Distribution network single-phase earth fault line selection method based on negative sequence impedance angles
A single-phase ground fault, negative-sequence impedance angle technology, applied in the direction of fault location, measuring electricity, measuring electrical variables, etc., can solve problems such as loss of function
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
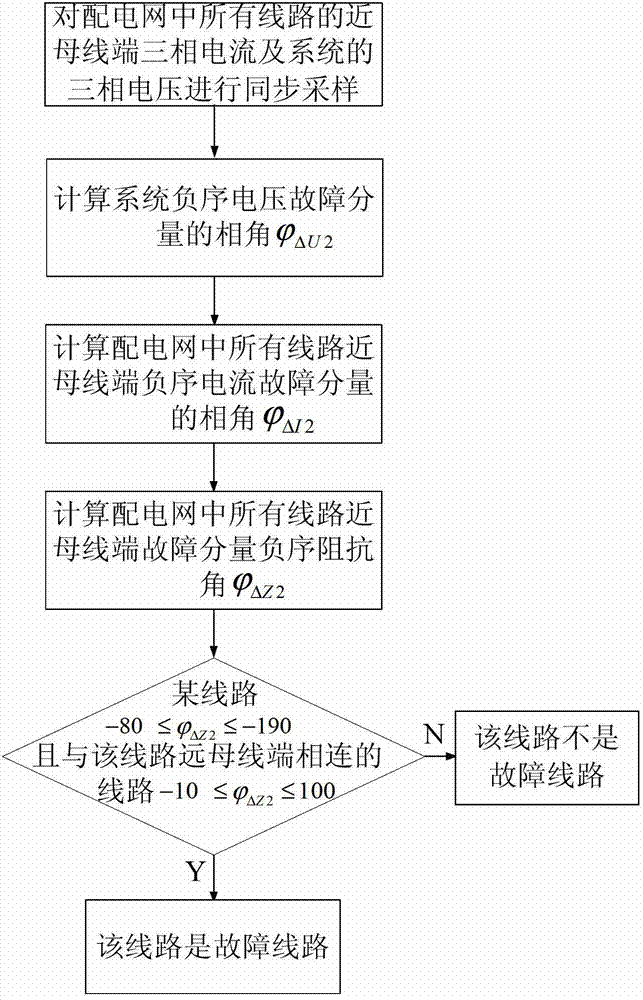
[0067] First, the basic principle of the present invention is briefly introduced.
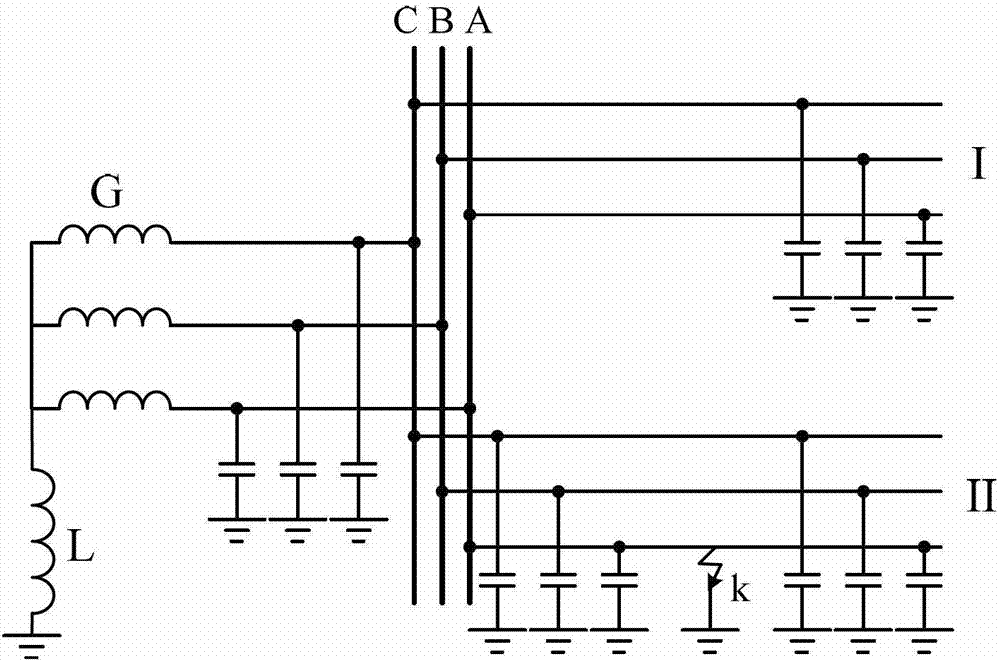
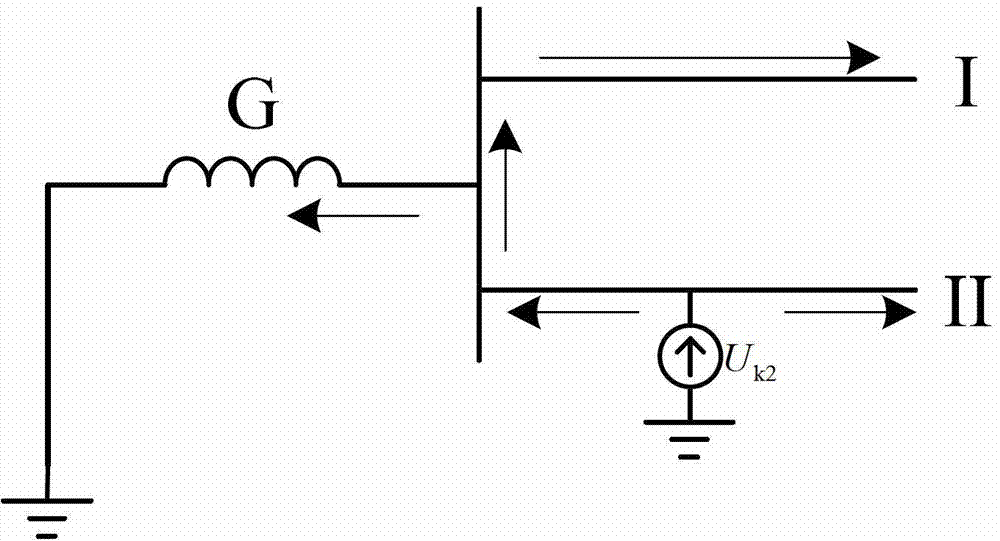
[0068] by figure 2 The distribution network whose neutral point is grounded through the arc-suppression coil is taken as an example for illustration. When a ground fault occurs on phase A of line II, the negative sequence equivalent network is as follows image 3 As shown, U in the figure k2 Add negative-sequence equivalent power to the fault point. Therefore, the negative-sequence power caused by the fault flows from the faulted line to the busbar and non-faulted lines, which reflects the difference in phase relationship between the negative-sequence voltage and negative-sequence current of the normal line and the faulty line.
[0069] For the normal line Ι, the actual negative-sequence current and negative-sequence voltage of the port near the power supply terminal should satisfy Figure 4 indicated direction. Since the actual power grid and load always present the nature of resistive i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com