Method for identifying traveling wave in initial reversed polarity direction
A technology of directional traveling wave and identification method, which is applied in the field of identification of initial reverse polarity directional traveling wave, can solve problems such as low reliability, serious attenuation of zero-mode components, and unusability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
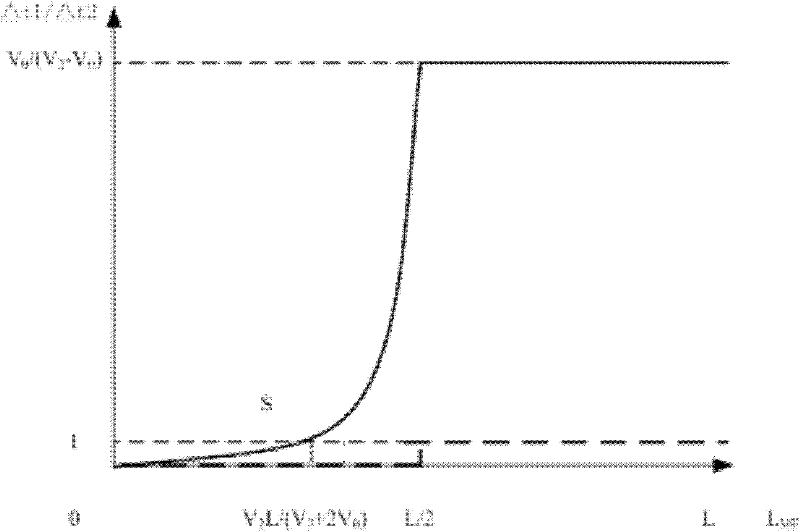
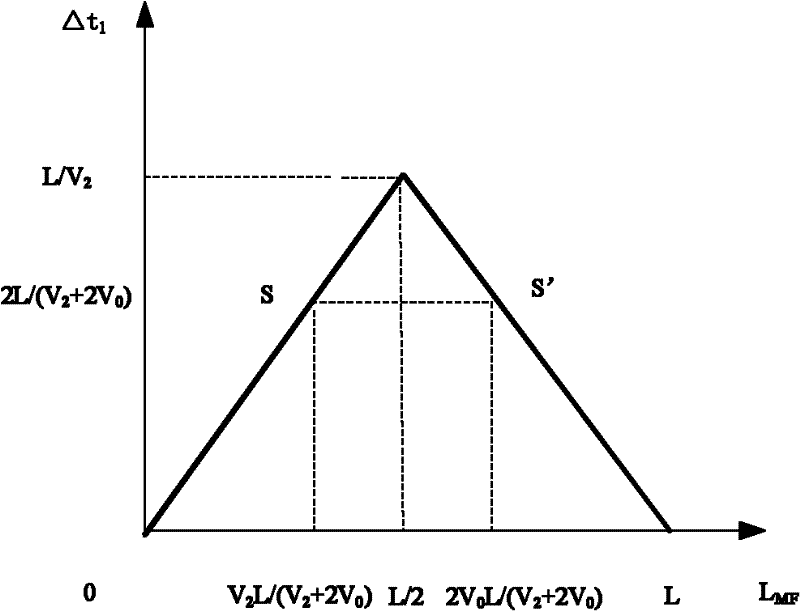
[0034] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and embodiment the present invention will be further described:
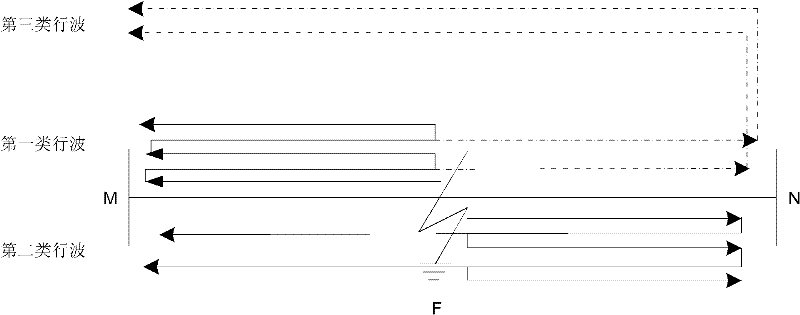
[0035] After the initial traveling wave of the current fault arrives at the measurement end, there will be a complex catadioptric process, such as figure 1 As shown, from the perspective of detection of traveling waves in the direction of initial reverse polarity, catadioptric traveling waves can be divided into the following three main types:
[0036] A type of traveling wave: a traveling wave that travels continuously between the fault point and the measurement terminal at the local end;
[0037] The second type of traveling wave: the traveling wave that continuously travels between the opposite end of the measurement end and the fault point and returns to the M end;
[0038] Three types of traveling wave: one type of traveling wave transmitted through the fault point and reflected back at the opposite end of the measurement end;
[0039] The type of busb...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com