Method of manufacturing lithium ion storage device
A technology for an electrical storage device and a manufacturing method, which is applied in the direction of electrolytic battery manufacturing, electrode manufacturing, and final product manufacturing, and can solve problems such as negative electrode degradation and poor cycle characteristics, and achieve the effect of increasing the charging rate and cycle characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
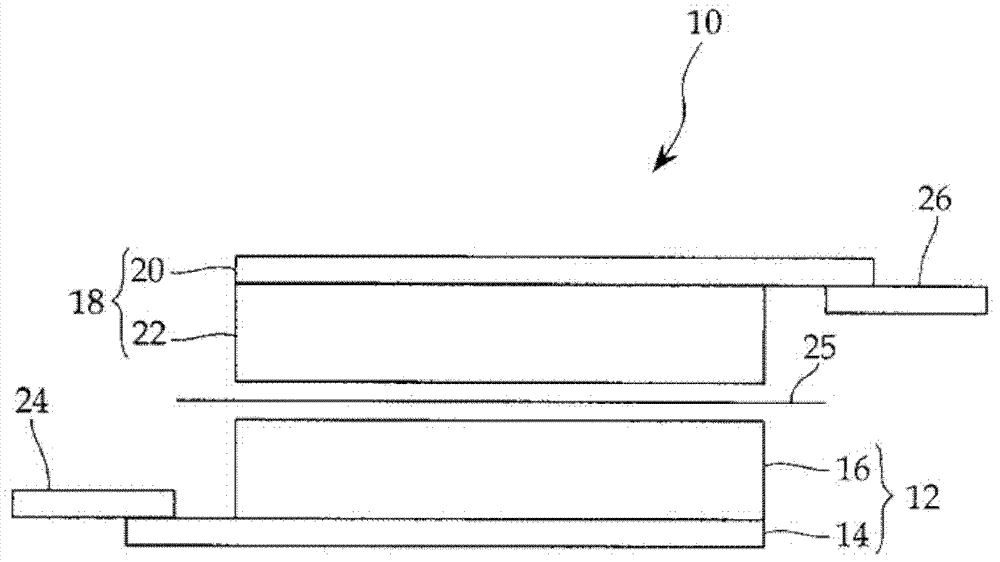
[0040] (1) Production of positive electrode
[0041] Weigh 90 parts by weight of LiCoO as the positive electrode active material 2 A positive electrode slurry was prepared by weighing 5 parts by weight of PVdF as a binder, weighing 5 parts by weight of carbon black as a conductive additive, and using 100 parts by weight of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP). On an Al foil current collector (coated portion 26×40 mm, thickness 10 μm, with convex ears for connecting leads), the positive electrode slurry is applied by the doctor blade method and dried, and then formed by punching A positive electrode active material layer with a thickness of 100 μm. The weight per unit area of the positive electrode active material layer is 20 mg / cm 2 .
[0042] (2) Production of negative electrode
[0043] As a negative electrode active material, 70 parts by weight of silicon powder obtained by pulverizing silicon (silicon powder manufactured by "Aldrich Corporation") to a particle size of less t...
Embodiment 2
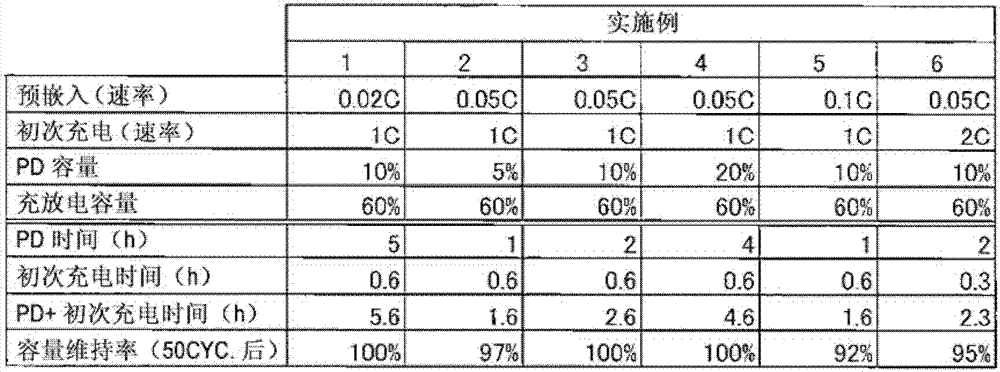
[0053] An experiment was carried out in the same manner as in Example 1, except that pre-doping was performed at a charging rate of 0.05C until the SOC reached 5% in the pre-doping step.
[0054] In the pre-embedding process, the time required to reach SOC 5% is 1 hour, and in the initial charging process, the time required to reach SOC 65% from SOC 5% is 0.6 hours. As a result, from SOC 0% to 65 % The time required is 1.6 hours. The initial charge can be completed in a very short time. In addition, the capacity retention rate was 97%, showing very good cycle characteristics.
Embodiment 3
[0056] An experiment was performed in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the charging rate was set to 0.05C in the pre-doping step.
[0057] In the pre-embedding process, the time required to reach SOC 10% is 2 hours, and in the initial charging process, the time required to reach SOC 70% from SOC 10% is 0.6 hours. As a result, from SOC 0% to 70 % The time required is 2.6 hours. The initial charge can be completed in a very short time. In addition, the capacity retention rate was 97%, showing very good cycle characteristics.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com