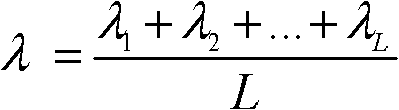Method for reducing error identification rate of text irrelevant speaker identification system
A speaker recognition, text-independent technology, applied in speech analysis, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of increased misrecognition rate and achieve the effect of reducing the misrecognition rate and reducing the high misrecognition rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
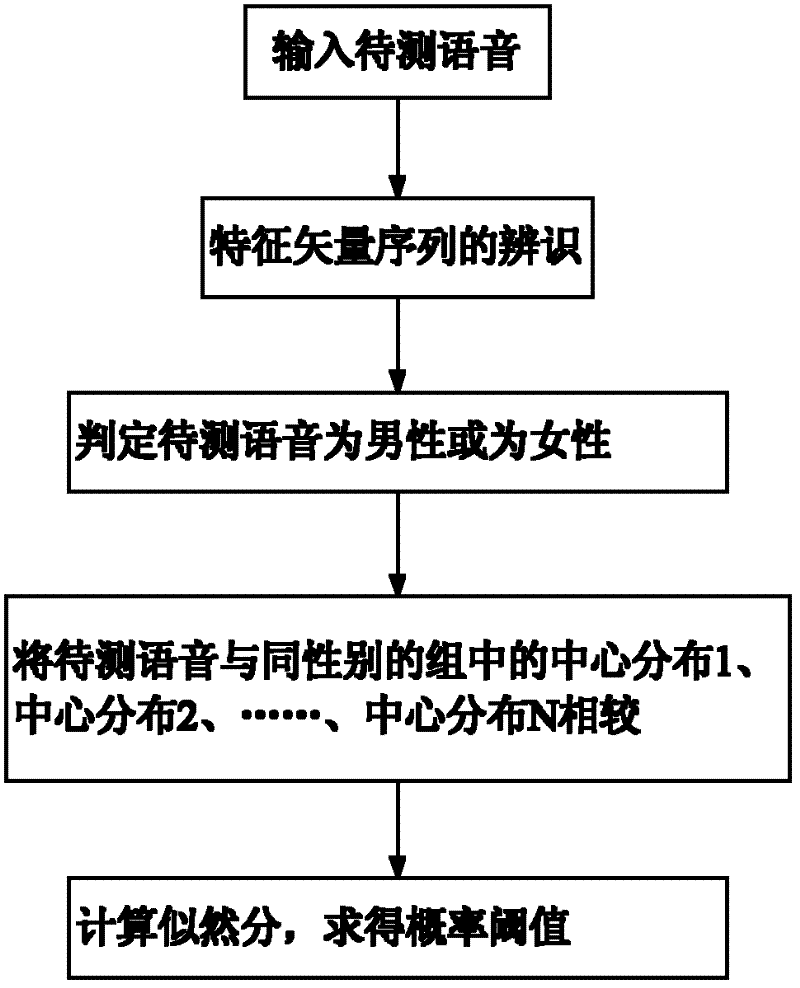
[0014] Specific embodiment one: a kind of method of reducing the misrecognition rate of the text-independent speaker recognition system of the present embodiment is carried out according to the following steps:
[0015] Step 1, using the training data of the closed set of the benchmark speaker recognition system to obtain the Gaussian mixture model of the feature vector of each known speaker and the threshold for correct identification thereof;
[0016] Step 2. Divide the speakers in the closed set into two groups according to male and female, arrange the thresholds for correct recognition of each group according to their size, and divide the thresholds into segments, each segment as a group;
[0017] Step 3. The speakers contained in each group obtained in step 2 are replaced by a model conforming to the Gaussian distribution, and the central distribution of each group of the male group and the central distribution of each group of the female group are obtained;
[0018] Step...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0023] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is that the calculation of the Gaussian mixture model in step 3 is carried out according to the following steps:
[0024] a. There are R speakers in the group, and the Gaussian distribution of the i-th speaker in the group is N(μ i , ∑ i ), where μ i represents the mean vector of the Gaussian distribution of the i-th speaker, ∑ i Represents the diagonal covariance matrix of the Gaussian distribution of the i-th speaker, where i=1,2,...,R, with μ i (k) means μ i The k-th dimension component of , with σ 2 i (k) means ∑ i The kth diagonal element of , w i is the weight of the Gaussian distribution,
[0025] b. Press Computes the sum of weights w over all Gaussian distributions in the group c ;
[0026] c. Press Computes the mean vector μ of the central distribution of the mixture Gaussian model of the subgroup c The k-th dimension component of :
[0027] d. Press C...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0030] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that the calculation method of the threshold value of the group in step four is as follows:
[0031] There are L Gaussian models in the group, and the threshold for each Gaussian model to be correctly identified is λ 1 ,λ 2 ,...,λ L , then the threshold λ of the group mixture Gaussian model is:
[0032] λ = λ 1 + λ 2 + . . . + λ L L
[0033] or λ for:
[0034] λ = 1 1 λ 1 + 1 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com