Distributed fault location method for T-circuit
A fault distance measurement and distributed technology, applied in the direction of fault location, etc., can solve the problem that the fault branch cannot be correctly and effectively judged, and achieve the effect of improving the distance measurement accuracy, simplifying the algorithm, and having a good application prospect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] Below in conjunction with the drawings, preferred embodiments of the present invention are given and described in detail.
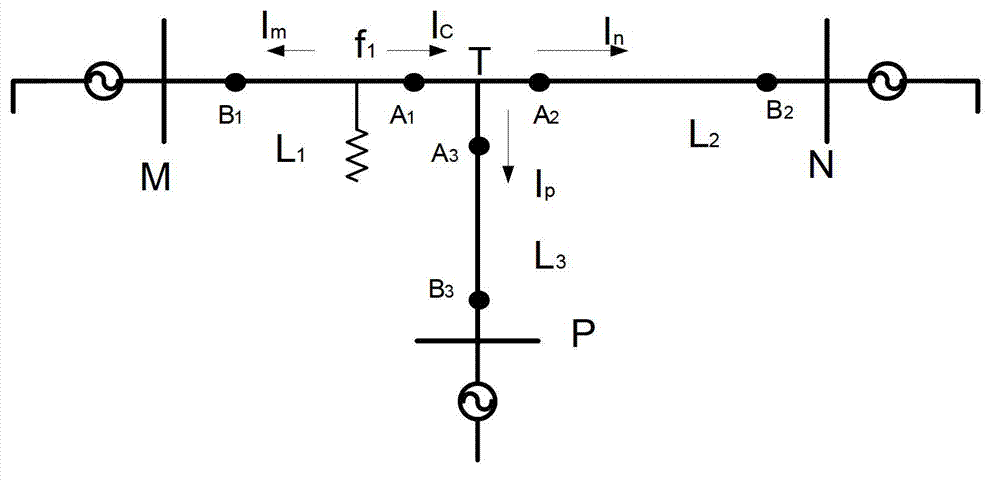
[0033] See 2, figure 2 It is the installation distribution diagram of the fault current detection device in the T-shaped circuit of the present invention. As shown in the figure, two Rogowski coils are installed on each branch in the T-shaped circuit as the fault current detection device, respectively A 1 , B 1 、A 2 , B 2 、A 3 , B 3 , where A 1 、A 2 、A 3 For the first group of fault current detection devices, they are the same distance from T node, B 1 , B 2 , B 3 They are respectively located on the three branches MT, NT and PT of the T-shaped line, and take the center point of each branch as the symmetrical point and A 1 、A 2 、A 3 Relatively symmetrical position, i.e. MB 1 、TA 1 、TA 2 , NB 2 、TA 3 , PB 3 The distance is Y. The wave impedance of each transmission line is Z. Since the distance measurement method is the same whe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com