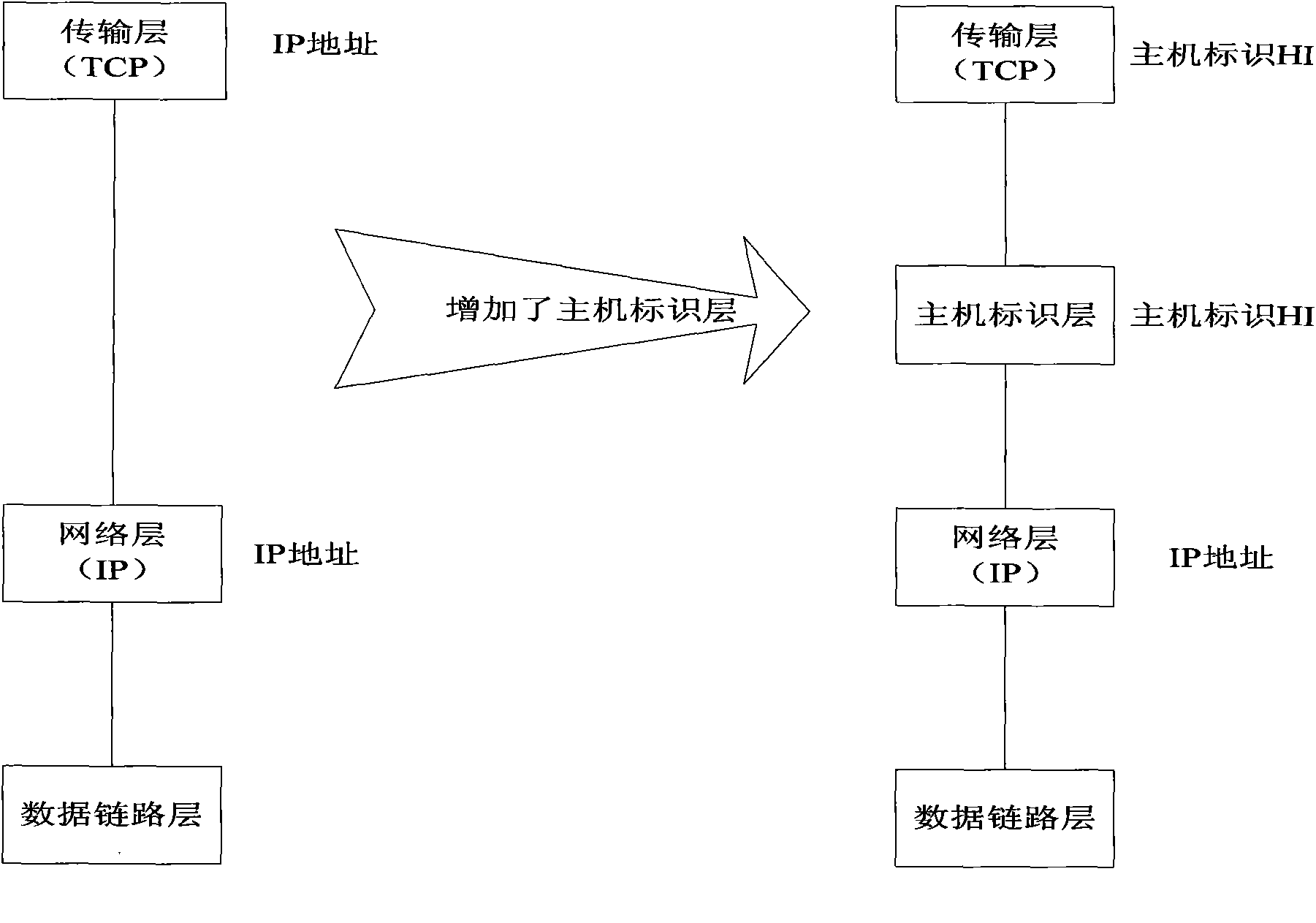
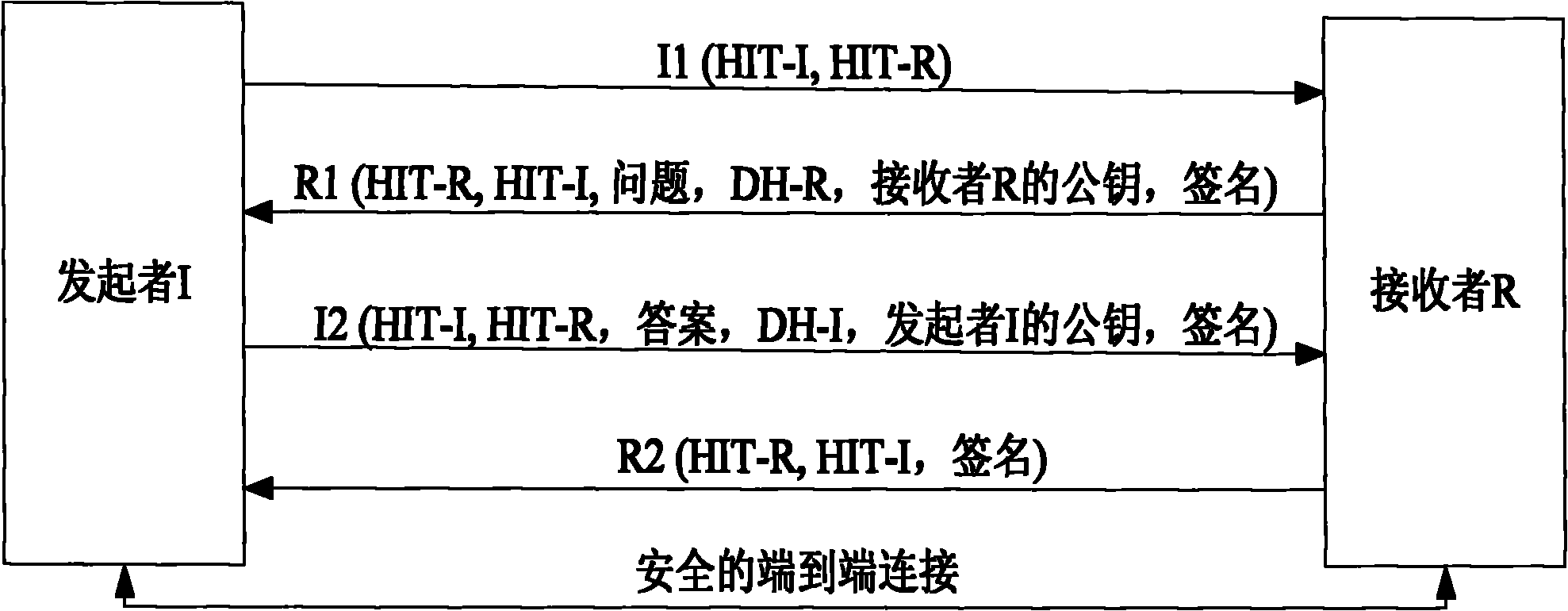
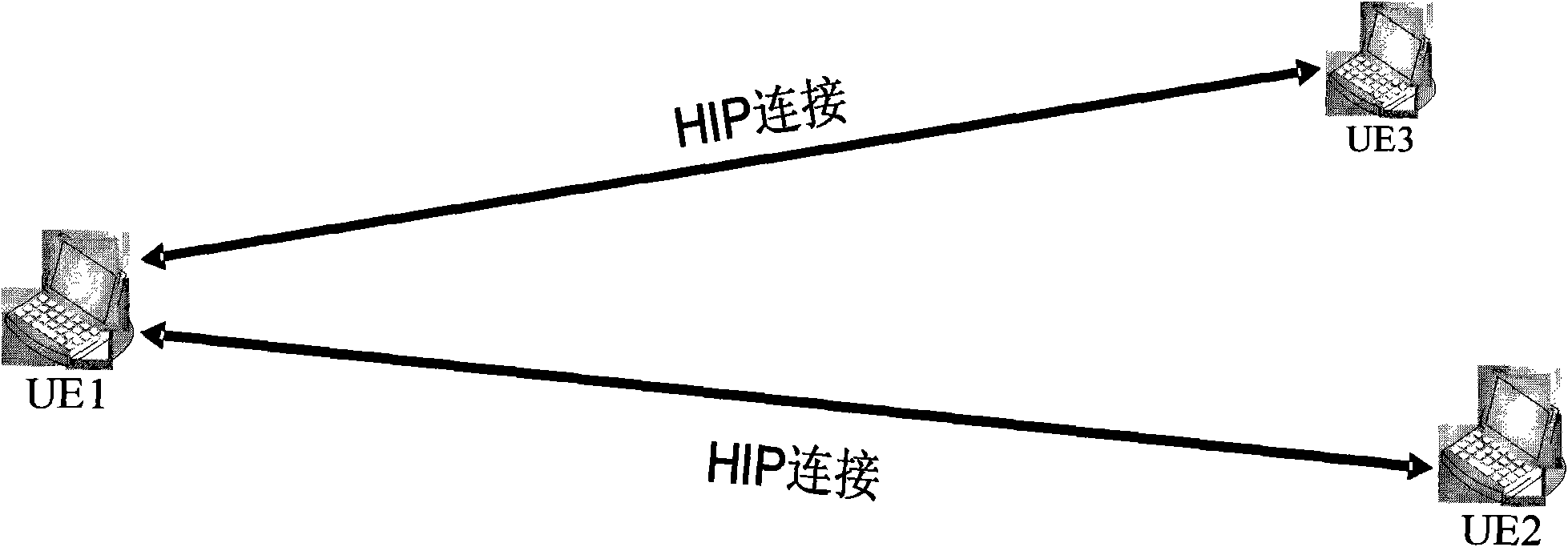
Communication method, system and equipment based on host identity protocol (HIP)
A communication method and equipment technology, applied in the field of telecommunications, can solve the problems of time delay, high overhead, large delay in establishing HIP connection, affecting user experience, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing HIP connection and delay and improving user experience.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0084] Figure 9 is based on Figure 8 The connection relationship maintenance system composed of SN nodes shown in the figure stores the binding relationship between the HIP device HIT and the HAP, and the HIP devices UE1 and UE2 at both ends of the communication are connected to different HAPs, including the following steps:
[0085] Step 901, UE1 establishes a HIP connection with HAP1, and UE2 establishes a HIP connection with HAP2;
[0086] Taking UE as an example, UE1 obtains the address of HAP1 with a smaller RTT by querying a statically configured server, DHCPv6 (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6) or DNS, and establishes a HIP connection with HAP1. HAP1 stores the correspondence between the HIT of UE1 and the IP address of UE1. HAP1 stores its binding relationship with the HIT of UE1 in the responsible SN node of UE1.
[0087] Step 902, UE1 uses its HIP connection with HAP1 to send the data packet it wants to send to UE2 to HAP1;
[0088] UE1 needs to tell ...
Embodiment 2
[0110] Figure 10 is an embodiment in which the HIP device of the present invention closes the HIP connection between it and the HAP, wherein, using Figure 8 The connection relationship maintenance system composed of the SN nodes shown is used to store the binding relationship between the HIP device and the HAP. The HIP devices UE1 and UE2 at the two ends of the communication are connected to different HAPs, including the following steps:
[0111] Step 1001 UE1 establishes a HIP connection with HAP1, and UE2 establishes a HIP connection with HAP2; taking UE as an example, UE1 obtains the address of HAP1 with a smaller RTT by querying a statically configured server, DHCPv6 (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6) or DNS, etc., UE1 Establish a HIP connection with HAP1. HAP1 stores the correspondence between the HIT of UE1 and the IP address of UE1. HAP1 stores its binding relationship with UE1's HIT in the responsible SN node of UE1.
[0112] Step 1002, UE1 uses its HI...
Embodiment 3
[0120] Such as Figure 11 Schematic diagram of IP address change for HIP devices, based on Figure 11 In the case of , the process of changing the IP address is as follows: Figure 12 shown, including the following steps:
[0121] Step 1201, UE1 obtains the HAP address by querying a statically configured server, DHCPv6 (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6), or DNS, etc., UE1 establishes a HIP connection with HAP1, and HAP1 stores the correspondence between UE1's HIT and the IP address;
[0122] Step 1202, the IP address of UE1 changes;
[0123] Step 1203, UE1 sends a HIP Update to its associated HAP1 to notify the change of the IP address. HAP1 records the change of UE1's IP address;
[0124] Step 1204, other devices communicating with UE1 such as UE2 send data to UE1;
[0125] Step 1205, HAP1 finds that the IP address notified by UE1 of the IP address change is the only address sent to UE1, then it can cache the data sent to UE1;
[0126]Step 1206, HAP1 sends a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com