Sparse Event Detection Method for Wireless Sensor Networks Based on Compressed Sensing and Game Theory
A wireless sensor and compressed sensing technology, applied in the field of wireless communication, can solve problems such as detection loopholes, large communication interference, and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
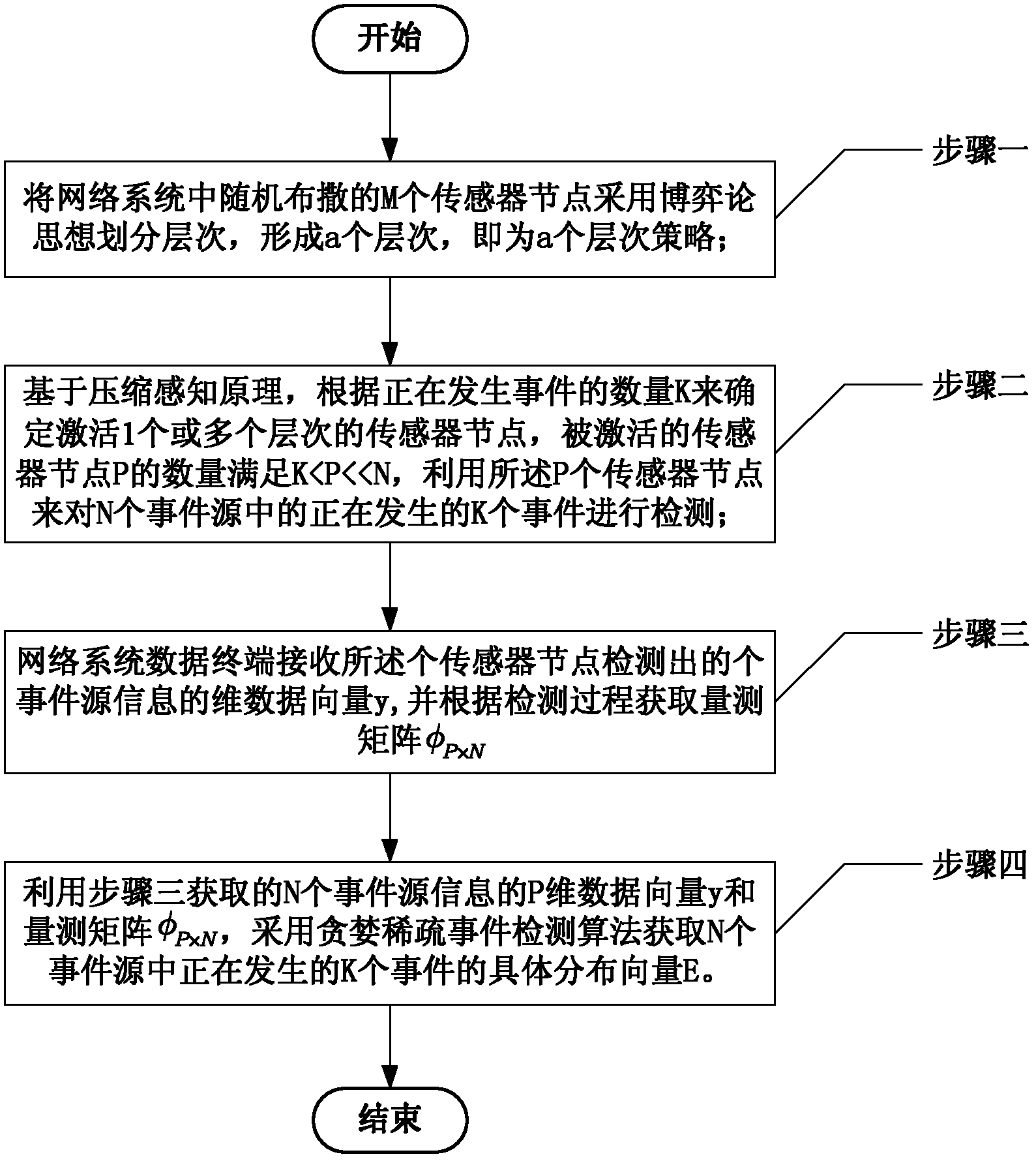
[0066] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the wireless sensor network sparse event detection method based on compressed sensing and game theory described in this embodiment is based on compressed sensing and game theory wireless sensor network sparse event detection method, the method includes the following steps:
[0067] Step 1. Divide the M sensor nodes distributed randomly in the network system into levels using the idea of game theory to form a level, which is a level strategy;
[0068] Step 2. Based on the principle of compressed sensing, determine the activation of one or more levels of sensor nodes according to the number K of ongoing events, and the number P of activated sensor nodes satisfies
[0069] K
[0070] Using the P sensor nodes to detect K events occurring in the N event sources;
[0071] Step 3: The network system data terminal receives the P-dimensional data vectors of the N event source...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0076] Specific implementation mode 2: This implementation mode further explains the implementation mode 1. In step 1, the M sensor nodes randomly distributed in the network system are divided into levels using game theory to form a level, which is the process of a level strategy for:
[0077] Step 11, each sensor in the network system determines the sensor IDs of all neighbor nodes within the communication radius and the positional relationship of the neighbor nodes relative to itself by sending information;
[0078] The sensor ID is set when leaving the factory. Each sensor ID is different and is set to distinguish its identity, that is, the ID card of the sensor. Each sensor ID has a certain communication radius, and the size of the communication radius varies according to the sensor model. When a sensor sends information to the sensors of its neighbor nodes within the communication radius, it sends its own sensor ID and communication radius and other inherent parameters t...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0088] Specific implementation mode three: this implementation mode further explains implementation mode one. In step two, the process of determining to activate one or more levels of sensor nodes according to the number K of ongoing events is:
[0089] The number P of activated sensor nodes satisfies K
[0090] P = Σ x = 1 y P x
[0091] The number y of activation levels can be determined,
[0092] In the formula, P x is the number of nodes in a certain level, y=1, 2, . . . a.
[0093] In order to achieve system optimization, when only K events occur, it is not necessary to call all the sensors, only a part of the sensors need to be called, and the other part of the sensors does not work. In this way, the requirements for detecting K events are met, and the minimum number of sensors is us...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com