Method and system for WLAN user fixed network access
A technology for users and user terminals, applied in access restrictions, transmission systems, network topology, etc., can solve problems such as WLAN network inability to perceive, user subscription information cannot be provided, etc., to achieve the effect of improving service quality and package flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
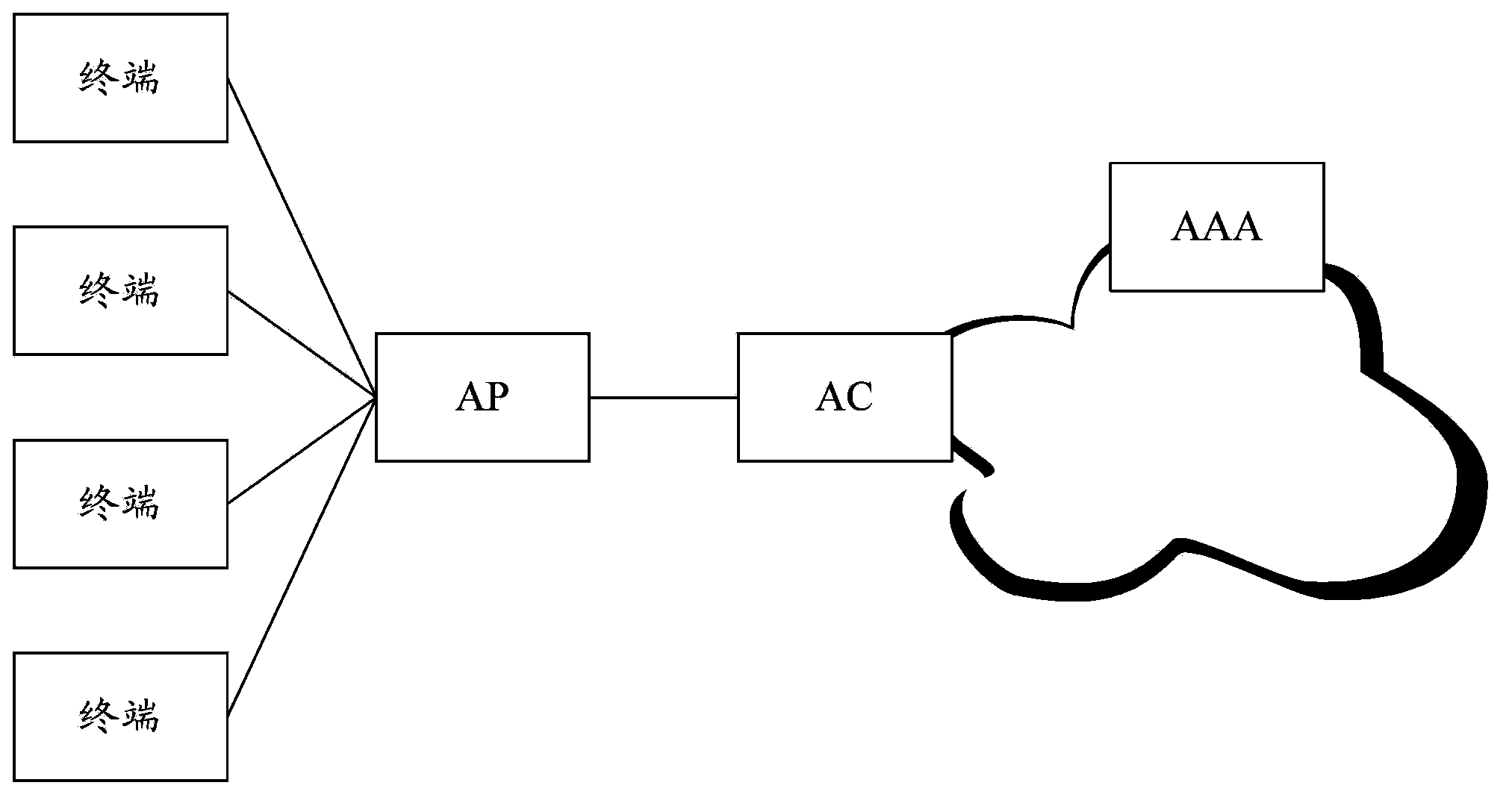
[0078] This embodiment is applicable to scenarios such as figure 2 As shown in the figure, the AC is between the AP and the BNG, and the data packets after the user passes the authentication flow through the AC, and the WLAN device is the AC, as shown in Figure 5 As shown, the process of WLAN user fixed network access includes:
[0079] Step 501, perform the following configurations in the AC: configure the AC as the authentication client, and configure the BNG as the authentication server of the AC.
[0080] Step 502, perform the following configurations in the BNG: configure the BNG as the authentication server, and configure the AC as the authentication client of the BNG.
[0081] Steps 501 and 502 are executed in no particular order.
[0082] Step 503, the user terminal (that is, the WLAN user) sends an EAPoL start (EAPoL-Start) message to the BNG to initiate an authentication request.
[0083] Step 504: After receiving the EAPol-Start message, the BNG sends an EAP-Re...
Embodiment 2
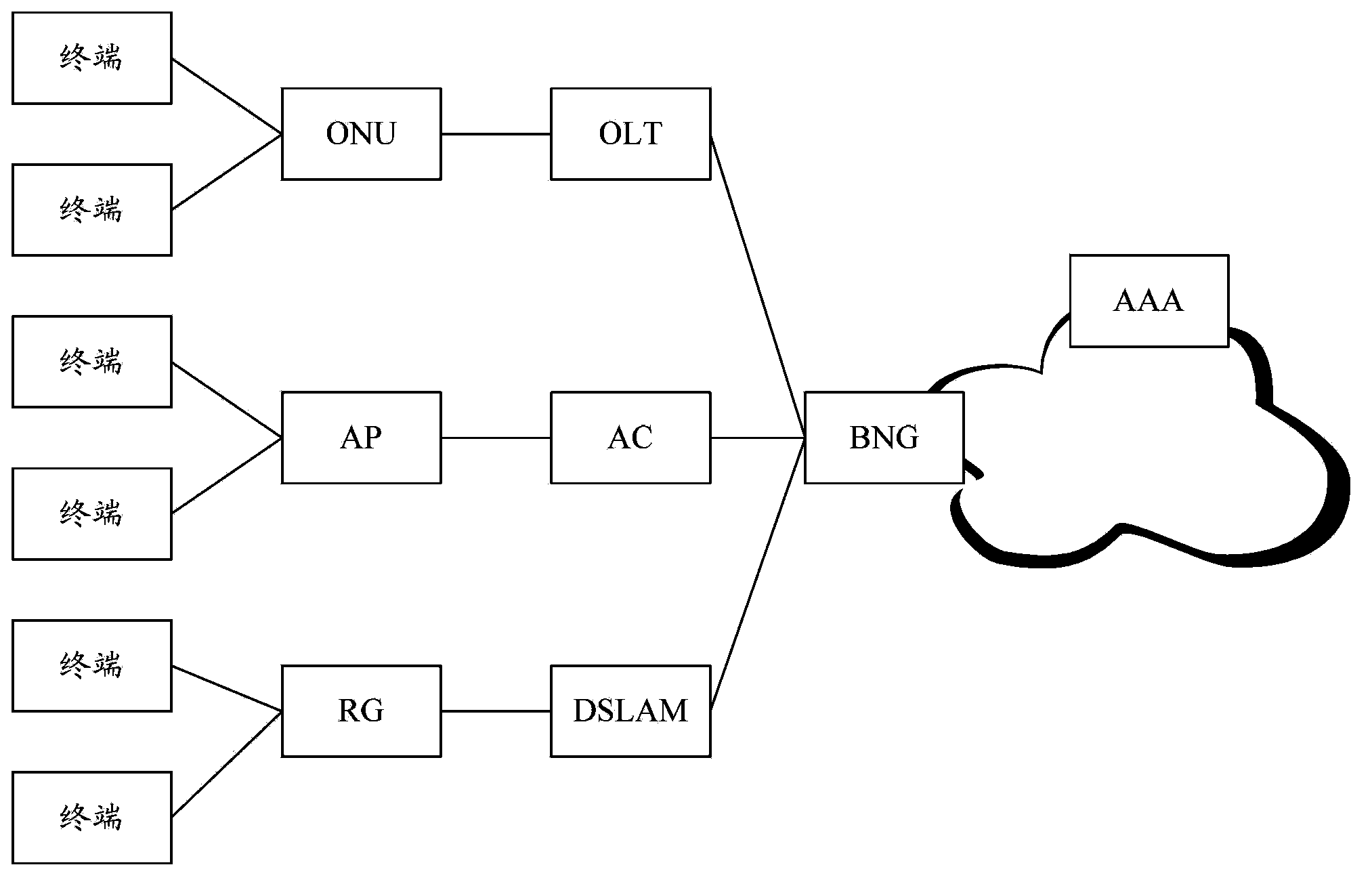
[0100] This embodiment is applicable to scenarios such as image 3 As shown in the figure, the AP and AC are connected through the BRAS. The AC controls the packets of the AP through the BRAS. The packets of the user accessing the network side do not pass through the AC. The WLAN device is the AP. For example, Image 6 As shown, the process of WLAN user fixed network access includes:
[0101] Step 601, perform the following configurations in the AP: configure the AP as the authentication client, and configure the BNG as the authentication server of the AP.
[0102] Step 602, perform the following configurations in the BNG: configure the BNG as the authentication server, and configure the AP as the authentication client of the BNG.
[0103] Steps 601 and 602 are executed in no particular order.
[0104] Step 603, the user terminal obtains an IP address from the BNG through the DHCP protocol.
[0105] Step 604, the user visits the message of the network side and redirects it ...
Embodiment 3
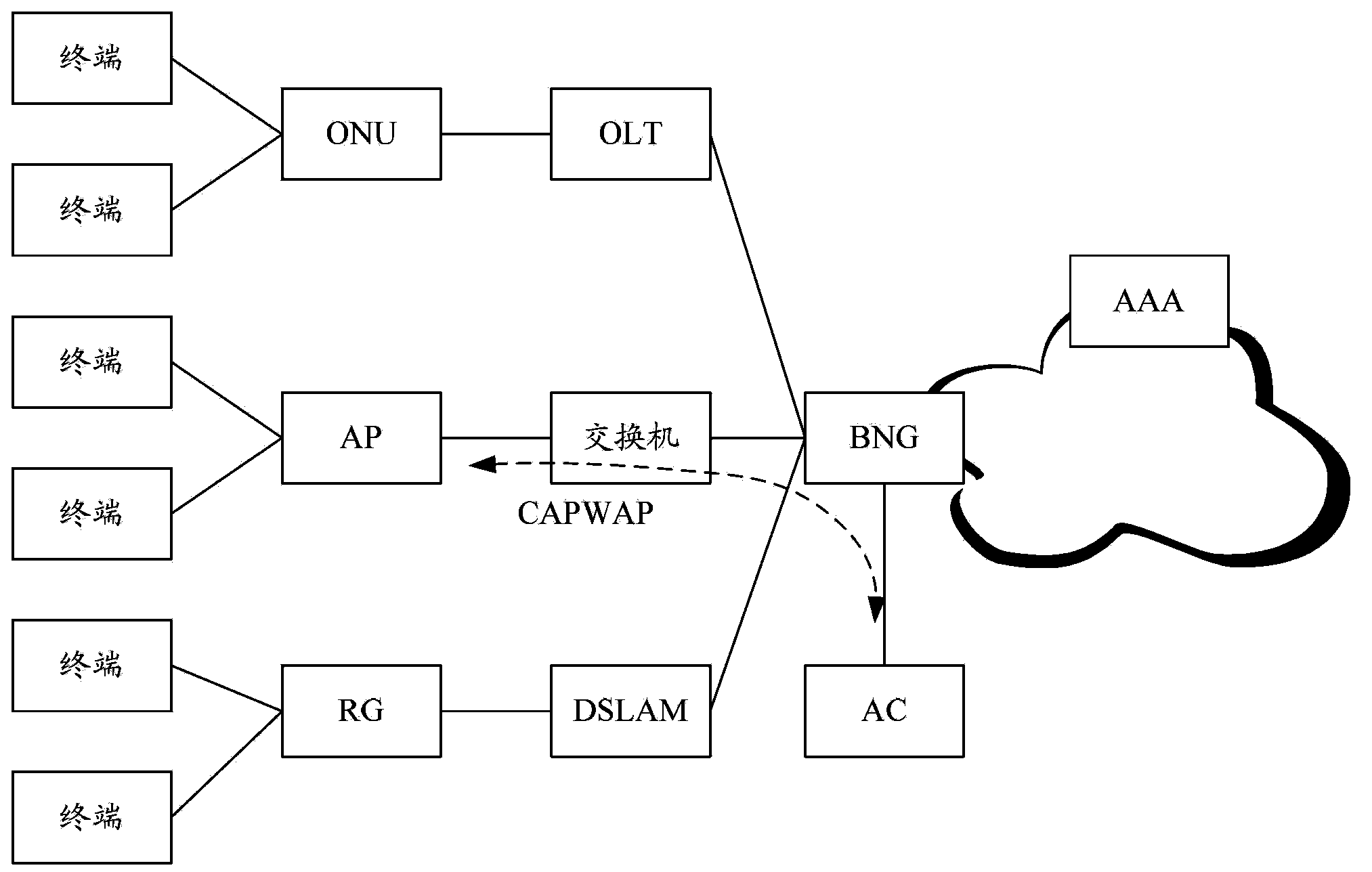
[0115] After a user accesses the network, he changes the user subscription information online by accessing the Portal server, and the process for the AP to obtain the user subscription information is as follows: Figure 7 shown, including:
[0116] Step 701, the user accesses the Portal server, and changes the user's subscription information online (such as changing the user's subscription bandwidth, priority, etc.).
[0117] Step 702, the Portal server sends the changed user subscription information to the AAA server;
[0118] Here, a private protocol message may be used between the Portal server and the AAA server to send user subscription information;
[0119] Step 703, the AAA server sends the changed user subscription information to the BNG through a Radius CoA message or a Diameter CCA message.
[0120] There are two ways for the subsequent BNG to send the changed user subscription information to the AP:
[0121] 1. When the WLAN device is an AC, it is:
[0122] Step...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com