A long downhill energy-dissipating deceleration pavement and its construction technology
A road surface and energy dissipation technology, applied in the direction of roads, roads, special pavements, etc., can solve the problems of less obvious speed limit effect, large vehicle damage, insufficient strength, etc., to achieve significant visual effects, prevent fatigue and numbness, and vibration. strong effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
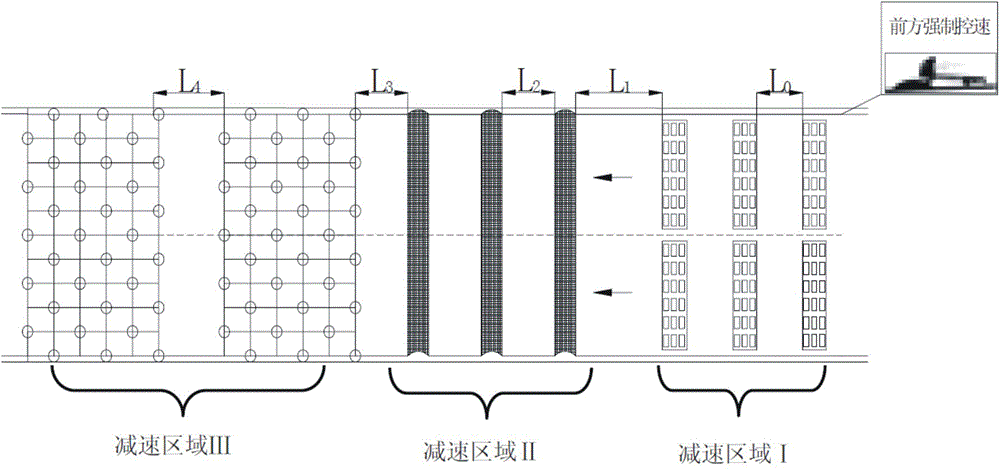
[0038] figure 1 The overall layout schematic diagram of the first embodiment provided by the present invention, by figure 1 It can be seen that the long-distance downhill energy dissipation deceleration pavement is composed of three thermoplastic protruding vibration markings perpendicular to the driving direction, the deceleration area I, and the deceleration area composed of three hump-type asphalt concrete base deceleration belts perpendicular to the driving direction. Ⅱ and deceleration area Ⅲ composed of two sections of asphalt concrete base deceleration spikes. Among them, the long downhill road surface refers to the downhill section with a continuous slope of more than 6 kilometers and an average longitudinal slope of more than 3%.
[0039] Among them, the interval L between deceleration zone I and deceleration zone II 1 10m, distance L between deceleration zone II and deceleration zone III 3 It is 20m. The thermoplastic protruding vibration markings are strip-shape...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The arrangement of embodiment 2 is basically the same as that of embodiment 1, the difference is that:
[0047] Distance L between deceleration zone Ⅰ and deceleration zone Ⅱ 1 is 12m, and the distance between deceleration zone II and deceleration zone III is L 3 It is 25m.
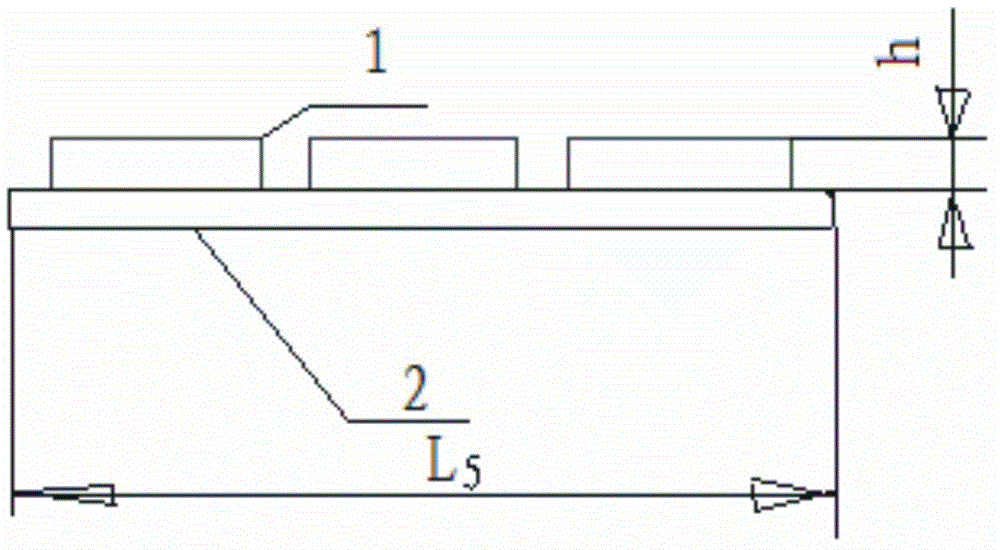
[0048] In the deceleration zone I, the longitudinal width L of each thermoplastic protruding vibration marking along the driving direction 5 is 400mm, the transverse width is the width of the road surface, the height h of the protruding block 1 in each thermoplastic protruding vibrating marking line is 6mm, and the distance L between two adjacent thermoplastic protruding vibrating marking lines 0 It is 8m.
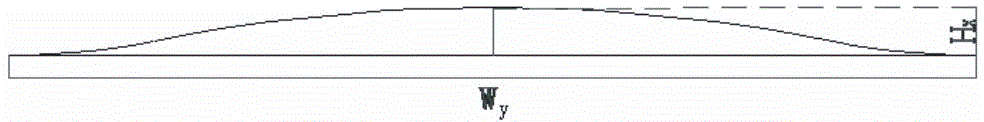
[0049] In deceleration area II, from the direction of driving, the first hump-type asphalt concrete base deceleration belt has a height H 1 20mm, width W 1 50mm, the height of the second hump-type asphalt speed bump is H 2 40mm, width W 2 80mm, the height of the third hump-type asphalt s...
Embodiment 3
[0053] The long-distance downhill energy-dissipating deceleration pavement provided in Example 3 consists of deceleration zone I composed of three thermoplastic protrusion-type vibration markings perpendicular to the driving direction, and two hump-type asphalt concrete-based deceleration belts perpendicular to the driving direction. The deceleration zone Ⅱ formed by the deceleration zone Ⅱ and the deceleration zone Ⅲ formed by a section of asphalt concrete base deceleration spikes.
[0054] Among them, the interval L between deceleration zone I and deceleration zone II 1 10m, distance L between deceleration zone II and deceleration zone III 3 is 10m.
[0055] Among them, in the deceleration area I, the thermoplastic protruding vibration markings are strip-shaped, and the longitudinal width of each thermoplastic protruding vibration marking along the driving direction is L 5 is 600 (300) mm, the transverse width is the width of the road surface, the height h of the protrudin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com