A method for recovering nickel and cobalt from superalloy scrap
A high-temperature alloy and waste technology, applied in the field of hydrometallurgy, can solve the problems of imperfect waste treatment means, separation effect not as good as wet process, high energy consumption, etc., achieve good industrial application prospects, good research and utilization value, simple and convenient operation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
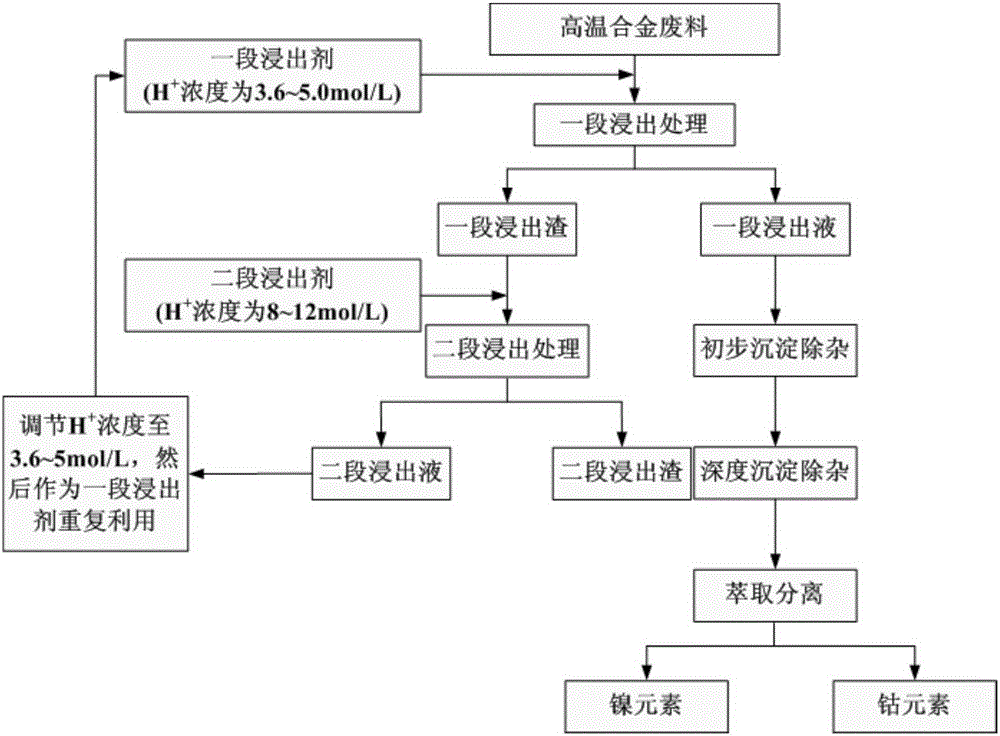
[0028] The chemical composition of the superalloy scrap to be treated in this embodiment is: Ni60%, Co15%, Cr5%, Al5%, Fe1%, W6%, Ta4%, Hf4%. combine figure 1 , the present embodiment reclaims the method for nickel and cobalt from superalloy scrap, comprises the following steps:
[0029] Step 1. Weigh the superalloy waste, and then measure H according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:6 + Inorganic acid with a concentration of 3.6mol / L was used as a primary leaching agent, and then the superalloy waste was mixed evenly with the primary leaching agent, and stirred at a temperature of 50°C for 0.5h to perform a primary leaching treatment to obtain a primary leaching residue and a primary leaching solution; The inorganic acid is preferably sulfuric acid;
[0030] Step 2, processing a section of leach residue and a section of leachate described in step 1 respectively:
[0031] Among them, the treatment process of one stage of leaching slag is:
[0032] Step 211, measure H acco...
Embodiment 2
[0040] The chemical composition of the superalloy scrap to be treated in this embodiment is calculated by mass percentage: Ni40%, Co20%, Cr10%, Al10%, Fe2%, W8%, Ta5%, Hf5%. combine figure 1 , the present embodiment reclaims the method for nickel and cobalt from superalloy scrap, comprises the following steps:
[0041] Step 1. Weigh the superalloy waste, and then measure H according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:7 + Inorganic acid with a concentration of 3.8mol / L was used as a primary leaching agent, and then the superalloy waste was mixed evenly with the primary leaching agent, and stirred for 1 hour at a temperature of 60°C to perform a primary leaching treatment to obtain a primary leaching residue and a primary leaching solution; The inorganic acid is preferably sulfuric acid;
[0042] Step 2, processing a section of leach residue and a section of leachate described in step 1 respectively:
[0043] Among them, the treatment process of one stage of leaching slag is:
...
Embodiment 3
[0052] The chemical composition of the superalloy scrap to be treated in this embodiment is: Ni60%, Co16%, Cr8%, Al8%, Fe0.5%, W3%, Ta2%, Hf2%. combine figure 1 , the present embodiment reclaims the method for nickel and cobalt from superalloy scrap, comprises the following steps:
[0053] Step 1. Weigh the superalloy waste, and then measure H according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:8 + Inorganic acid with a concentration of 4mol / L was used as a first-stage leaching agent, and then the superalloy waste was mixed evenly with the first-stage leaching agent, and stirred for 1.5 hours at a temperature of 70°C to perform a first-stage leaching treatment to obtain a first-stage leaching residue and a first-stage leaching solution; The inorganic acid is preferably sulfuric acid;
[0054] Step 2, processing a section of leach residue and a section of leachate described in step 1 respectively:
[0055] Among them, the treatment process of one stage of leaching slag is:
[0056]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com