A busbar protection method based on the sudden change direction of fault current in the power frequency band
A technology for fault current and busbar protection, which is applied in the direction of the fault location, etc., to achieve the effect required by the reliable sampling rate of protection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Embodiment 1: A busbar protection method based on the sudden change direction of the fault current in the power frequency band. When the busbar or the line fails, the three-phase current data of each line on the busbar within the short time window after the fault is extracted, and passed through the three-phase The current data is calculated to obtain the line-mode current including the fault phase; the db4 wavelet transform is performed on the line-mode current, and the frequency band where the power frequency is located is used for straight line fitting. According to whether the polarity of the line slopes obtained by fitting the lines is the same, it is judged that it is a bus Fault or wiring fault.
[0045] The specific steps of the method are:
[0046] (1) When the bus or line fails, the measuring unit reads 2τ min Current data in the time window, τ min is the time for the traveling wave to propagate through the full length on the shortest outgoing line connected...
Embodiment 2
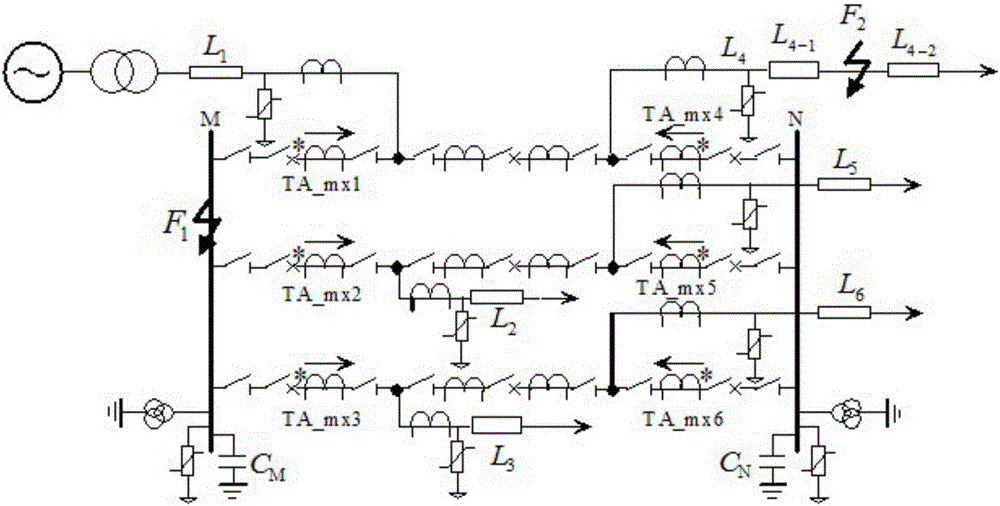
[0055] Embodiment 2: with figure 1 Take the simulation system of , as an example, the system is a 3 / 2 connection mode, and TA_mxi (i=1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) is the i-th current transformer. The sampling frequency is 20kHz, and F1 and F2 are set as phase A metal ground faults, and the initial fault angle is 90°. Line L 4 Fault, the length of the shortest outgoing line connected to the busbar in the simulation system is 180km, calculated from 2τmin=2lmin / v to get 2τmin=1.2ms.
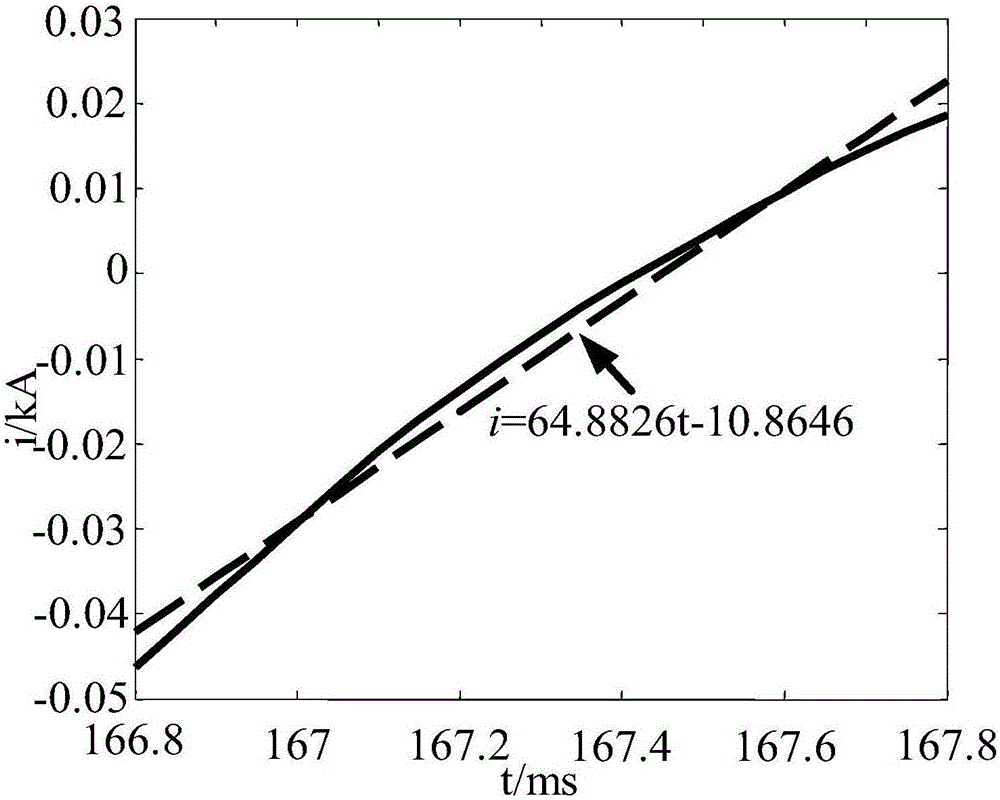
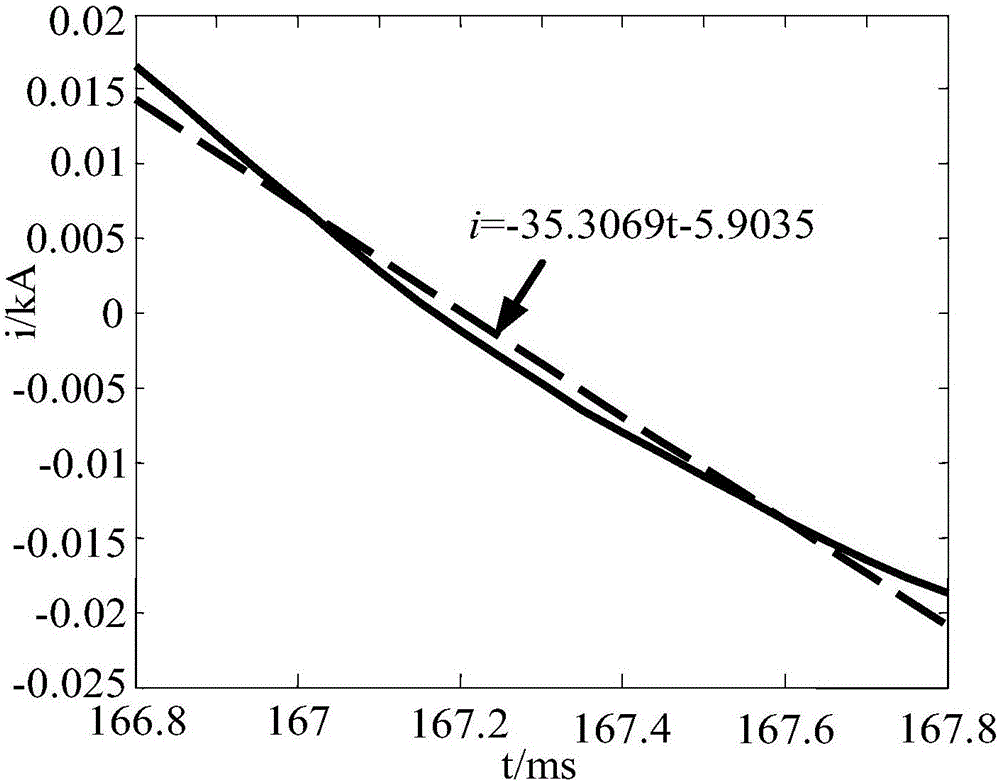
[0056] The linear fitting result of the initial current waveform under the power frequency band is calculated as figure 2 with image 3 shown.
[0057] From the simulation results, it can be seen that the slope of the straight line obtained by fitting the data of the frequency band where the fault current power frequency quantity is: a 1 =64.8826, a 2 =-35.3069,a 3 =-26.4415. According to formula (1), it can be seen that the calculation result is G M = 0, it is judged as a line fault, consistent with ...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Embodiment 3: Still with figure 1 Take the simulation system of , as an example, the system is a 3 / 2 connection mode, and TA_mxi (i=1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) is the i-th current transformer. The sampling frequency is 20kHz, and F1 and F2 are set as phase A metal ground faults, and the initial fault angle is 90°. When a bus failure occurs, the length of the shortest outgoing line connected to the bus in the simulation system is 180km, and 2τmin=1.2ms is calculated by 2τmin=2lmin / v.
[0059] The linear fitting result of the initial current waveform under the power frequency band is calculated as Figure 4 with Figure 5 shown.
[0060] From the simulation results, it can be seen that the slope of the straight line obtained by fitting the data of the frequency band where the fault current power frequency quantity is: a 1 =-130.7087,a 2 =-390.3307,a 3 =-337.0287. Also according to formula (1), it can be seen that the calculation result is G M = 1, it is judged as a bus faul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com