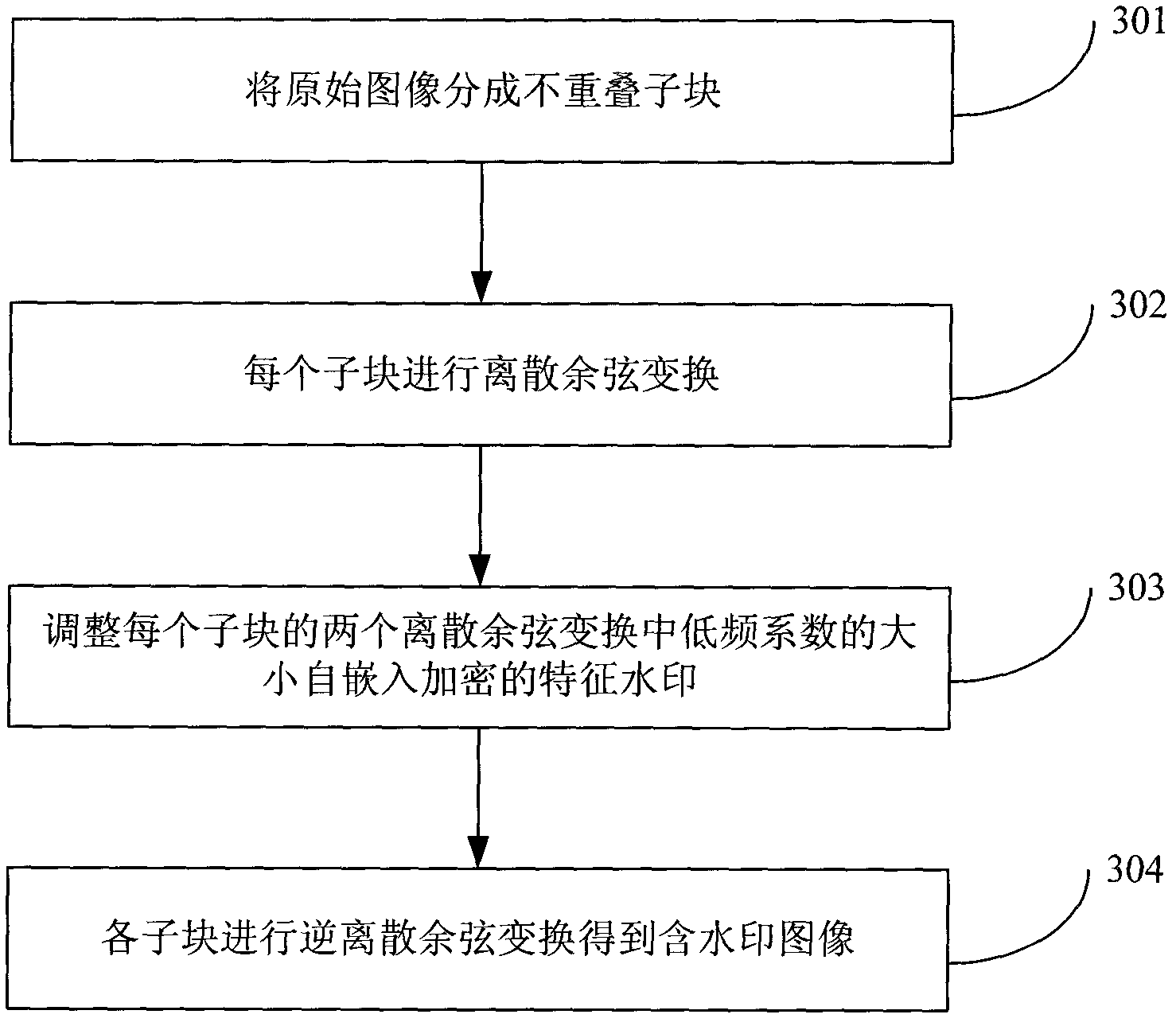
Network image copyright real-time distinguishing method
A network image and copyright technology, applied in the field of information security, can solve the problems of difficult to completely prevent passive Internet attacks, interfere with copyright identification, and the original watermark cannot be used to identify copyright.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0181] 1 Description of Experimental Parameters
[0182] Three grayscale images of Lena, Barbara and Elain with a size of 512×512 in 256 levels are selected as the experimental images, as shown in Image 6 , 7 and 8 are shown. The size of the sub-blocks is 16×16, so the length of the feature watermark W is 1024bit. Logistic chaos map initial value x 0 The value is 0.28, the parameter γ is 1.5, and the first κ=200 random numbers are discarded when the Logistic chaotic sequence encrypts the characteristic watermark W. Encrypted feature watermark W e Adaptively self-embed the DCT coefficients of each sub-block in the (3, 5) and (4, 4) positions of the original Lena, Barbara and Elain images. The scale factor μ of the adaptive embedding is taken as 0.028. The resulting watermarked Lena, Barbara and Elain images are shown in Figure 9 , 10 and 11, the PSNRs between them and the original Lena, Barbara and Elain images are 35.9595, 36.1211 and 35.7637. Therefore, good invis...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com