Quick comparative method for integrated circuit domain data base
A technology of integrated circuits and databases, applied in the direction of electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of complex implementation process and low efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 2
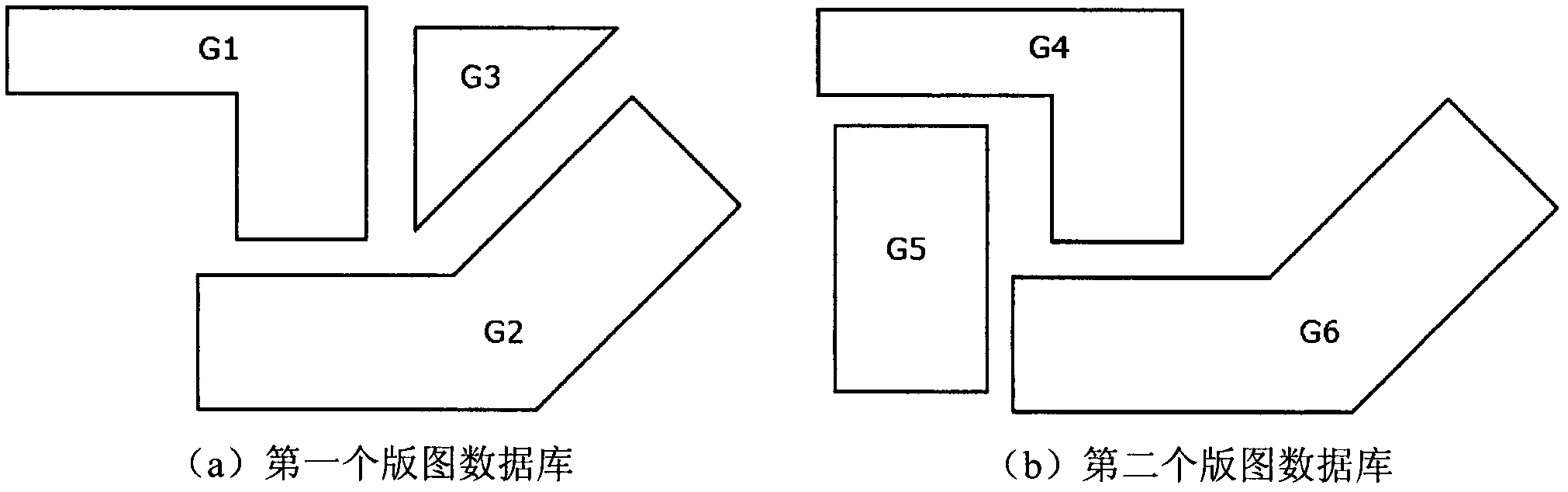
[0041] still with figure 1 As an example, but using only one hash table A. The changes in the content of the hash table during the read-in process are as follows: image 3
[0042] When G5 is read, it is marked to only appear on the second layout. After deleting the common graphics G1 and G2, output the remaining graphics G3 and G5.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0043] still with figure 1 As an example, but use 3 hash tables: hash tables A, B, and C respectively store graphics only from the first layout, graphics only from the second layout, and common graphics. After G1, G2, and G3 are read in, these three graphics are stored in hash table A, and hash tables B and C are empty. When reading into G4, move G1 from hash table A to hash table C. G5 inserts into hash table B. G6 is similar to G4. Finally, there is graph G3 in hash table A, graph G5 in B, and graphs G1 and G2 in C. Output graphs G3 and G5 in hash tables A and B.
specific Embodiment approach 4
[0044] In addition to comparing polygons, the present invention can also compare other geometric figures such as rectangles, circles, Paths (wires), and texts. Different types of geometry have different characteristics, but the comparison process is not substantially different from comparing polygons. For example, there is a text graphic represented by coordinates, character strings, font size, direction, etc. in the layout of the integrated circuit. The comparison of this text graphic can also use any one of the above-mentioned specific embodiments 1-3, compared with the polygon The main differences are:
[0045] (1) The calculation of the hash code depends on different features
[0046] The polygon calculates the hash code based on the number of vertices and the coordinates of each vertex. For text graphics, the hash code is calculated based on the coordinates, character strings, and font attributes of the text.
[0047] (2) Comparing whether the two graphics are the same...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com