Method for regulating and controlling mRNA (messenger Ribonucleic Acid) level of zebra fish vitellogenin
A vitellogenin and zebrafish technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as low accuracy, poor sensitivity, and obvious changes
Active Publication Date: 2012-09-12
中检科健(天津)检验检测有限责任公司
View PDF0 Cites 3 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
When aquatic organisms are poisoned or polluted by low concentrations of estrogen-like disruptors, neither the external morphological characteristics nor the internal physiological indicators will show obvious changes. In addition, the existing methods for evaluating estrogen-like interference The biomarkers for the endocrine dis
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
 Login to View More
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
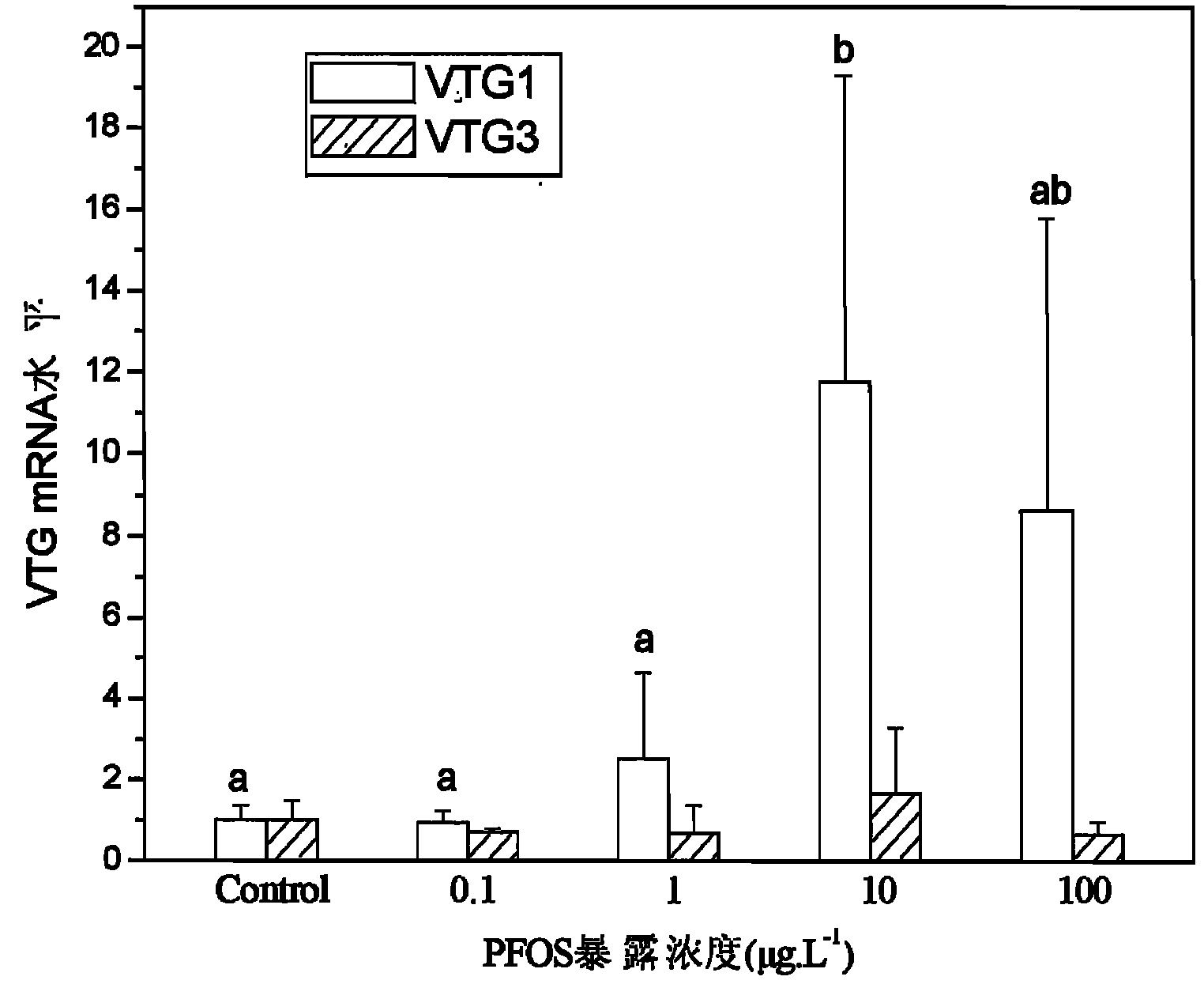
The invention discloses a method for regulating and controlling the mRNA (messenger Ribonucleic Acid) level of zebra fish vitellogenin. The method is used for checking the toxicity or interference for aquatic organisms caused by low-concentration estrogen disruptors. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, respectively extracting total RNA of livers of the aquatic organisms to be detected and a control aquatic organism; secondly, quantifying the mRNA expression level of VTG1 (Vitellogenin 1) and/or VTG3 of the vitellogenin of the extracted total RNA of the livers; and thirdly, if the mRNA expression level of the VTG1 and/or VTG3 of the vitellogenin of a sample to be detected is higher than the expression level of the VTG1mRNA or VTG3mRNA of the vitellogenin of a control sample, showing that the endocrine secretion in the aquatic organisms to be detected is poisoned or interfered by the low-concentration estrogen disruptors. According to the method disclosed by the invention, whether the aquatic organisms are poisoned or interfered by the low-concentration estrogen disruptors in an external environment or not can be accurately and sensitively detected; and the method has the advantages of favorable sensitivity, high accuracy and the like and can be applied to the field of detection of estrogen disruptors for the aquatic organisms.
Description
technical field [0001] The invention relates to a method for testing the toxicity or interference of organic pollutants to aquatic organisms, in particular to a method for testing whether the endocrine of aquatic organisms is poisoned or interfered by low-concentration estrogen-like disruptors in the exogenous environment. The field of inspection of biological estrogen disruptors. Background technique [0002] The chemical pollutants in the ecological environment interfere with the endocrine function of humans and wild animals, thereby exerting various effects on individual reproduction, development, and sexual behavior, and even affecting the survival and reproduction of humans (Tilghman S L, Nierth-Simpson E N, Wallace R, et al. Environmental hormones: Multiple pathways for response may lead to multiple disease outcomes [J]. Steroids, 2010, 75(8-9): 520-523). Therefore, international organizations and developed countries implement mandatory management on monitoring the ha...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More IPC IPC(8): C12Q1/68
Inventor 程艳陈会明崔媛谢文平周新于文莲
Owner 中检科健(天津)检验检测有限责任公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com