Method for producing slit material
A manufacturing method and slit technology, applied in the direction of manufacturing tools, knives for shearing machines, shearing devices, etc., can solve the problems of waste, large materials, losses, etc., and achieve the effect of suppressing material costs and preventing bad shapes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
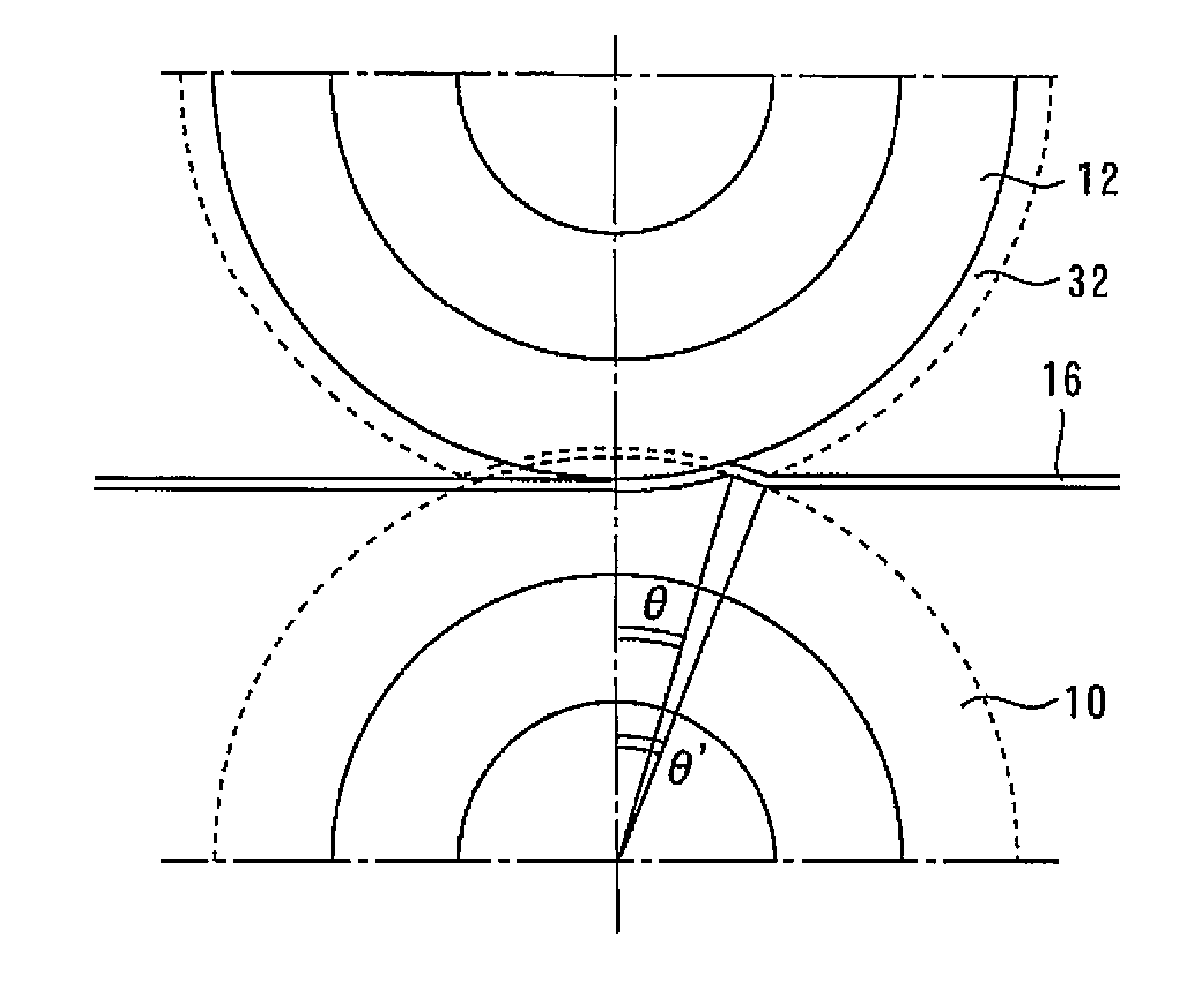
[0033] FIG. 1 is a front view illustrating a method of manufacturing a slit material according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. Fig. 2 is a sectional view along A-A' direction in Fig. 1, and Fig. 3 is a sectional view along B-B' direction in Fig. 1 . Fig. 4 is a plan view showing a slit material according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
[0034] First, as shown in Figures 1 to 3, the first and second circular blades 10, 12, which are arranged transversely and have a plurality of rectangular blades in cross-section, face each other, and each blade of the first circular blade 10 is positioned relative to the first circular blade 10. The corresponding blades of the 2 circular blades 12 are arranged so as to be shifted to the same side in the lateral direction.
[0035] Then, by the guide roller 14, the metal strip 16 is introduced from the side closer to the first round blade 10 than the second round blade 12, so that the metal strip 16 is wound on the second ...
Embodiment approach 2
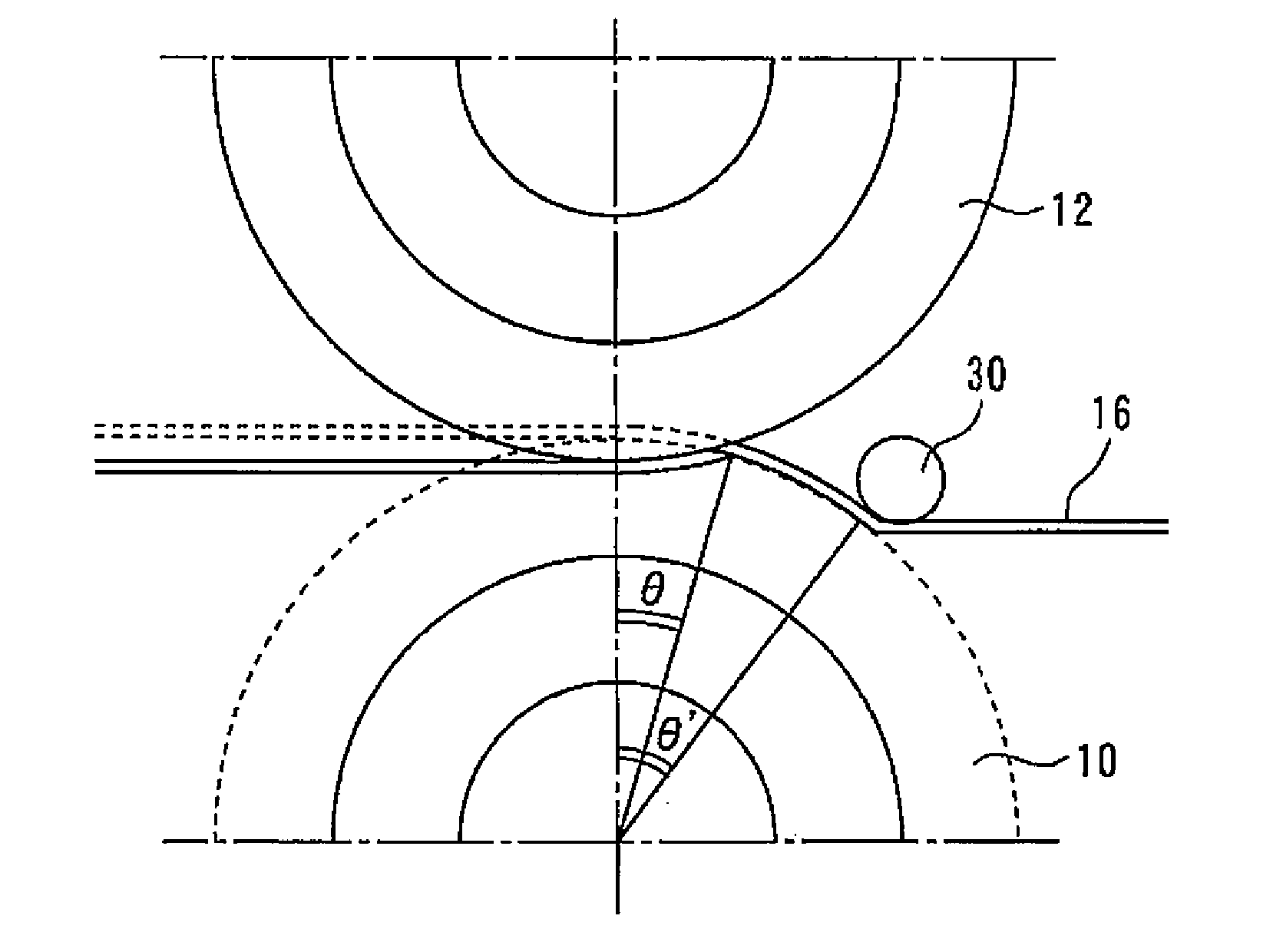
[0046] FIG. 10 is a front view illustrating a method of manufacturing a slit material according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. Fig. 11 is a sectional view along the A-A' direction in Fig. 10, and Fig. 12 is a sectional view along the B-B' direction in Fig. 10 . In this embodiment, a guide roller 30 is provided on the entrance side of the first and second round blades 10 and 12 . Then, the metal strip 16 is wound around the first circular blade 10 by pressing the metal strip 16 against the first circular blade 10 with the guide roller 30 before cutting the metal strip 16 .
[0047]Thus, the slit strain of the first edge portion 20 of the slit material 18 is smaller (substantially zero) than the slit strain of the second edge portion 22 . Therefore, similarly to Embodiment 1, material costs can be suppressed, and shape defects due to slit strain can be prevented.
Embodiment approach 3
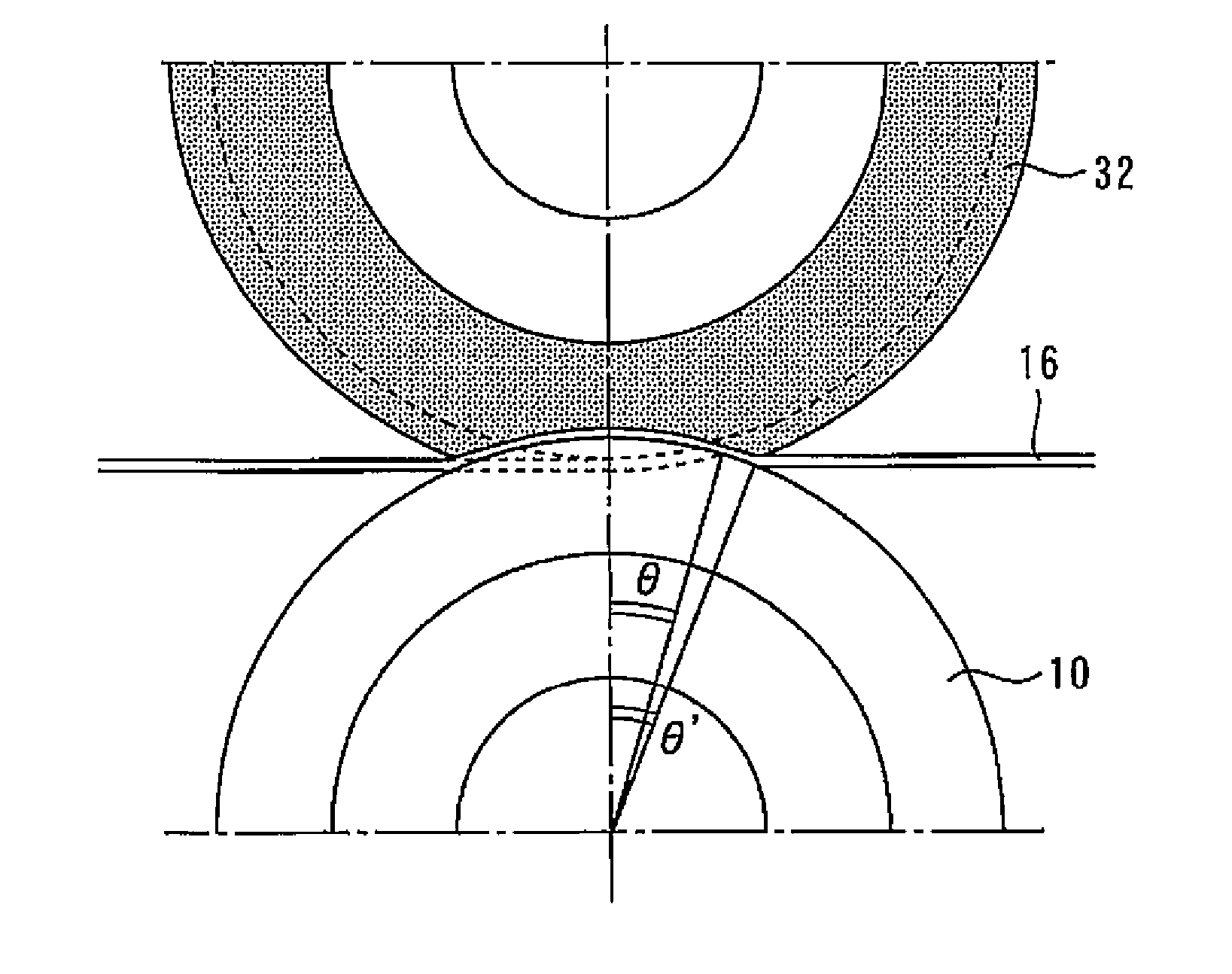
[0049] 13 is a front view for explaining a method of manufacturing a slit material according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention. Fig. 14 is a sectional view along the A-A' direction in Fig. 13, and Fig. 15 is a sectional view along the B-B' direction in Fig. 13 . In this embodiment, the rubber ring 32 is provided on the lateral side of the first round blade 10 so as to face the first round blade 10 . And when the metal strip 16 is cut, the metal strip 16 is pressed against the first circular blade 10 with the rubber ring 32 .
[0050] Thus, the slit strain of the first edge portion 20 of the slit material 18 is smaller (substantially zero) than the slit strain of the second edge portion 22 . Therefore, similarly to Embodiment 1, material costs can be suppressed, and shape defects due to slit strain can be prevented.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com