Energy recovery in hot strip mills by converting the cooling heat of the continuous casting plant and the residual heat of slabs and coils into electrical energy or otherwise utilizing the captured process heat
A technology of casting equipment and slabs, applied in mechanical equipment, sustainable manufacturing/processing, heat exchangers, etc., can solve problems such as heat loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
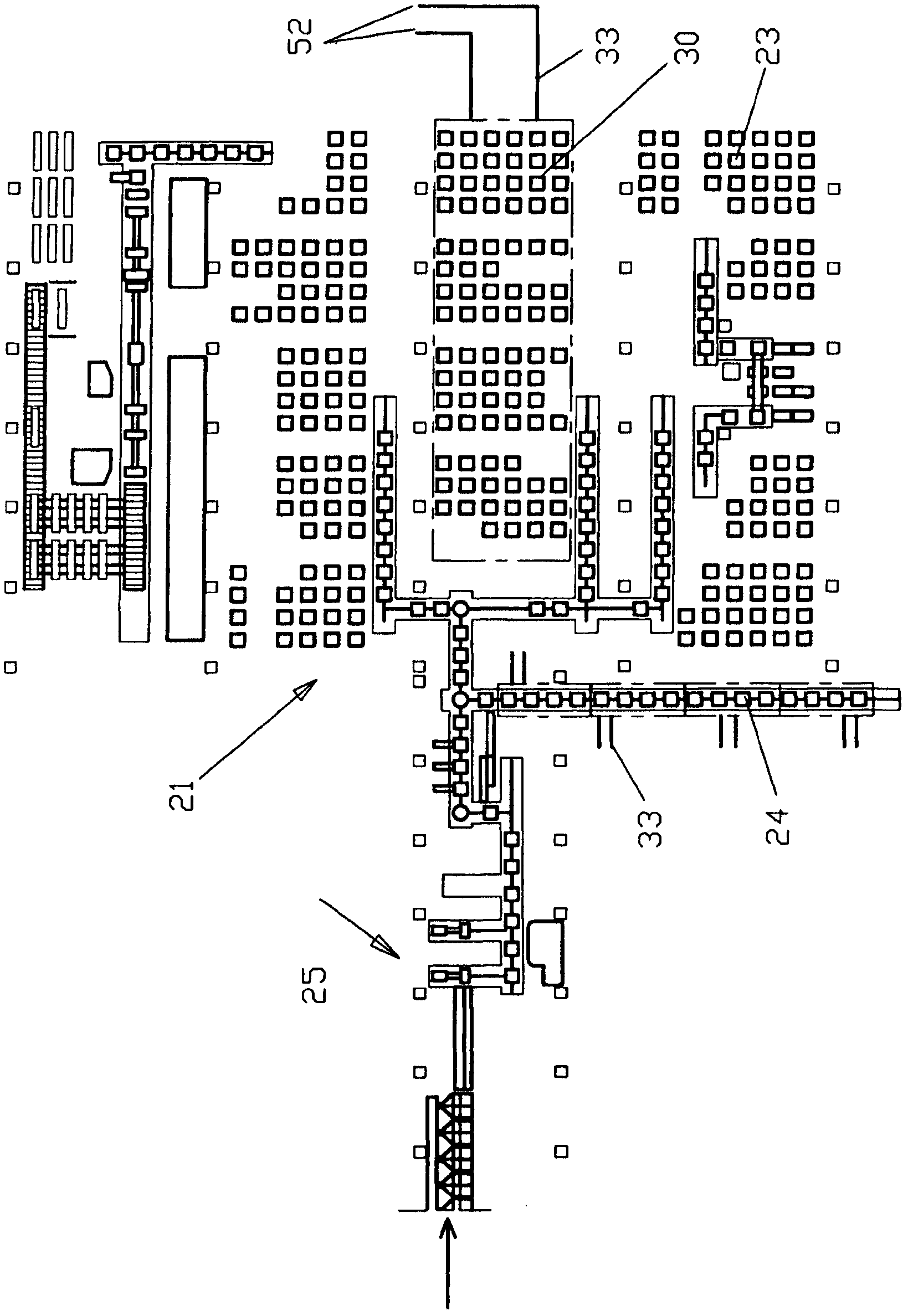
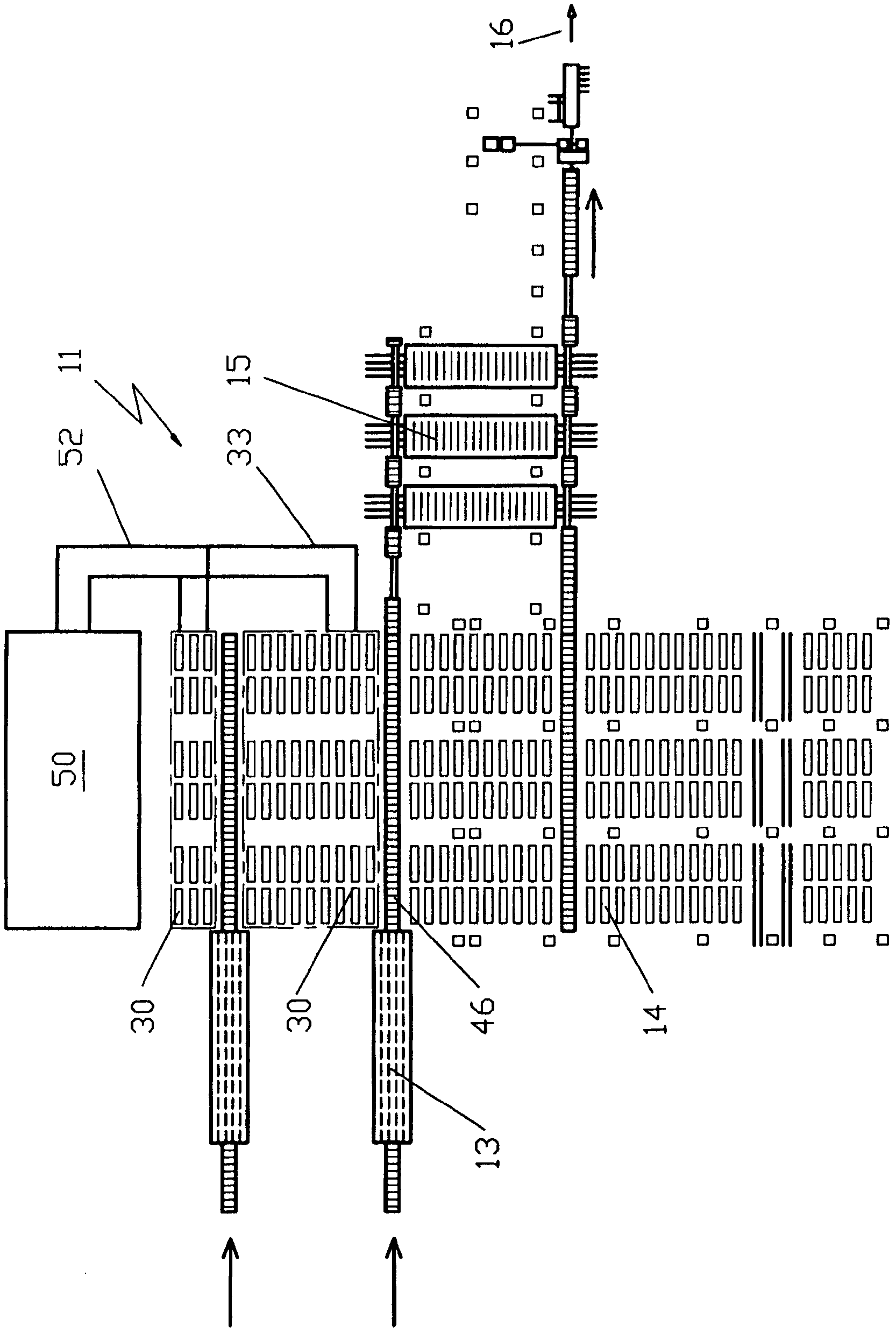
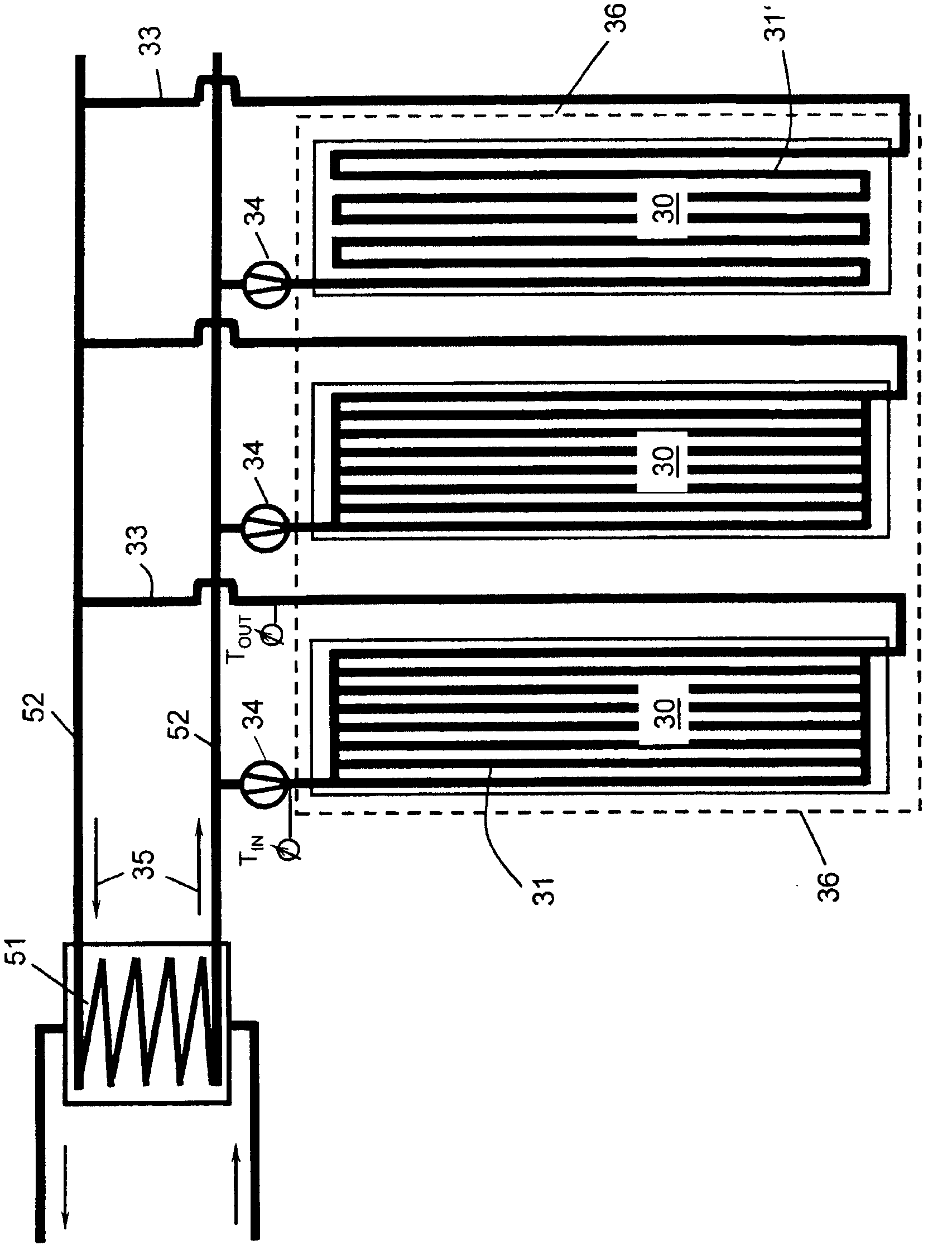
[0097] exist figure 1 , the coil warehouse 21 is shown in plan view. The coil produced by the winch 25 reaches its storage location via a coil-conveying line 24 (which can be configured, for example, with a heat exchanger cover or heat shield). According to the invention, these storage locations are partially configured as storage locations 30 with heat exchangers 31 (see Figure 8a and 8b ), leaving the rest as usual coil-storage locations 23 without heat exchangers. Depending on the still existing temperature and cooling progress of the coils, between the storage position 23 and the storage position 30 , a change of the coils takes place which is controlled by the process model. The heat carrier medium heated in the storage location 30 then reaches the power generation equipment (power generation equipment not shown) via the heat carrier-conveying pipeline 33 and the heat carrier-collecting pipeline 52, or can be transported to other internal or External heat users (e.g....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com