SAR?target variant recognition?method based on multi-information joint dynamic sparse representation
A sparse representation and recognition method technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, instruments, computer components, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient recognition rate and poor recognition effect of target variants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
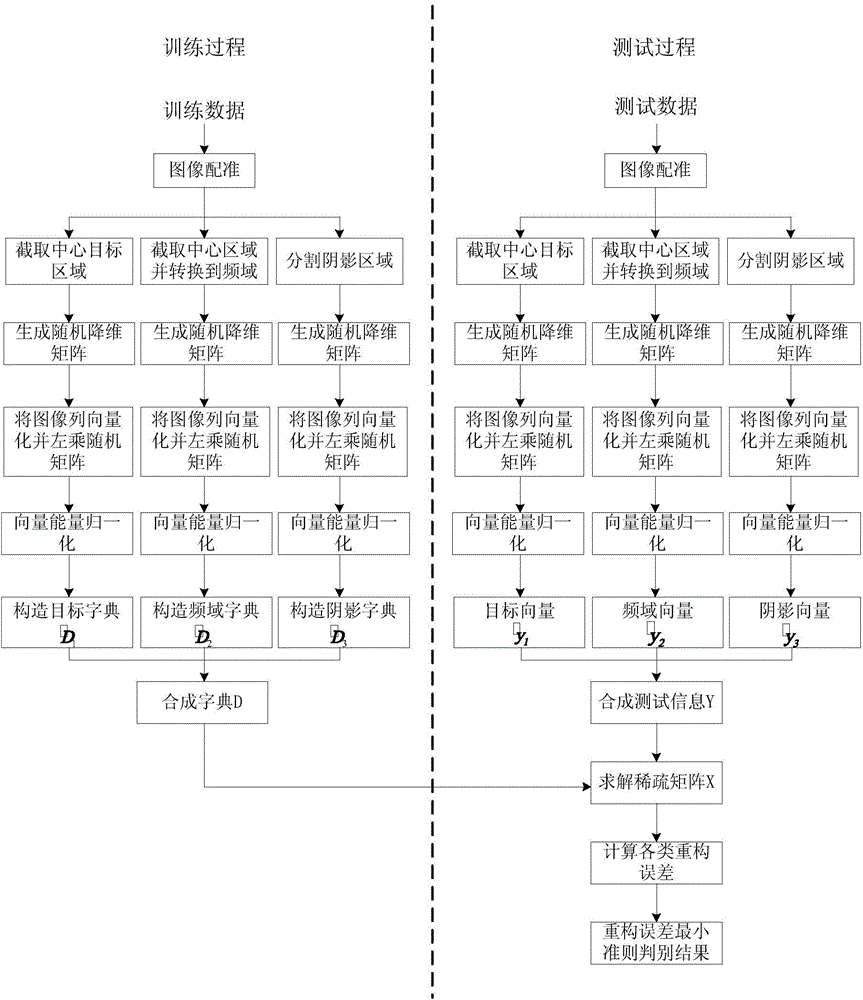
[0083] refer to figure 1 , which specifically illustrates the SAR target variant recognition method based on multi-information joint dynamic sparse representation of the present invention.
[0084] 1. Training stage
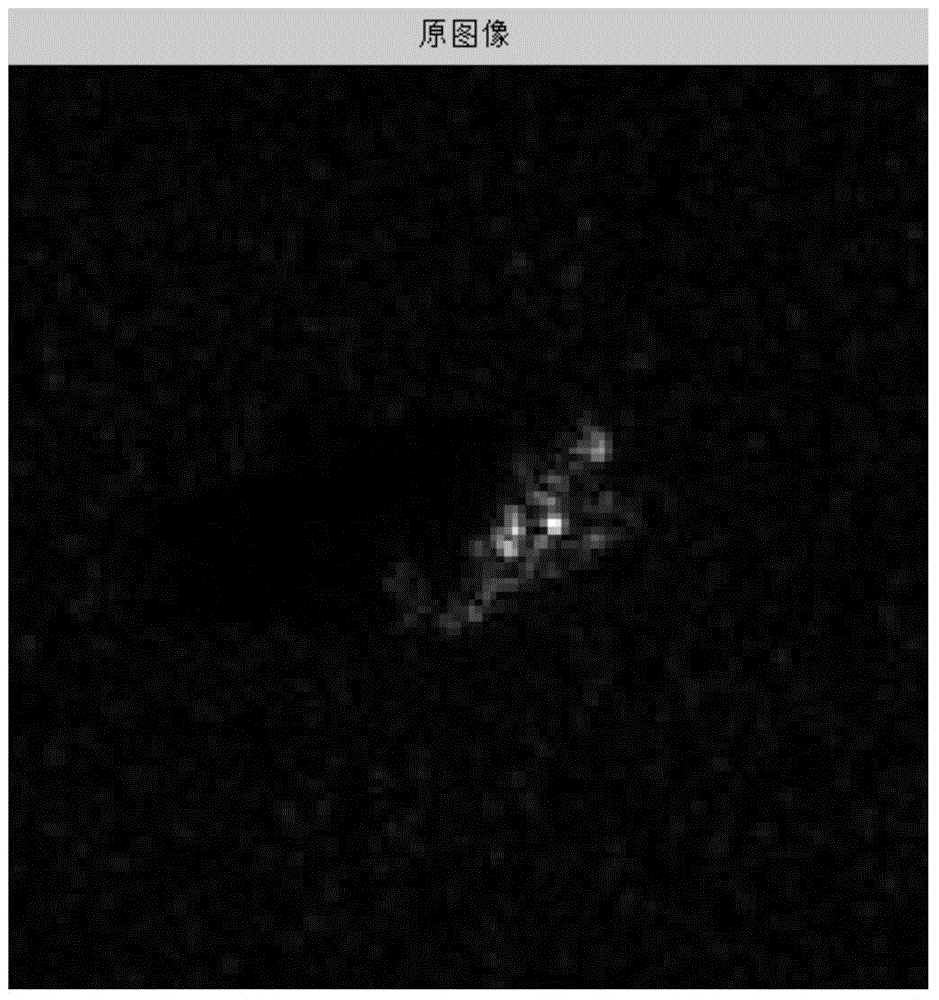
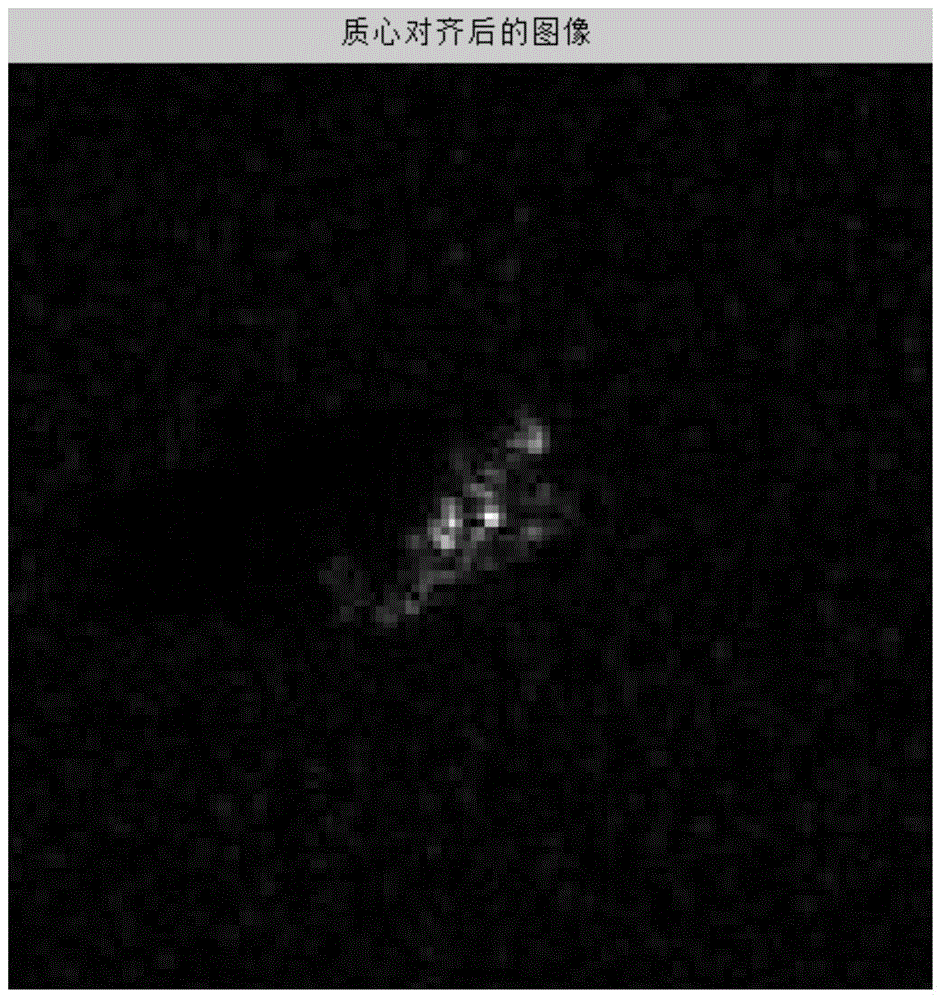
[0085] In step 1, the original SAR image F of the training sample is aligned to the center of mass to obtain the matched training registration image G.
[0086] The target area in the original SAR image slice is not necessarily located in the center of the image, which has a great impact on template matching. In order to avoid the negative impact brought by this aspect, the target area of the used original SAR image must be aligned first. Alignment methods include centroid alignment, gravity center alignment, etc. In this embodiment, the original SAR image F is registered using the centroid alignment method.
[0087] First, sequentially use adaptive threshold segmentation, morphological filtering, and geometric clustering methods to process and segment the ta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com