Logic operation-based distributed feeder automatization fault judgment method
A feeder automation and logic operation technology, applied in fault locations, electrical components, emergency protection circuit devices, etc., can solve the problems of long fault isolation time, small system impact, low equipment service life, etc., to increase the loss of pressure reclosing function, Avoid the effect of influence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
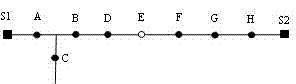
[0033] Such as figure 1 In the distribution network shown, when the system is running in open loop, if a fault occurs in the switch BD section, the switches S1, A, and B experience a fault current, and the switches C and D do not experience a fault current. According to the formulas (1) ~ (5), there are:
[0034] The switch S1 flows through the fault current, and the direction of active power is from the switch to the area S1A, so VN S1 =1, its adjacent switch A experiences a fault current, and the direction of active power flows out of the region S1A, so VN S11 =0, by formula (2) Vgroup S11 ={1&&0}=0, so A S1 =0, switch S1 does not act.
[0035] The fault current flows through switch A, and the direction of active power is to flow out from area S1A and flow into area ABC. So for its first adjacent group, the logical value of switch A VN A is 0, the logic value of switch S1 VN A1 is 1, then its first adjacent switch group Vgroup A1 The value of 0; for...
Embodiment 2
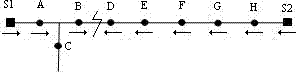
[0042] When the system operates in closed loop, for figure 1 In the distribution network shown, if a fault occurs in the switch BD section, the switches S1, A, B, D, E, F, G, H, and S2 all experience a fault current, and the switch C does not experience a fault current. The fault active power flow direction is as follows: figure 2 Shown:
[0043] The analysis of switches S1, A, and C is exactly the same as that of the open-loop operation, and will not be repeated here.
[0044] Switch B experiences a fault current, for its first adjacent switch group ABC, the logical value of switch A is 1, the logical value of switch B is 0, the logical value of switch C is 1, and the logical value of the first adjacent group Vgroup B1 is 0; for the second adjacent switch group BD, the logic value of switch B VN B is 1, the switch D flows through the fault current, and the direction of active power flows into the interval BD, so its switch logic value VN B1 is 1, so the logical val...
Embodiment 3
[0048] If the system has a temporary fault, after the fault is isolated, the temporary fault will be eliminated. In order to ensure the power supply in the normal area, it is necessary to add the function of reclosing when the switch side loses voltage. In order to ensure the success of the switch reclosing function, the circuit breaker at the outlet of the substation should be equipped with a delay current speed protection function.
[0049] If the fault current is detected again after the switch is reclosed, it means that the fault is a permanent fault, and the switch will be locked in the open state.
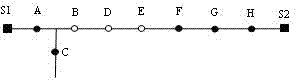
[0050] for figure 1 As shown in the distribution network, when a temporary fault occurs in the BD area, the switch BD will open to isolate the fault, such as image 3 shown. After the switch BD is opened, if the fault is eliminated, switch B detects the loss of voltage on one side, and starts the function of reclosing on one side of the loss of voltage, such as Figure 4 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com