Base station antenna selecting method based on interference alignment in multi-cell system
A base station antenna and antenna selection technology, applied in diversity/multi-antenna systems, baseband system components, space transmit diversity, etc., can solve the problems of no consideration, inability to expand, and increase system hardware costs, reducing computational complexity, The effect of realizing multi-cell interference coordination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
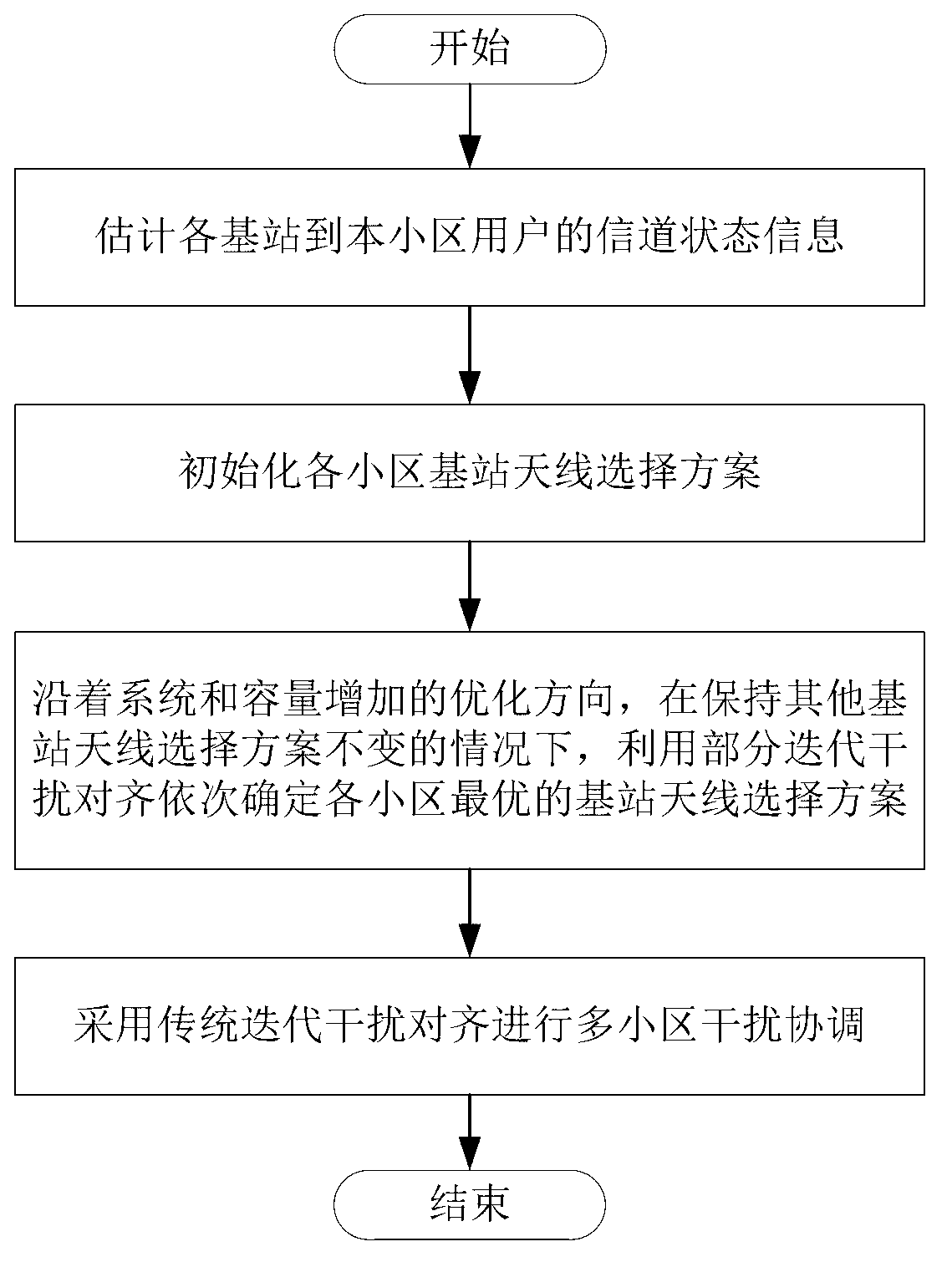
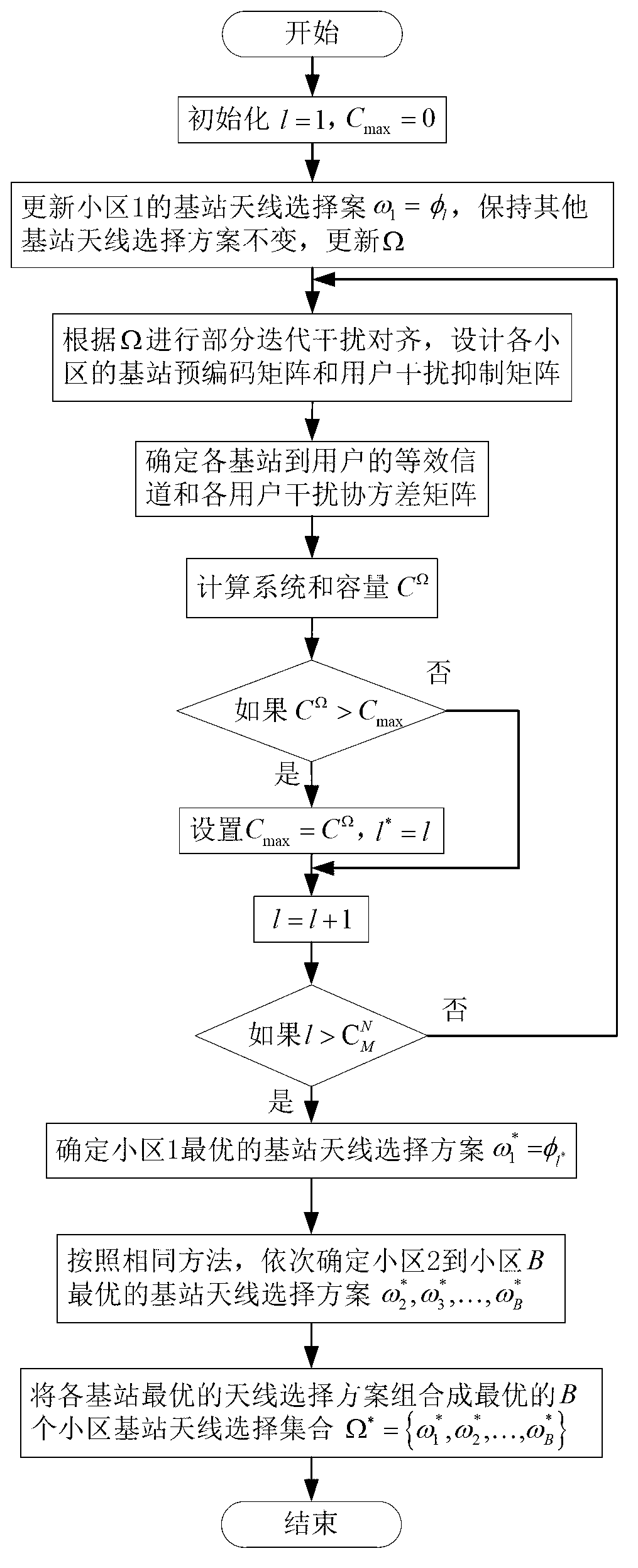
[0046] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
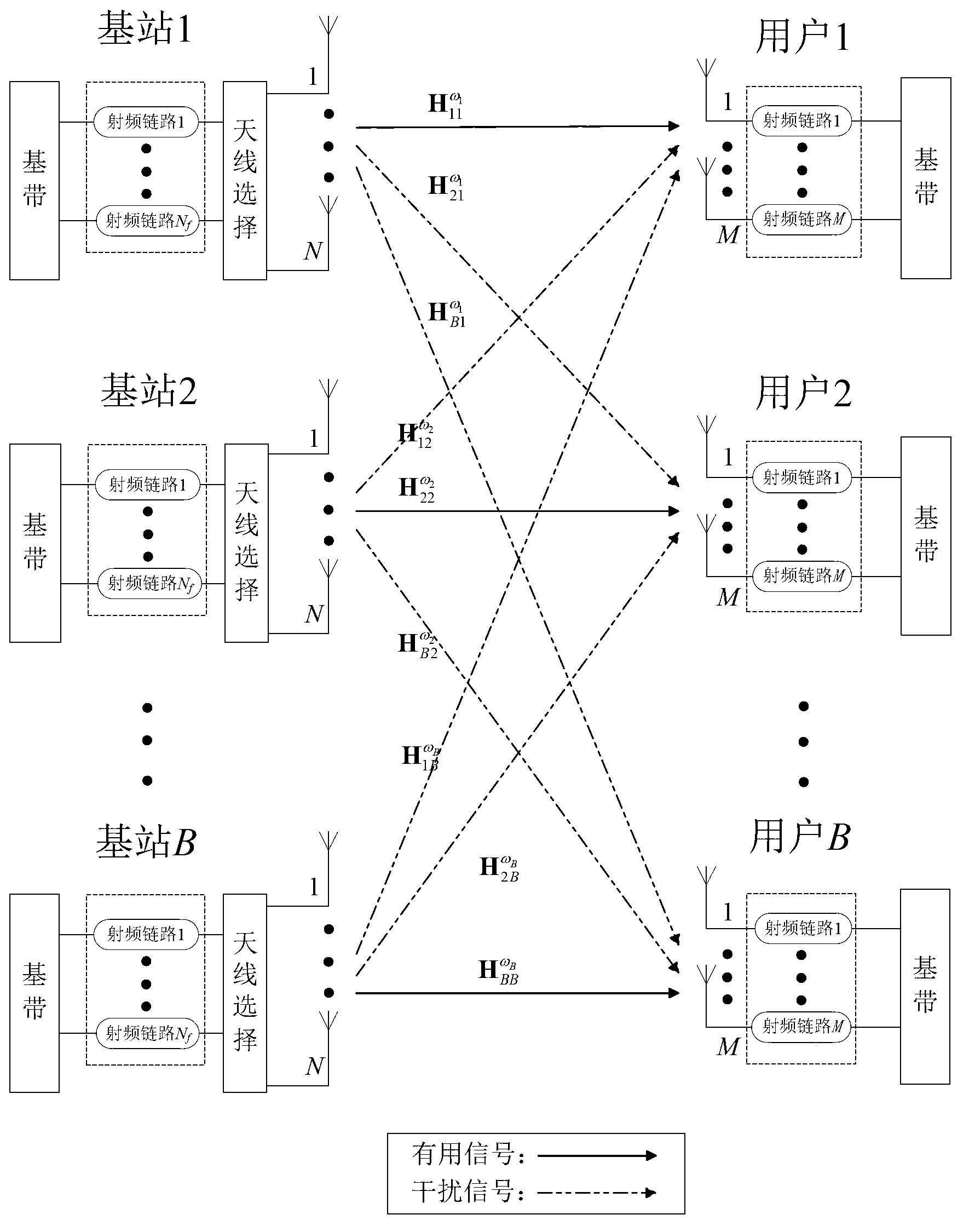
[0047] refer to figure 1 , in the B cell system, the base station of each cell serves one user, and the number of antennas and radio frequency links of the base station are N and N respectively f , the number of antennas and the number of radio frequency links of the user are both M. The serial number of the cell is represented by k, and k=1,...,B, then the base station k and the user k represent the base station and the user of the cell k respectively. For a system with multiple users in each cell, it can be simplified to a system with only one user in each time slot by using, for example, time division multiplexing. Suppose N>N f , each base station needs to select N from all N antennas f antennas, and connected to the corresponding radio frequency link, so the set of candidate antennas Φ of the base station contains candidate antenna selection vector...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com