Method for controlling carbon equivalent of base iron and application of method
A control method and carbon equivalent technology, which is applied in the field of cast iron alloys, can solve problems such as unscientific, large fluctuations in casting shrinkage and waste rate, and difficulty in determining the carbon equivalent of ductile iron.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
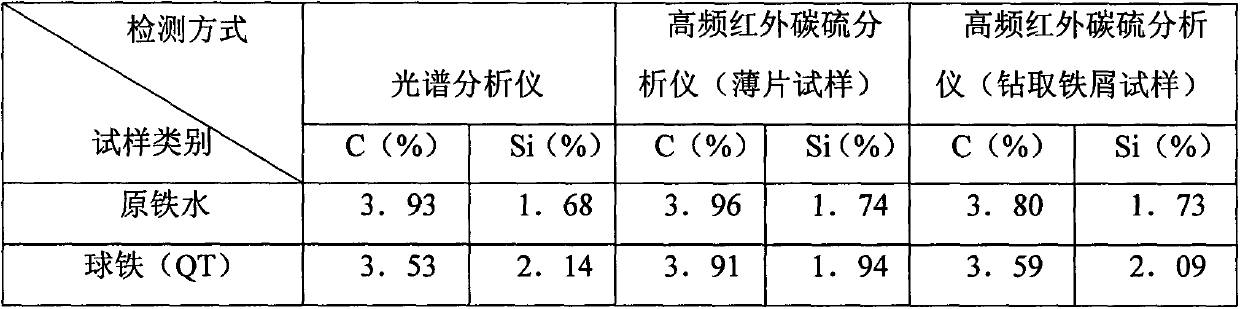
[0018] A certain product requires C: 3.95%, Si: 2.1%, so the calculated carbon equivalent is 4.65%. Since the amount of hot metal treatment agent added is quantitative, ΔSi: 0.66%, so the original hot metal C and Si values are calculated as carbon The equivalent CE2=CE-ΔSi / 3 is 4.43%, that is, the carbon equivalent CE1 value measured in the original molten iron is controlled at about 4.43%, which can meet the product requirements, thereby realizing effective control of the carbon equivalent in the molten iron casting process.
[0019] Among them, CE represents the carbon equivalent of molten iron after spheroidization, that is, the carbon equivalent of the finished ductile iron; CE1 represents the measured value of the carbon equivalent of the original molten iron; CE2 represents the theoretically calculated value of the carbon equivalent of the original molten iron; CE=CE2+ΔSi / 3, where CE2≈CE1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com