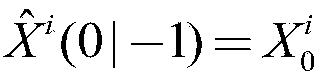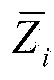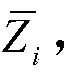Large intelligent light energy-saving control method based on wireless sensor actuator network
A wireless sensor, smart lighting technology, applied in energy-saving control technology, wireless communication, energy-saving ICT and other directions, can solve the problems of power consumption, lack of natural light, waste of resources, etc., to achieve the effect of improving communication efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0094] For distributed state estimation in wireless sensor-actuator networks, consider the following state equation for a discrete linear time-invariant system:
[0095] X(k+1)=AX(k)+Bw(k), (1)
[0096] Among them, X(k) is the state variable of the system at time k, which are respectively the abscissa and ordinate of the car’s position, the abscissa and ordinate of the speed, A and B are matrices with appropriate dimensions, and w(k) is the mean is zero and the state noise with variance Q.
[0097] We use a wireless sensor network to measure the state variables of the system, and use the Kalman filter algorithm to make a one-step optimal prediction of the state of the system. At time k, when the vehicle is at s i When within the monitoring range, the corresponding measurement equation is:
[0098] Z i (k)=HX(k)+v(k), (2)
[0099] where Z i (k) is the sensor node s i For the measurement at time k, v(k) is the value with mean zero and variance R 0 Gaussian random noise. ...
Embodiment 2
[0135] This embodiment is the same as Embodiment 1 except for the following:
[0136] A large-scale intelligent lighting energy-saving control method based on a wireless sensor actuator network, mainly including the following steps:
[0137] Step 1: Initialize the state of each filter Error covariance matrix P i (0|-1)=P 0 , where i ∈ {1,2,...,N}. N is the number of nodes. Let i=1 be the initial cluster head node;
[0138] Step 2: Turn on the sensor node to detect the monitoring area, if the vehicle is in the current node s i Within the monitoring range of k, the measured value at time k can be obtained:
[0139] Z i (k)=HX(k)+v(k),
[0140] Otherwise, let Z i (k) = 0;
[0141] Step 3: Select the cluster head node and receive the state prediction value of the last cluster head node Error covariance matrix P(k|k-1);
[0142] The sensor node with measurement information sends its measurement information to the cluster head node, and after the transmission is comple...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com