A passive autofocus method and device
An automatic focusing and passive technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve the problems of slow focusing speed and achieve the effects of increased speed, accurate video automatic focusing, and good subjective visual effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
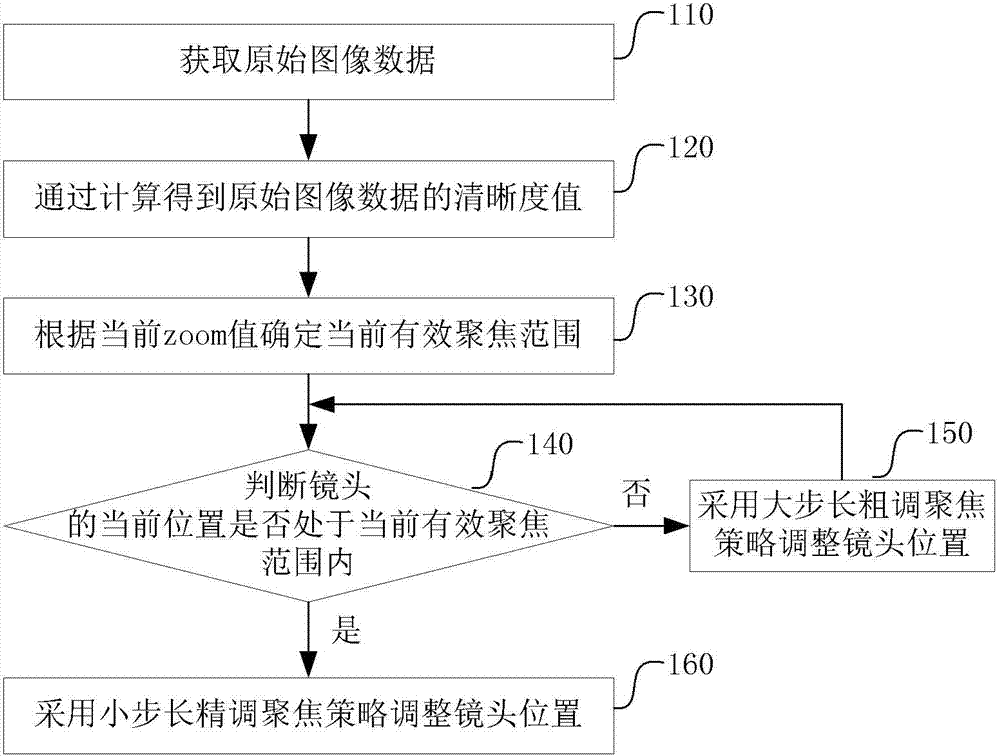
[0042] This embodiment introduces a passive auto-focus method, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps 110-160:
[0043] Step 110, obtaining original image data;
[0044] Step 120, performing sharpness calculation to obtain the sharpness value of the original image data;
[0045]Preferably, before calculating the sharpness, in order to obtain a better result, the acquired original image data is firstly subjected to denoising processing.
[0046] Step 130, determine the current effective focus range according to the current zoom value;
[0047] Step 140, judging whether the current position of the lens is within the current effective focus range, if not, then perform step 150, if it is, then perform step 160;
[0048] Step 150, adjust the position of the lens using a large-step coarse focus strategy, and return to step 140, the large-step coarse focus strategy includes: using the first step to move the lens until the current position of the lens is within the c...
Embodiment 2
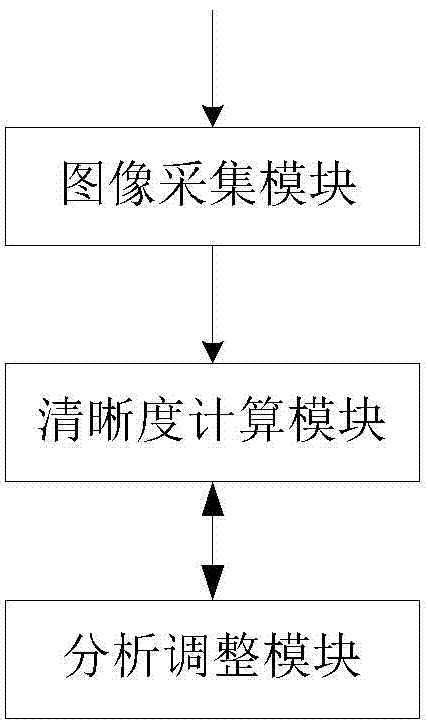
[0053] This embodiment introduces the device for realizing the method of Embodiment 1, such as figure 2 As shown, it includes an image acquisition module, a definition calculation module, and an analysis and adjustment module, where:
[0054] The image acquisition module is used to acquire original image data;
[0055] The sharpness calculation module is used for calculating the sharpness to obtain the sharpness value of the original image data;
[0056] The analysis and adjustment module is used to determine the current effective focus range according to the current zoom value. If the current position of the lens is not within the current effective focus range, the large-step coarse focus strategy is used to adjust the lens position until the current position of the lens is within the current effective focus range. Within the effective focus range, adjust the lens position with a small-step fine-tuning strategy; if the current position of the lens is within the current effe...
Embodiment 3
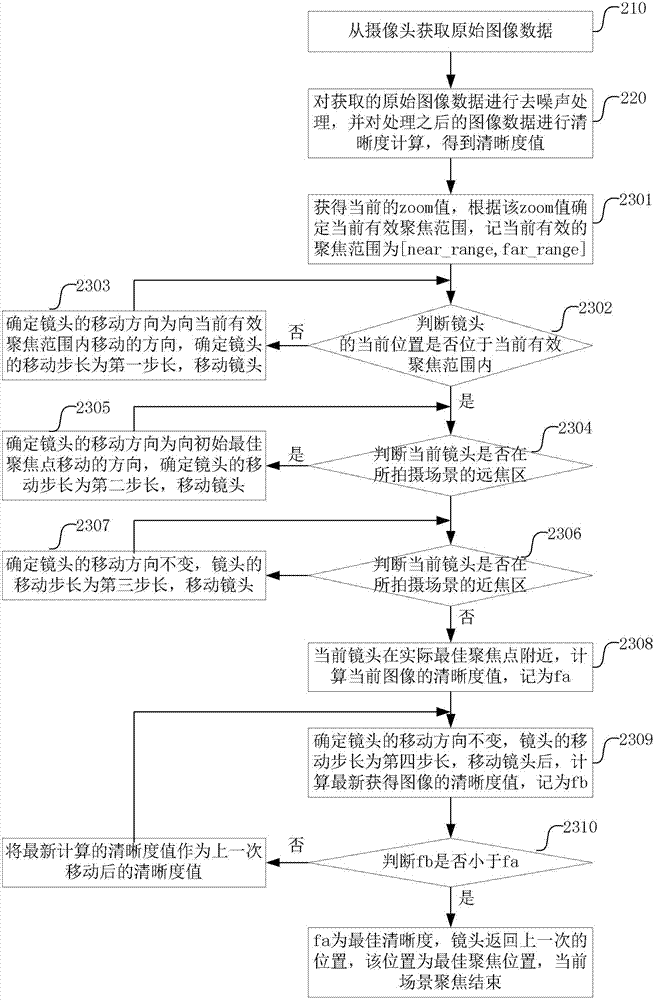
[0064] This embodiment is a concrete description of the method of embodiment 1, as image 3 shown, including the following steps:
[0065] Step 210, obtaining raw image data from the camera;
[0066] Step 220, performing denoising processing on the acquired original image data, and performing sharpness calculation on the processed image data to obtain a sharpness value;
[0067] For example, use a gradient operator or a method such as contrast to calculate the sharpness.
[0068] The steps of sharpness calculation are here only for example, and may not be performed here, but may be calculated later whenever necessary.
[0069] Step 230, using the zoom value of the current lens, the position of the current lens and the sharpness value of the image to determine the moving direction and the moving step of the lens, and finally obtain the best sharpness value and the best focus position of the lens;
[0070] In the following automatic focusing process, every time the lens posit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com