Static and dynamic exchange-type thighbone interlocking intramedullary nail
An exchange-type, static-dynamic technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve problems such as lack of fracture longitudinal stress stimulation at the fracture end, affect fracture healing, and delayed fracture healing, and achieve the effects of increasing effective physiological stimulation, promoting fracture healing, and stress dispersion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
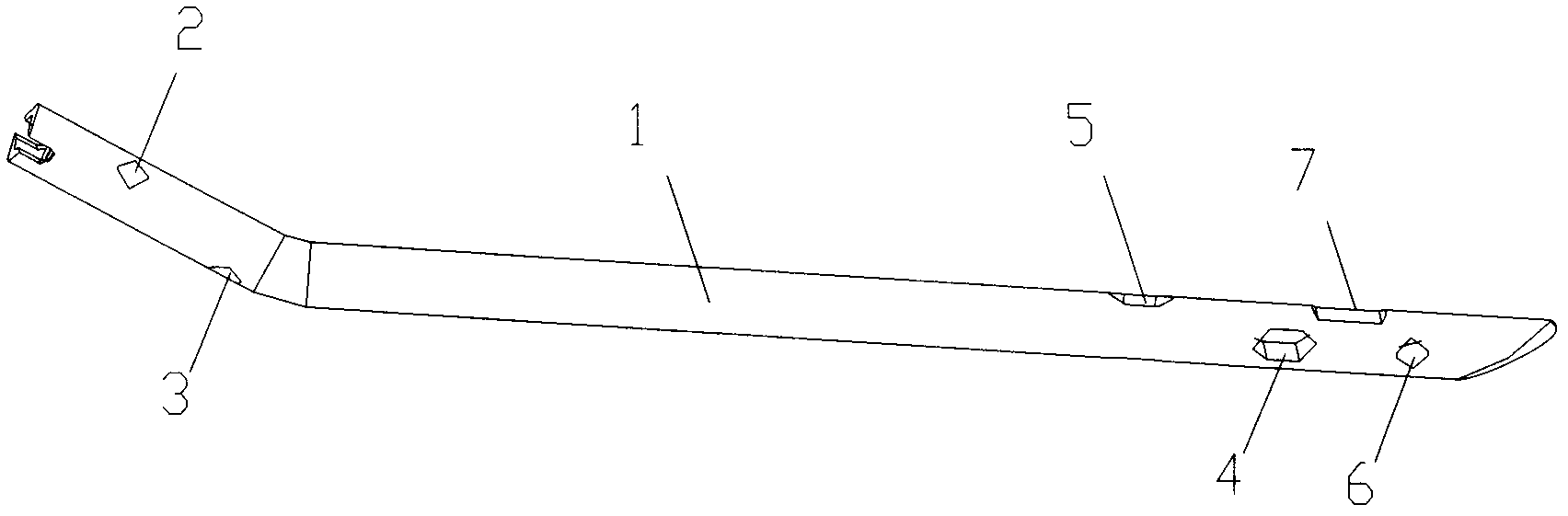
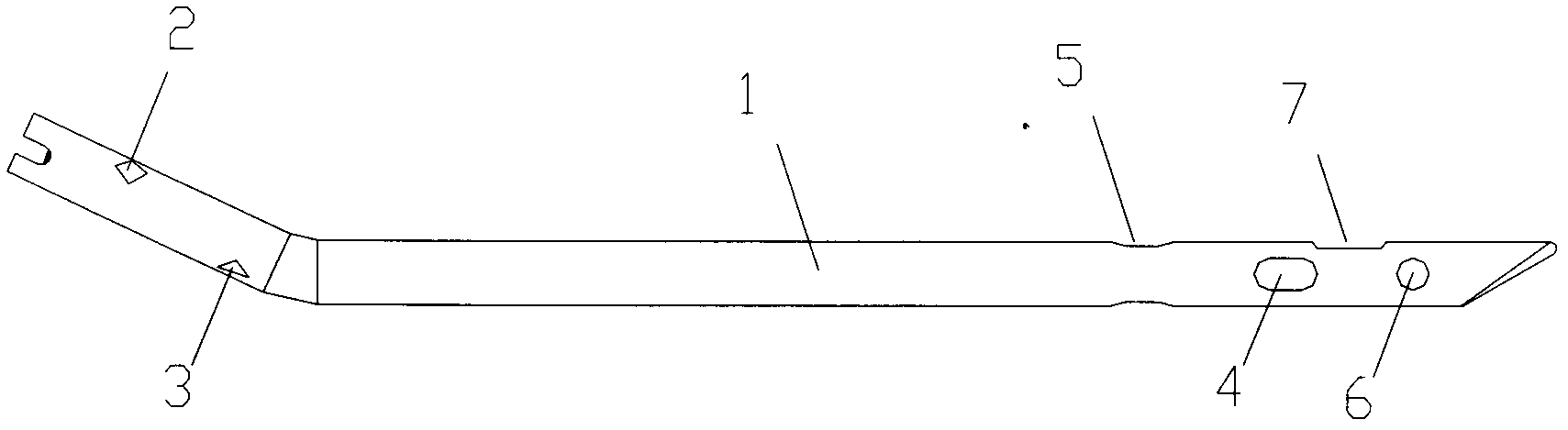
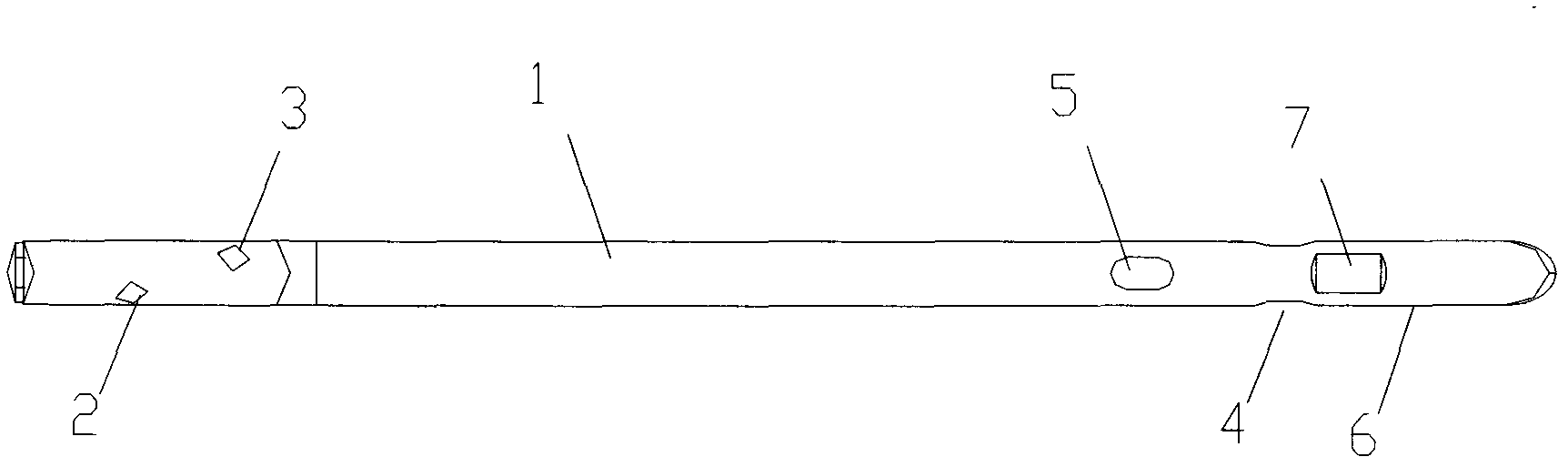
[0025] as attached Figure 1-3 The shown static and dynamic exchange type femoral interlocking intramedullary nail of the present invention includes a nail body 1, and the coronal surface of the distal end of the nail body 1 is provided with a first sliding locking hole 4 and a static force hole 6 , the sagittal plane of the distal end of the nail main body 1 is provided with a second sliding lock hole 5, the first sliding lock 4 holes and the second sliding locking hole 5 are elongated holes; the static force hole 6 is arranged at the second The distal end of a sliding locking hole 4 and the second sliding locking hole 5, and at the distal end of the nail main body 1; the proximal end of the nail main body 1 is provided with a first fixing hole 2 and a second fixing hole 3; The first fixing hole 2 and the second fixing hole 3 are arranged on mutually perpendicular surfaces; the length of the first sliding locking hole 4 is shorter than the second sliding locking hole 5; the s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com