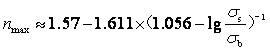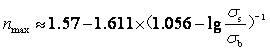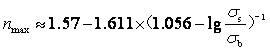Method for determining maximum strain hardening exponent according to strength of steel-iron material
A hardening index, maximum strain technique used to test material strength and other directions using a stable tension/compression applied
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0083] For a medium-carbon low-alloy steel obtained by normalizing, the structure is ferrite + pearlite, including the following steps:
[0084] First, the formula between the yield strength and tensile strength of the steel material and the maximum strain hardening exponent is firstly deduced. The specific operation is:
[0085] The hardened strength of a material can be determined by the Hollomon relation:
[0086] (1)
[0087] In the formula:
[0088] S ——true stress / MPa;
[0089] K ——intensification coefficient / MPa;
[0090] e ——True strain;
[0091] n - strain hardening exponent;
[0092] because n The generalized mechanical definition of the value refers to the sensitivity of deformation stress to strain at any instant in tensile deformation, n The geometric meaning of the value is the slope of the strain hardening curve on the stress-strain logarithmic coordinate plane;
[0093] (2)
[0094] For the data collected by the computer during the tensi...
Embodiment 2
[0162] For a medium-carbon low-alloy steel obtained by quenching and then tempering, the structure is ferrite + upper bainite + tempered sorbite, including the following steps:
[0163] First, the formula between the yield strength and tensile strength of the steel material and the maximum strain hardening exponent is firstly deduced. The specific operation is:
[0164] The hardened strength of a material can be determined by the Hollomon relation:
[0165] (1)
[0166] In the formula:
[0167] S ——true stress / MPa;
[0168] K ——intensification coefficient / MPa;
[0169] e ——True strain;
[0170] n - strain hardening exponent;
[0171] because n The generalized mechanical definition of the value refers to the sensitivity of deformation stress to strain at any instant in tensile deformation, n The geometric meaning of the value is the slope of the strain hardening curve on the stress-strain logarithmic coordinate plane;
[0172] (2)
[0173] For the data c...
Embodiment 3
[0241] For a medium-carbon low-alloy steel that is first quenched and then tempered, the structure is complete martensite, including the following steps:
[0242] First, the formula between the yield strength and tensile strength of the steel material and the maximum strain hardening exponent is firstly deduced. The specific operation is:
[0243] The hardened strength of a material can be determined by the Hollomon relation:
[0244] (1)
[0245] In the formula:
[0246] S ——true stress / MPa;
[0247] K ——intensification coefficient / MPa;
[0248] e ——True strain;
[0249] n - strain hardening exponent.
[0250] because n The generalized mechanical definition of the value refers to the sensitivity of deformation stress to strain at any instant in tensile deformation, n The geometric meaning of the value is the slope of the strain hardening curve on the stress-strain logarithmic coordinate plane;
[0251] (2)
[0252] For the data collected by the compute...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com