Intelligent data service method based on distributed system
A technology of distributed systems and data services, applied in the field of intelligent data services based on distributed systems, can solve the problems of difficult data services, difficult to form intelligent data services, adding preprocessing, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing bandwidth requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0027] The invention is an intelligent data service method for data-intensive applications derived from a traditional distributed system.
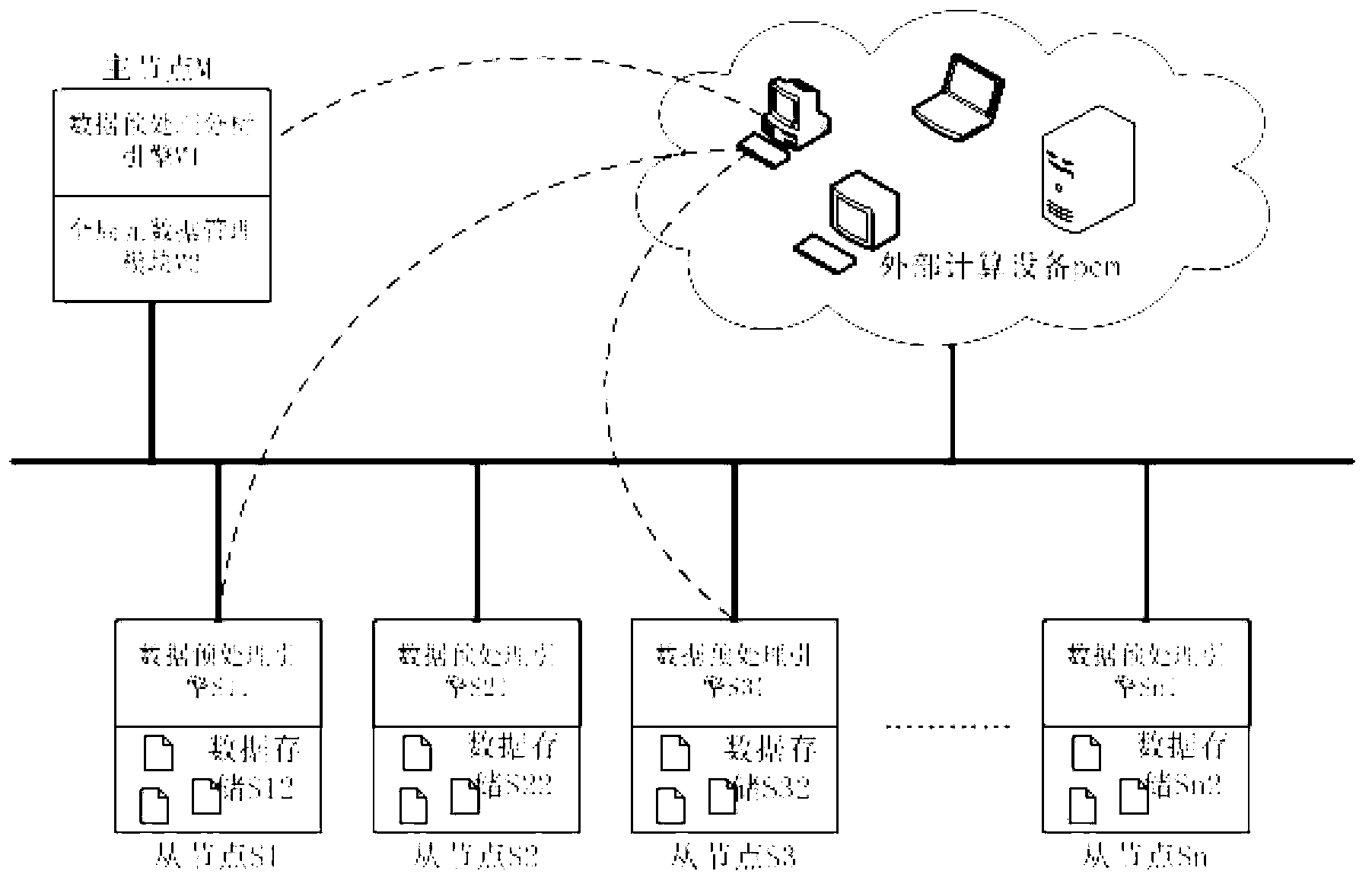
[0028] specifically, figure 1 The architecture of an intelligent data service platform based on a distributed system according to the first embodiment of the present invention is schematically shown.
[0029] Such as figure 1 As shown, similar to most distributed file systems and distributed databases, the entire architecture is a typical Master / Slave architecture. E.g, figure 1 The intelligent data service platform architecture based on the distributed system shown includes a master node M and multiple slave nodes; specifically, figure 1 A case where n slave nodes are included in is shown, that is, the first slave node S1, the second slave node S2, the third slave node S3, ..., the nth slave node Sn.
[0030] Among them, the master node M includes a data preprocessing analysis engine M1 and a global metadata management module M2. Each slave nod...
no. 2 example
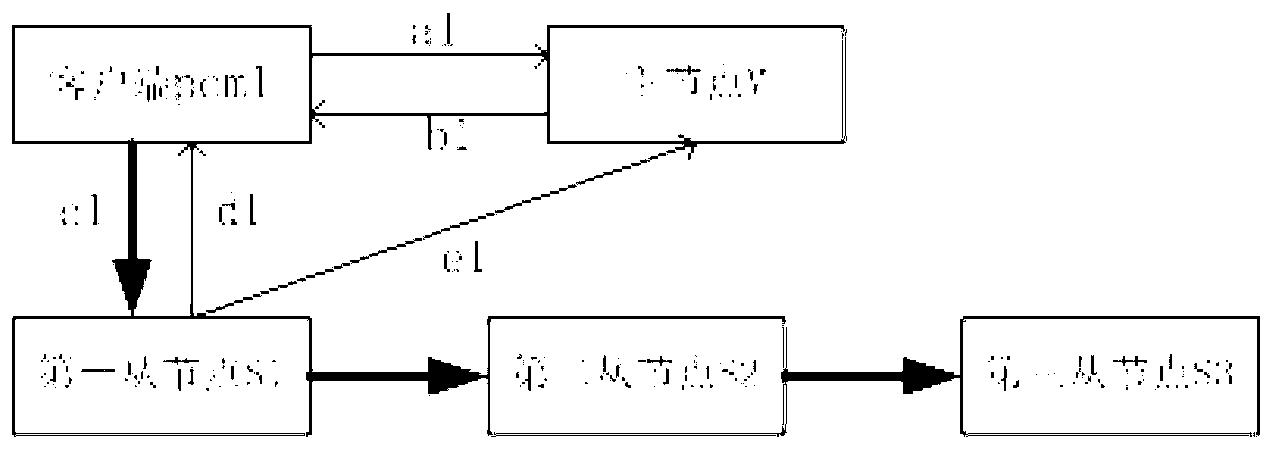
[0038] figure 2 It schematically shows a schematic diagram of a process of writing a file to a distributed system according to the second embodiment of the present invention. Among them, the process of writing files to the distributed system does not preprocess the data. Here, it is assumed that there are three slave nodes in the distributed system: the first slave node S1, the second slave node S2, and the third slave node S3, but obviously the number of slave nodes in the distributed system is not limited to three, but can Is any suitable number.
[0039] Specifically, such as figure 2 As shown, the process of writing files to the distributed system according to the second embodiment of the present invention includes:
[0040] The first writing step a1: the client pcm1 asks the master node M whether the file to be written exists in the distributed system.
[0041] Second writing step b1: If the file to be written exists in the distributed system, the master node M sends the fil...
no. 3 example
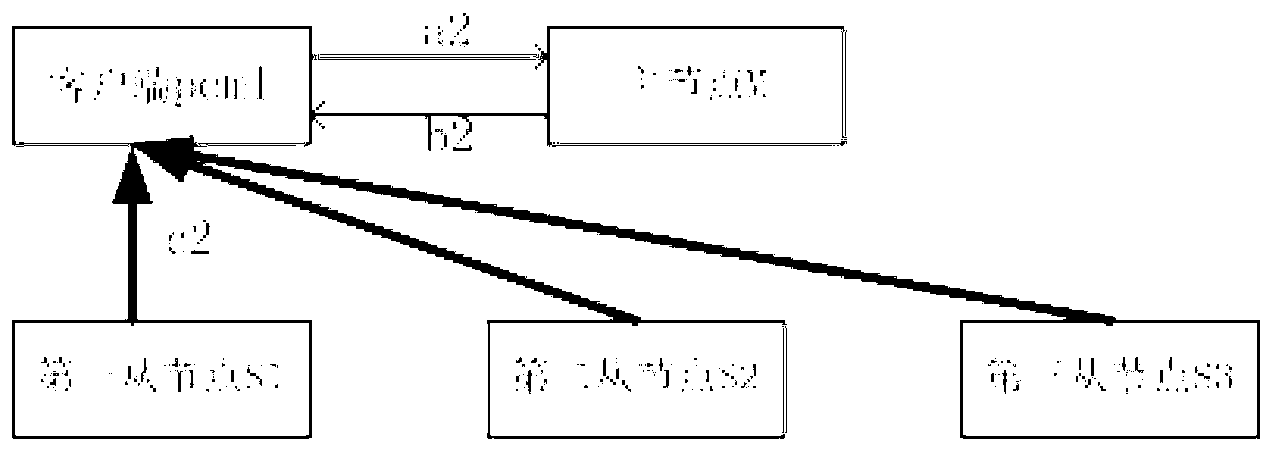
[0046] image 3 It schematically shows a schematic diagram of a process of reading a file from a distributed system according to the third embodiment of the present invention. Here, it is assumed that there are three slave nodes in the distributed system: the first slave node S1, the second slave node S2, and the third slave node S3, but obviously the number of slave nodes in the distributed system is not limited to three, but can Is any suitable number.
[0047] The process of reading files from the distributed system according to the third embodiment of the present invention includes:
[0048] The first reading step a2: the client pcm1 sends a data request to the master node M, which includes the file path and the required preprocessing.
[0049] Second reading step b2: The master node M analyzes the data request of the client pcm1, can determine the slave node where the required file is located and the required preprocessing program, directly preprocess the required file, and sen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com