Method for measuring curved surface temperature through infrared microscope
A technology for measuring curved surfaces and microscopes, which is applied in the field of image processing, can solve problems such as inaccurate temperature, unclear local positions of infrared images, etc., and achieve the effect of precise measurement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] The present invention is described in further detail below in conjunction with embodiment.
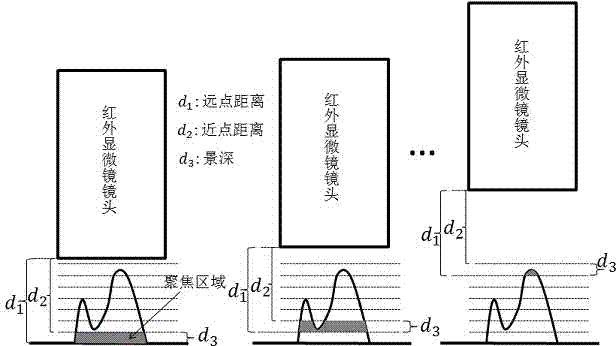
[0023] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, a method for measuring surface temperature using an infrared microscope has the following steps:
[0024] 1) Put the U disk circuit board embedded with the chip into the observation area of the infrared microscope;
[0025] 2) Through the step-length controllable automatic lifting system, move the infrared microscope lens from top to bottom (or bottom to top) so that the highest (or lowest) position of the circuit board is in the focus position;
[0026] 3) Use the infrared CCD in the infrared microscope system to obtain the infrared image of the test piece at this focal position;
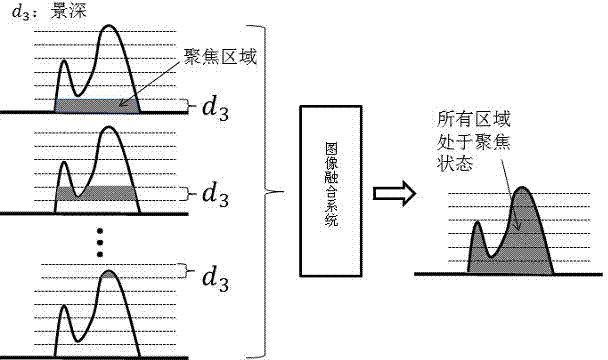
[0027] 4) Through the step length controllable automatic lifting system, the step length is set according to the depth of field of the infrared microscope lens, so that the infrared microscope lens moves periodically in the vertical direction to co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com