Test element for analyzing body fluid
A technology for testing components, body fluids, applied in the field of systems, which can solve problems such as difficult for patients to perform, time-consuming and uncomfortable handling steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
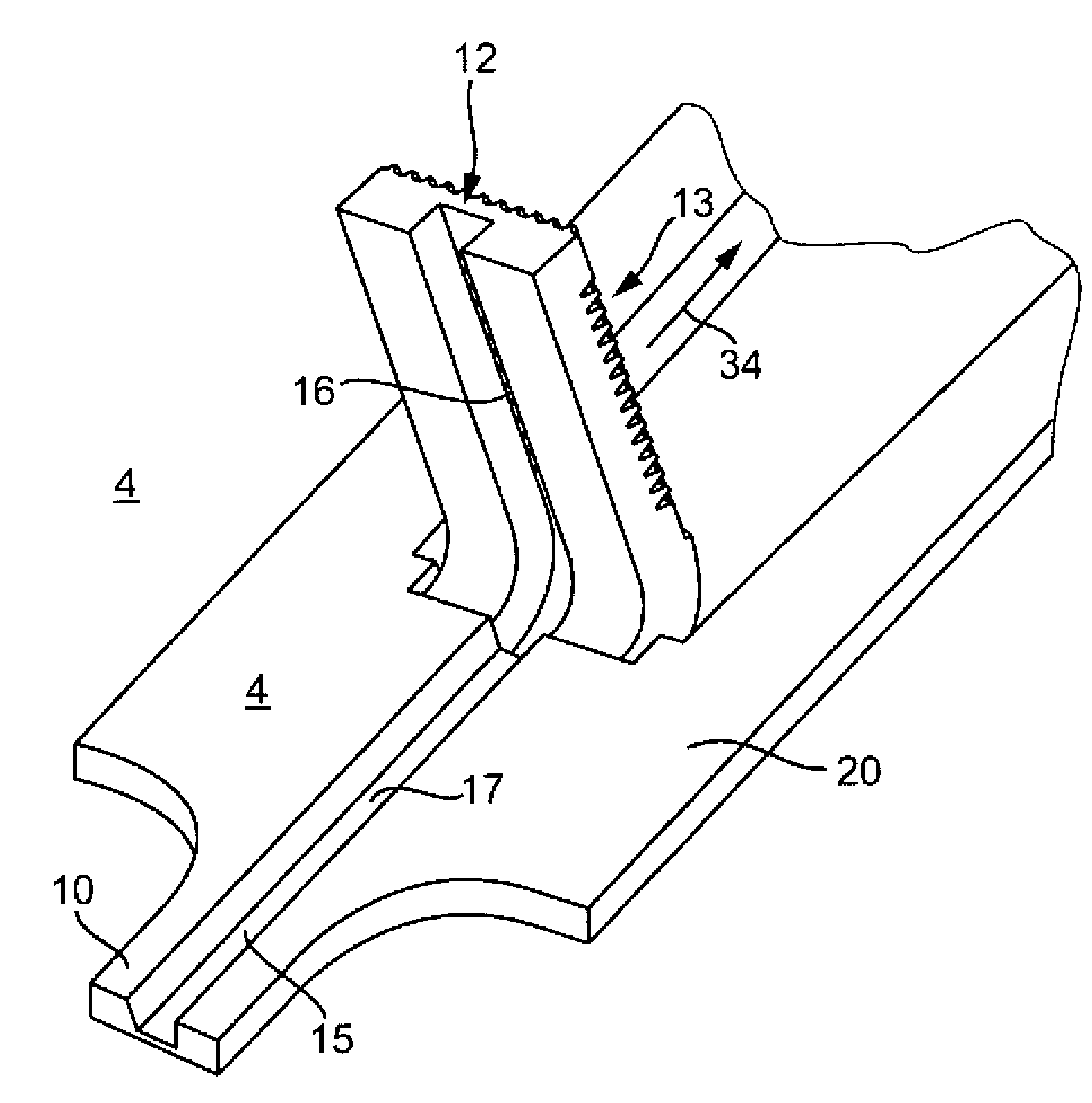
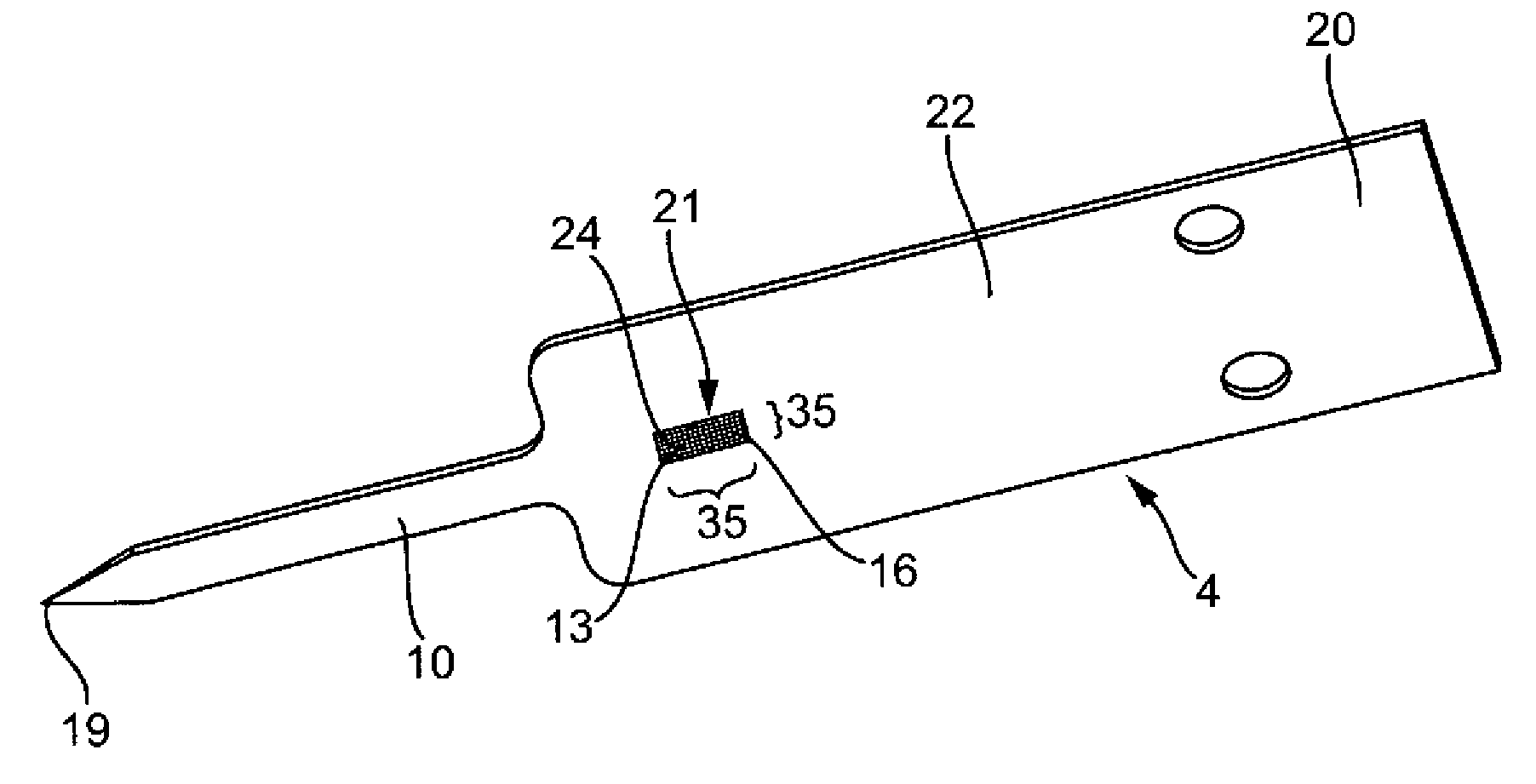
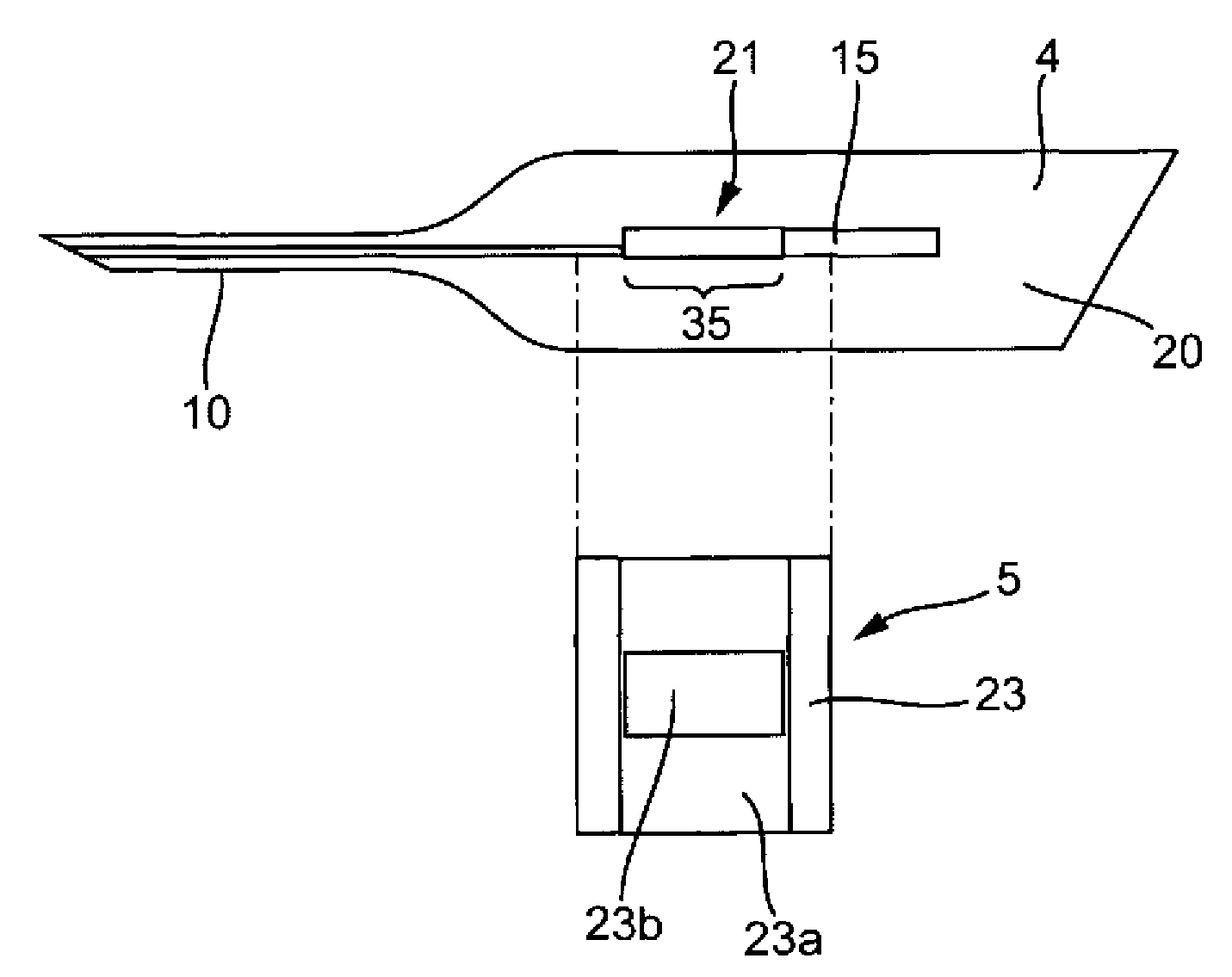
[0071] figure 1 An analysis system 1 is shown, which has an analysis device 2 and a magazine 2 a contained in the device 2 , which has a test element 3 . The test elements 3 each comprise a piercing element 4 and a test panel 5 .
[0072] The evaluation device 2 has a housing 6 and a coupling mechanism 7 for coupling to the piercing element 4 in order to move the piercing element 4 along a movement path in the piercing direction. The coupling mechanism 7 is coupled to a drive unit 7a which moves a coupling structure 7b which can be coupled to the piercing element 4 .
[0073] The measurement and evaluation unit 8 is used to measure changes in reagents which react with the body fluid of the analysis element 5 in order to analyze the body fluid for an analyte. Ability to perform quantitative and qualitative analysis. Preferably, the glucose content in the blood is studied. In the example shown, the measurement and evaluation unit 8 operates according to the photometric princ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com