A Passive Target Location Method Based on Random Deployment of Wireless Sensor Nodes
A wireless sensor and sensor node technology, applied in wireless communication, electrical components, network topology, etc., can solve problems such as no prior knowledge, non-compliance, and prior knowledge required
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
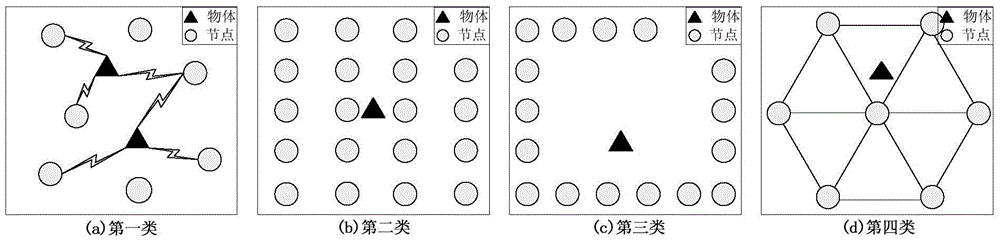
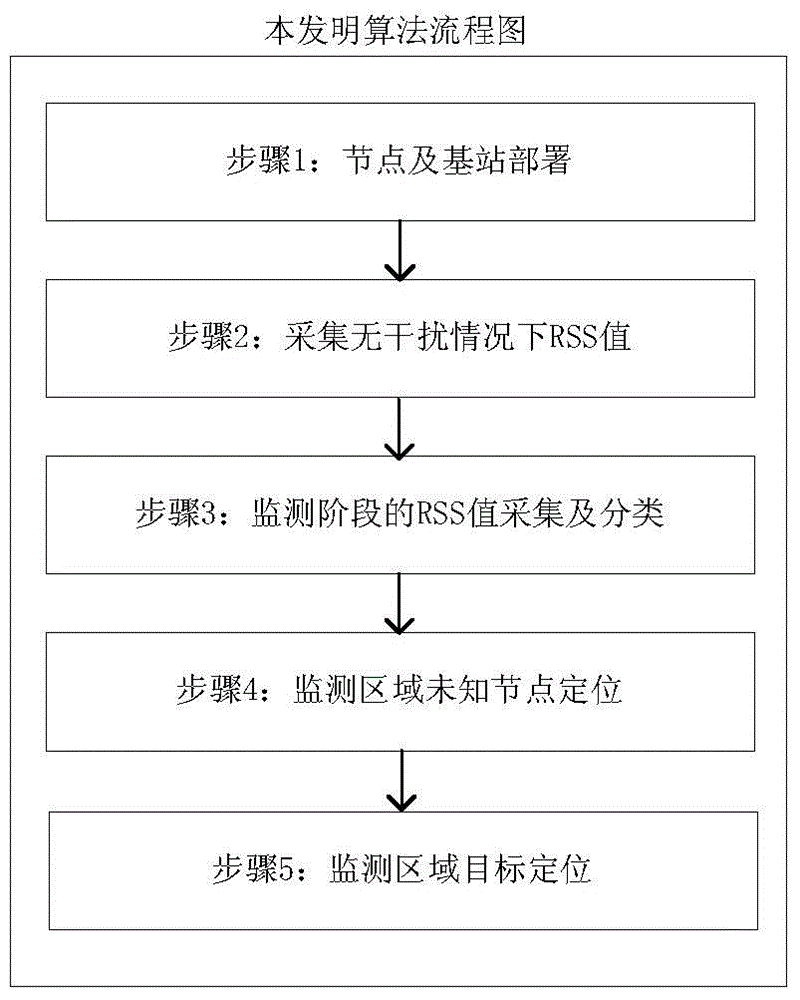
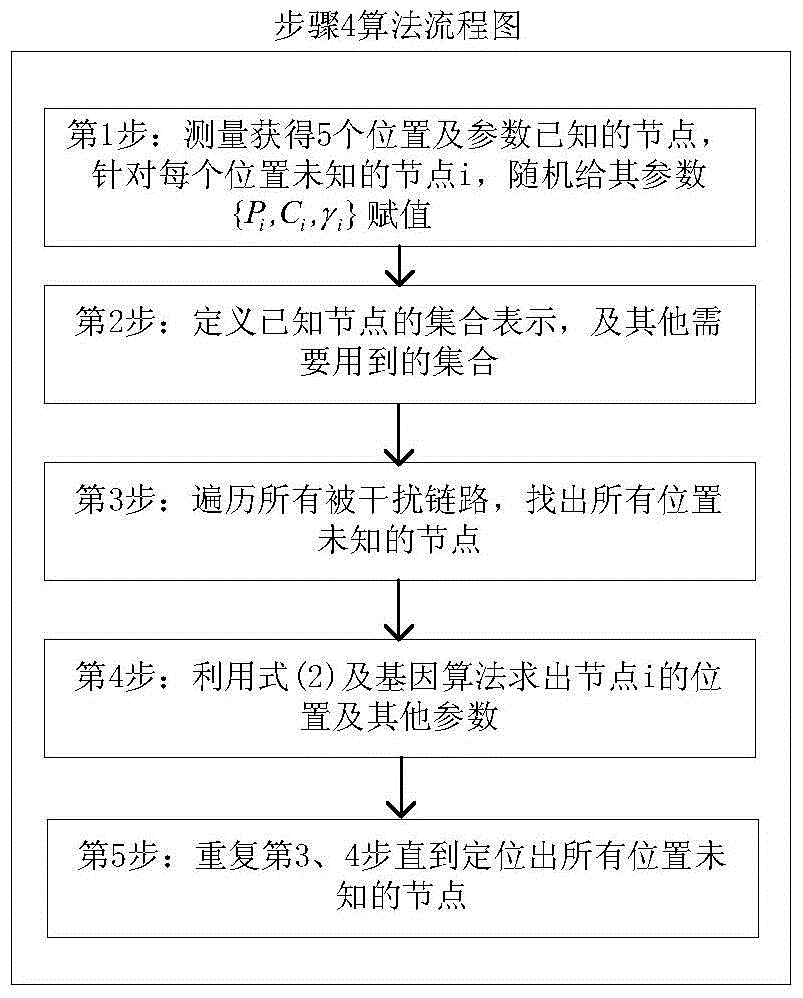
[0126] According to the technical solution of the present invention, in the Qinling Golden Monkey Protection Area, a monitoring area of a × b = 100m × 100m is selected, a base station is deployed at a distance of 50m from the border of the monitoring area, and the base station is connected to a PC. The experiment selects a target with a height of 1.75 meters, and conducts a passive positioning test on it. Under this monitoring area, the number of nodes N is increased from 30 to 300 with a step size of 15, and all nodes are numbered from 1-N, and a total of 18 real-scene target positioning experiments are carried out. In each experiment, N nodes are randomly deployed in the monitoring area, and each node position C i At the time of initialization, the vertical and horizontal coordinate ranges are between 0 and 100m, and at the same time, the transmit power of each node P i The value is randomly given at 0~-20dBm, and the path loss is therefore γ i The value is randomly give...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com