Method and device for determining size and number of resource block group (RBG) after fragmentation carrier configuration
A technology for determining methods and devices, applied in network traffic/resource management, electrical components, wireless communication, etc., can solve problems such as resource allocation confusion and inconsistent RBG sizes, and achieve the effect of increasing flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
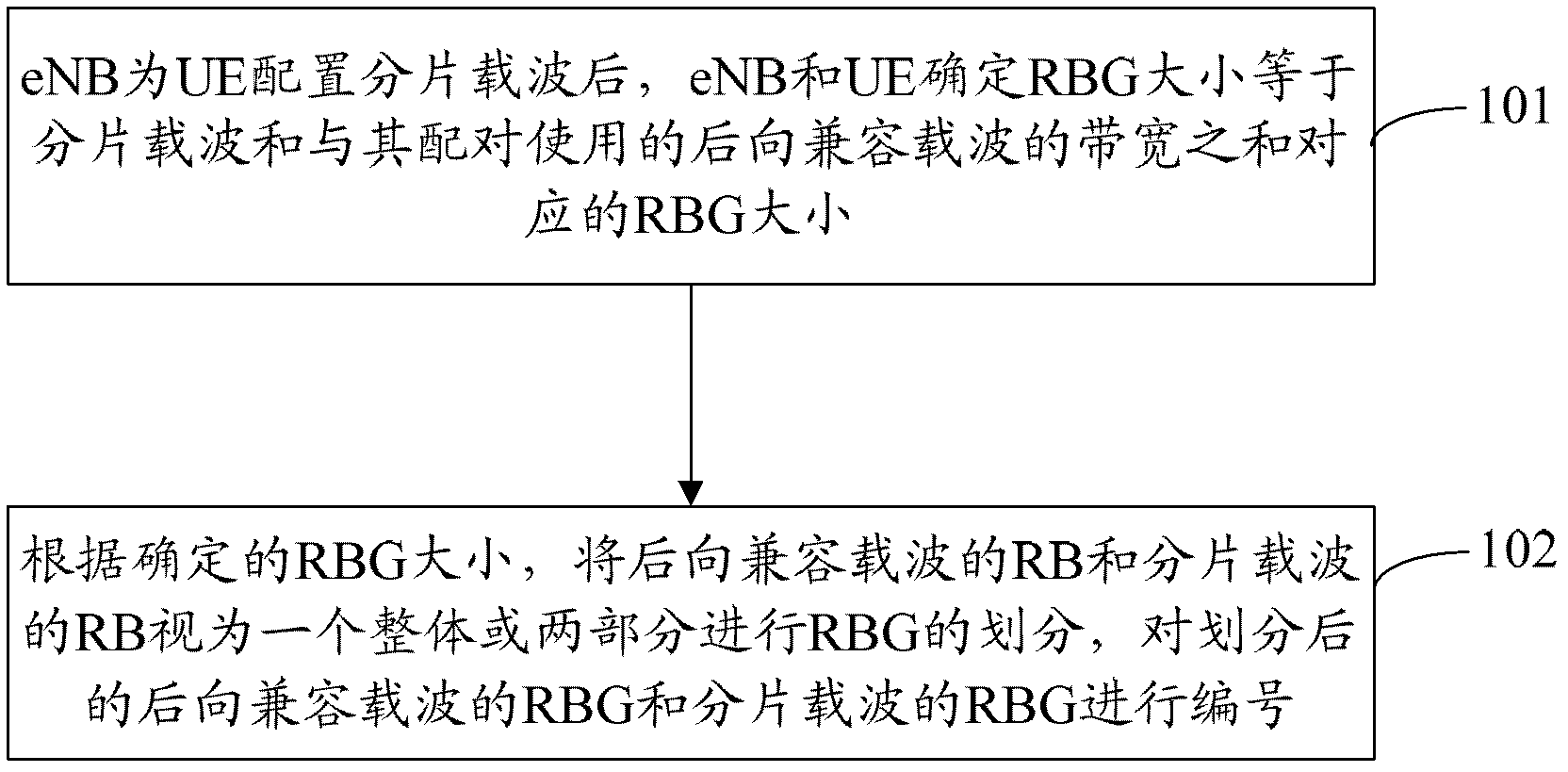
[0085]In this embodiment, a 5MHz (including 25 RBs) backward compatible carrier and a 1.4MHz (including 6 RBs) fragmented carrier are used for aggregation of the UE of the new version.
[0086] 1. Determination of RBG size:
[0087] Such as figure 2 As shown, UE 1 only uses a 5MHz backward-compatible carrier, and the RBG size corresponding to UE1 is determined as follows: After the eNB configures UE 1 to use a 5MHz backward-compatible carrier, the new carrier bandwidth is 25 (that is, the number of RBs is 25), According to Table 1, the corresponding RBG size is 2;
[0088] UE 2 aggregates and uses a 5MHz backward compatible carrier and a 1.4MHz fragmented carrier, and determines the RBG size corresponding to UE 2 as follows: After the eNB configures UE 2 to use a 1.4MHz fragmented carrier and a 5MHz backward compatible carrier The sum of carrier bandwidths is 31 (that is, the number of RBs is: 6+25=31). According to Table 1, the corresponding RBG size is 3.
[0089] This w...
Embodiment 2
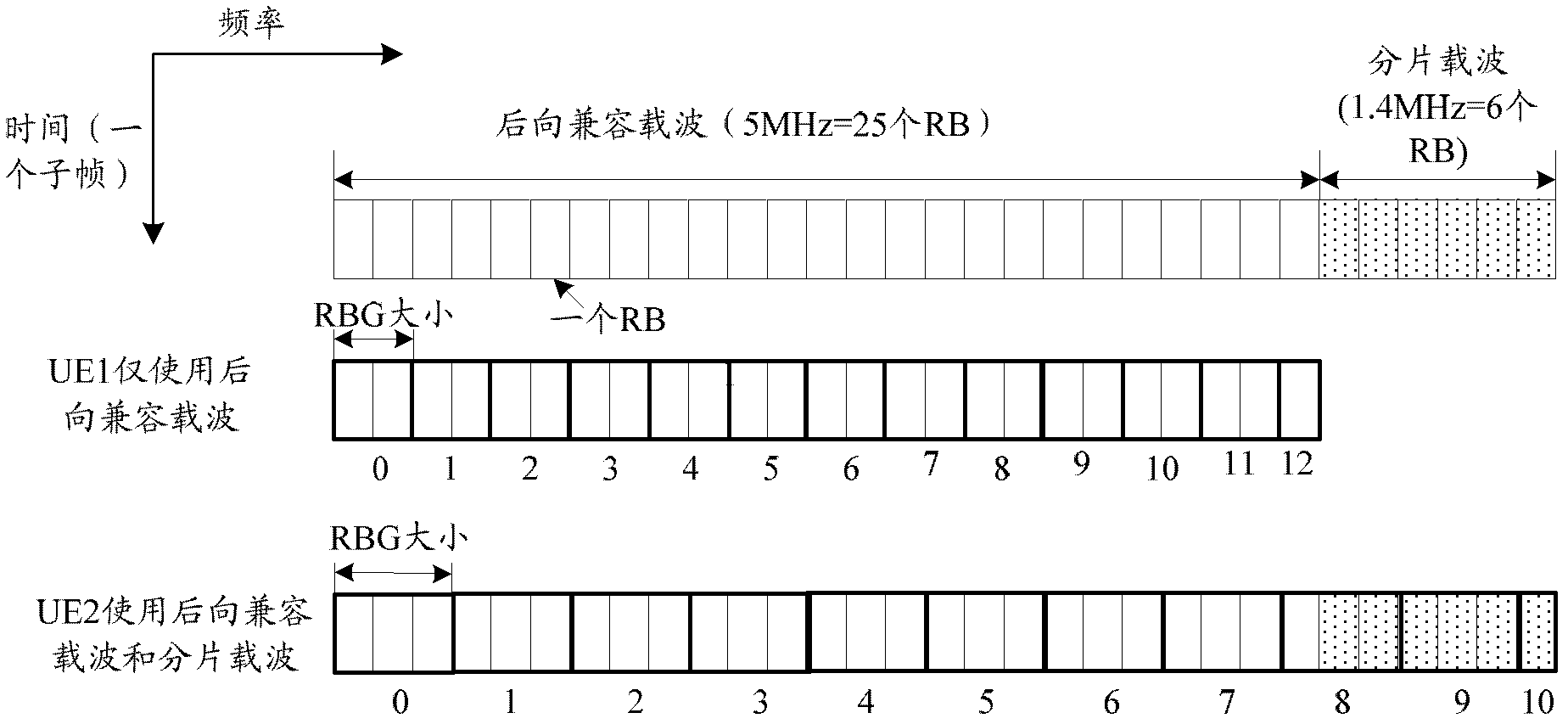
[0096] The main difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment lies in the different RBG division methods when the UE aggregates and uses backward compatible carriers and fragmented carriers.
[0097] Specifically, in the first embodiment, all RBs contained in the compatible carrier and the fragmented carrier are regarded as a whole, and the RBG division is performed; while in this embodiment, the RBs contained in the backward compatible carrier and the fragmented carrier are regarded as two parts, and the RBG is performed separately. divided.
[0098] Such as image 3 As shown, for UE 2, RBG division is performed on the RBs of the backward compatible carrier and the RBs of the fragmented carrier according to the determined RBG size (3). The numbering rules are as follows: RBGs of backward compatible carriers are numbered from 0, and RBGs of fragmented carriers are numbered continuously from the maximum value of RBG numbers of backward compatible carriers.
[00...
Embodiment 3
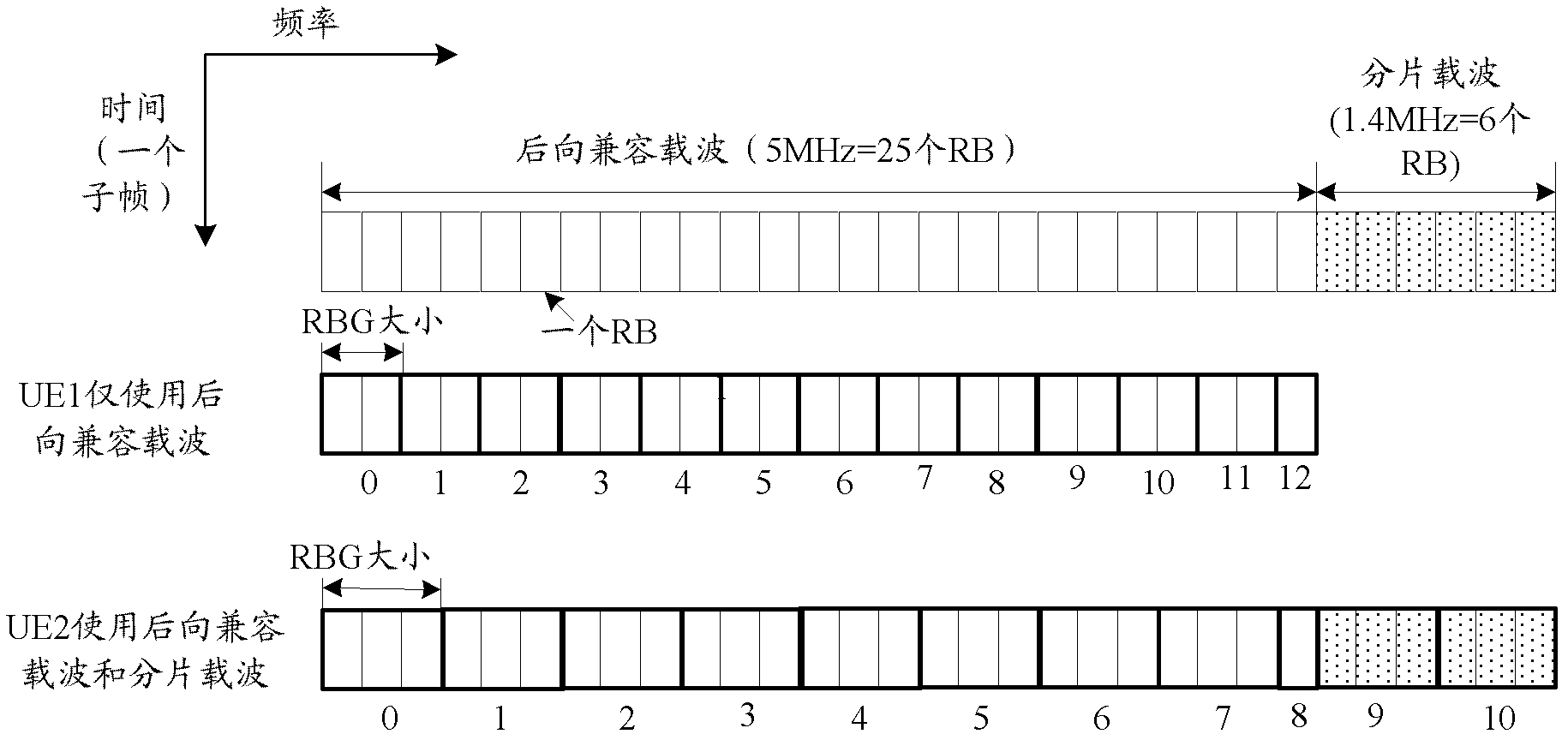
[0103] The method of determining the RBG size in this embodiment is the same as that in Embodiment 1, the main difference lies in the method of RBG numbering.
[0104] Wherein, the RBG encoding method when UE 1 only uses the backward compatible carrier is the same as that in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here. For the case where the UE 2 uses the backward compatible carrier and the fragmented carrier, in this embodiment, the RBs included in the backward compatible carrier and the fragmented carrier are respectively divided into RBGs, and the numbers start from 0 respectively.
[0105] Such as Figure 4 As shown, for UE 2, the RBs (31) contained in its carrier bandwidth are divided into two parts: backward compatible carrier and fragmented carrier, and the RBs in these two parts are divided into RBG according to the determined RBG size (3). , the numbering rule is: RBGs of backward compatible carriers are numbered from 0, and RBGs of fragmented carriers are also numbe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com