Vinyl ester/ethylene-based binders for paper and paperboard coatings
A vinyl ester and latex adhesive technology, applied in paper coating, papermaking, coating, etc., can solve problems such as opposition to commercial use and lack of
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] Aqueous adhesive latex emulsions were prepared by the following method:
[0059] In 3190 g of deionized water, dissolve 115 g of 20% sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate active solution, 234 g of 65% fatty alcohol ethoxylate (30EO) active solution, 173 g of 30% sodium vinyl sulfonate and 13 g of sodium acetate. An iron salt is added as a redox catalyst.
[0060] After adding 216 g of vinyl acetate and pressurizing with 518 g of ethylene, the mixture was heated to 65°C and at this temperature 455 g of 4% FF6 (sulfinic acid derived reducing agent) solution and 320 g of 3.2% tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP) solution were used for polymerization. Simultaneously, a monomer mixture comprising 4140 g of vinyl acetate, 6 g of diallyl phthalate and 9 g of maleic anhydride was added.
[0061] After the start of the polymerization, a further 312 g of ethylene were added, keeping the pressure below 80 bar. The monomer mixture was fed over a period of 4 hours while the initiator was r...
Embodiment 2-9
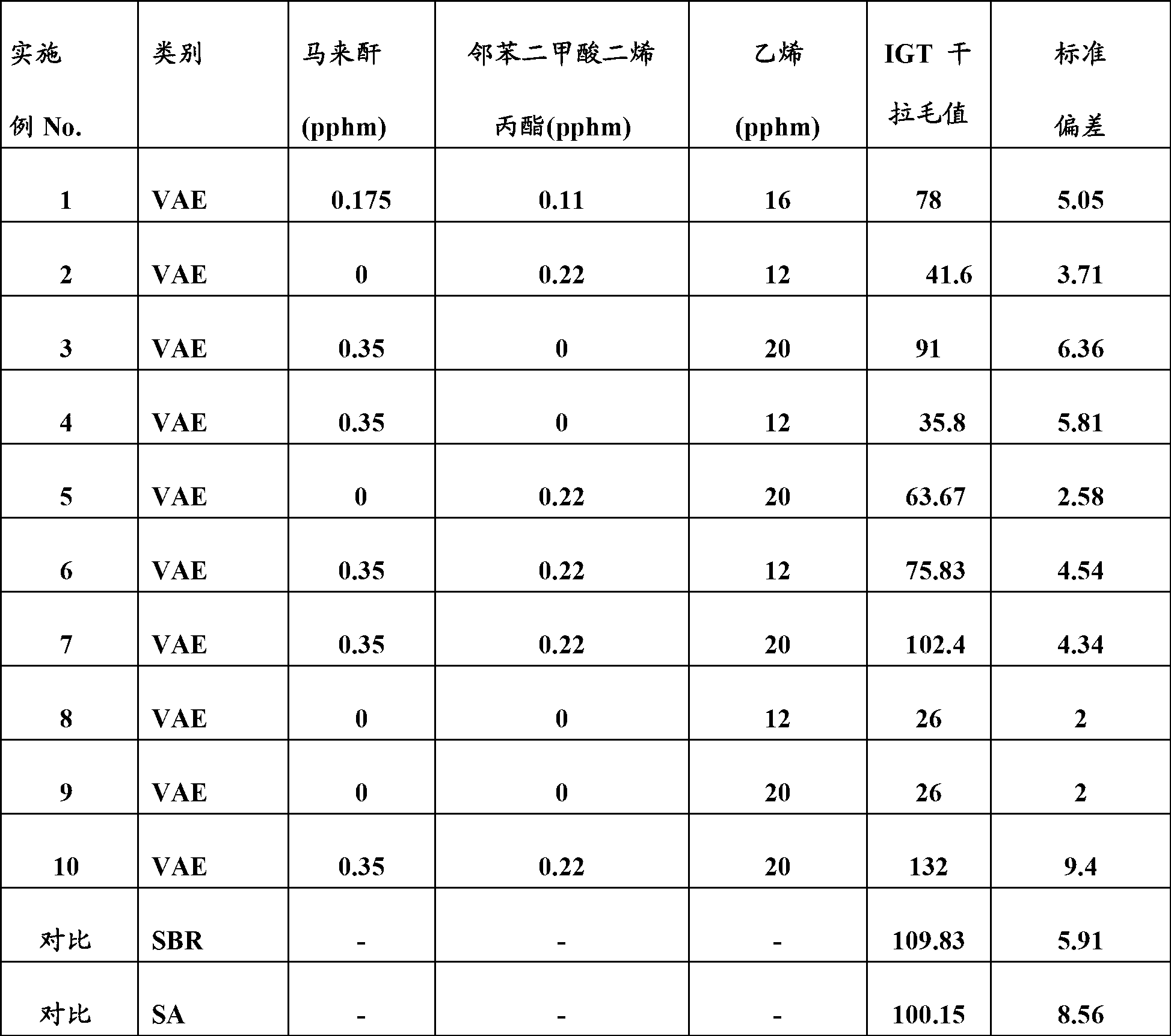
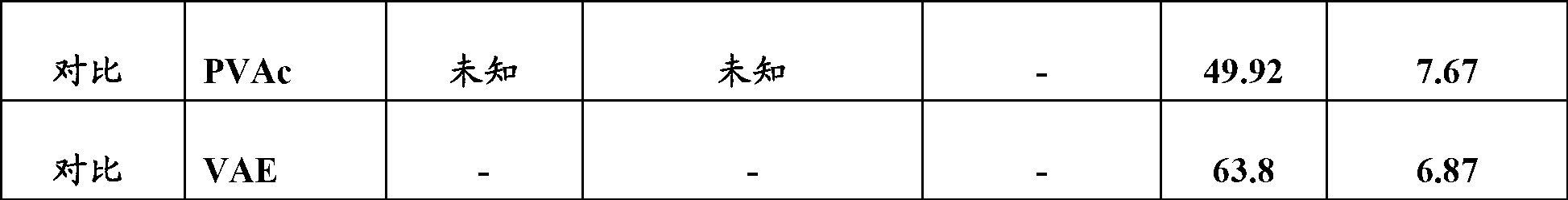
[0064] Using the same general procedure of Example 1, another eight adhesive latex emulsions were prepared, but with varying amounts of ethylene, maleic anhydride, and diallyl phthalate were used in their preparation. In some of these additional emulsions for comparison, only maleic anhydride comonomer or only diallyl phthalate crosslinker was used. In the rest of these comparative emulsions, neither maleic anhydride nor diallyl phthalate was incorporated into the formed VAE interpolymer. A description of the comonomer content of the interpolymers for each of the emulsions of Examples 2-9 is also presented in Table I below.
Embodiment 10
[0066] Aqueous adhesive latex emulsions were prepared by the following method involving the use of pre-emulsions:
[0067] In 2500 g of deionized water, dissolve 62 g of 20% sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate active solution, 158 g of 65% fatty alcohol ethoxylate (30EO) active solution, 93 g of 30% sodium vinyl sulfonate and 13 g of sodium acetate. Iron salts are added as redox catalysts.
[0068] After adding 750 g of vinyl acetate and pressurizing with 500 g of ethylene, the mixture was heated to 65°C and at this temperature 343 g of 5% FF6 solution and 345g6% ammonium persulfate solution were polymerized.
[0069] A monomer pre-emulsion was also added to the mixture at the same time. Such a pre-emulsion was prepared by making 3250 g vinyl acetate in 6 g diallyl phthalate solution, 9 g maleic anhydride, 154 g 20% sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate active solution, 67 g 65% Fatty alcohol ethoxylate (30EO) active solution, and 73g of 30% sodium vinyl sulfonate emulsification co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com