Physical simulation experiment device and method for determining buoyancy lower limit and power balance
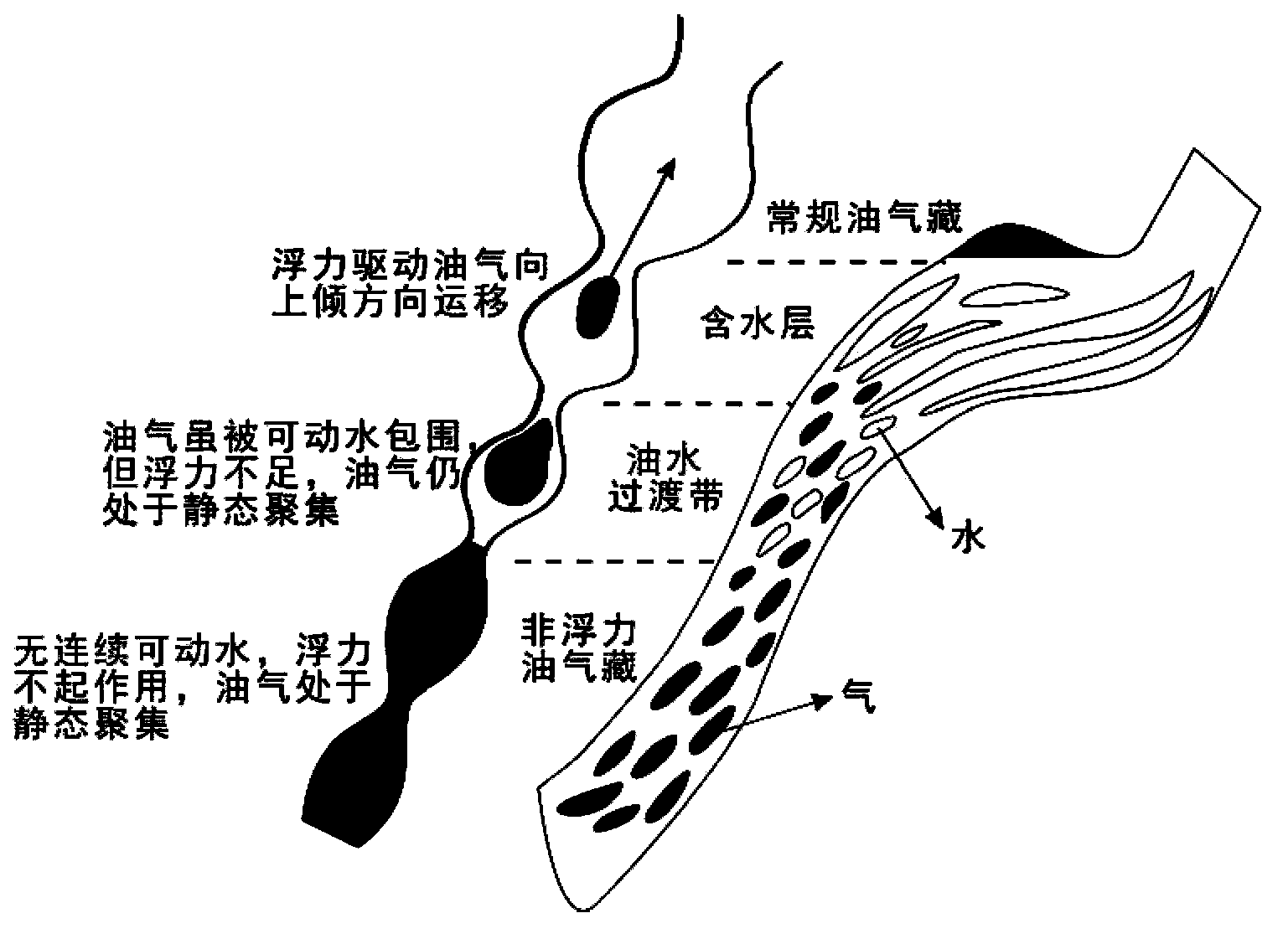
An experimental device and physical simulation technology, applied in the field of petroleum geological research, can solve the problems of no simulation influence, lack of comprehensive understanding, and interpretation of changes in the top boundary of deep basin gas reservoirs, and achieve the effect of great guiding value and broad application prospects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0052]The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
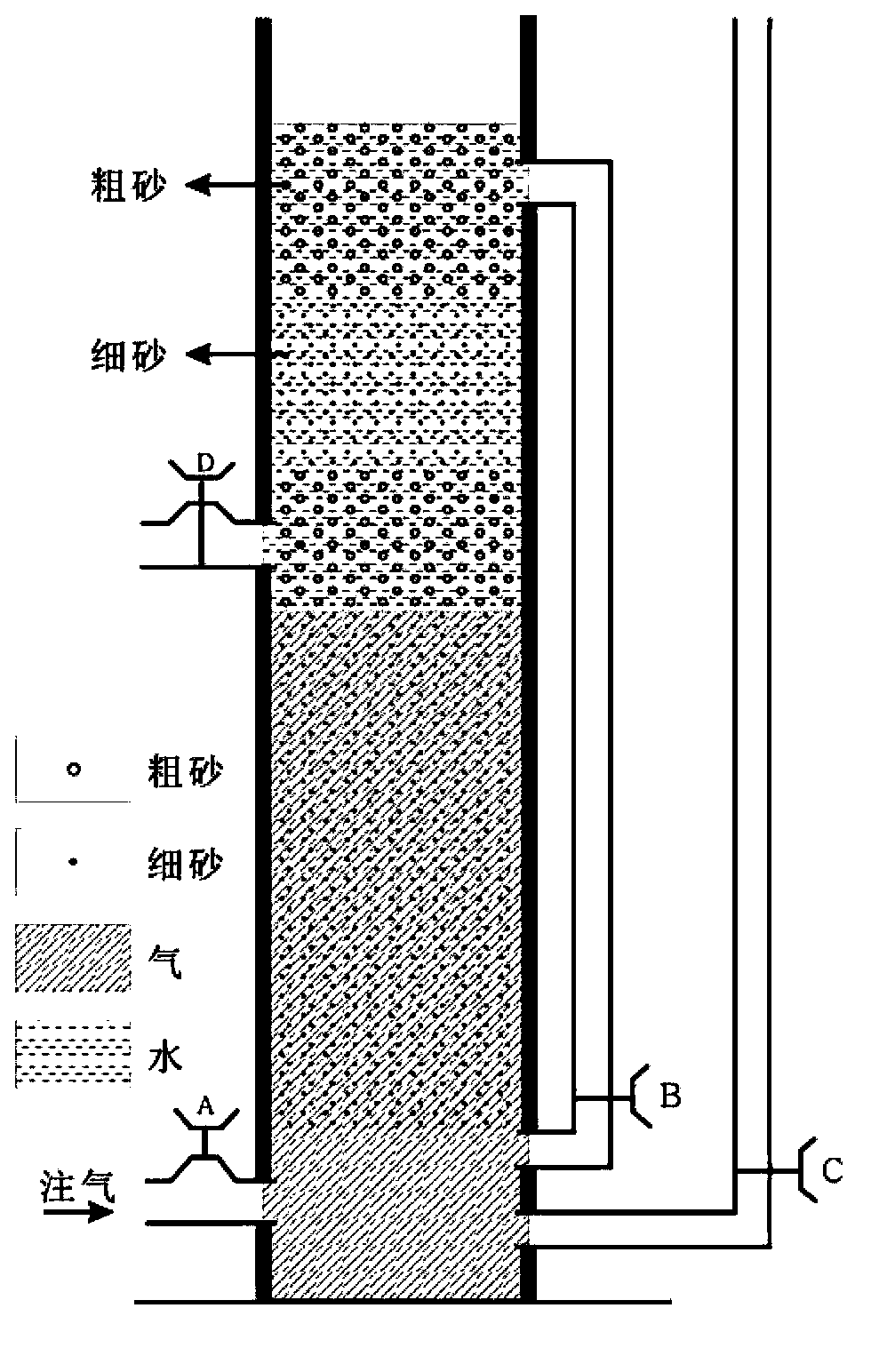
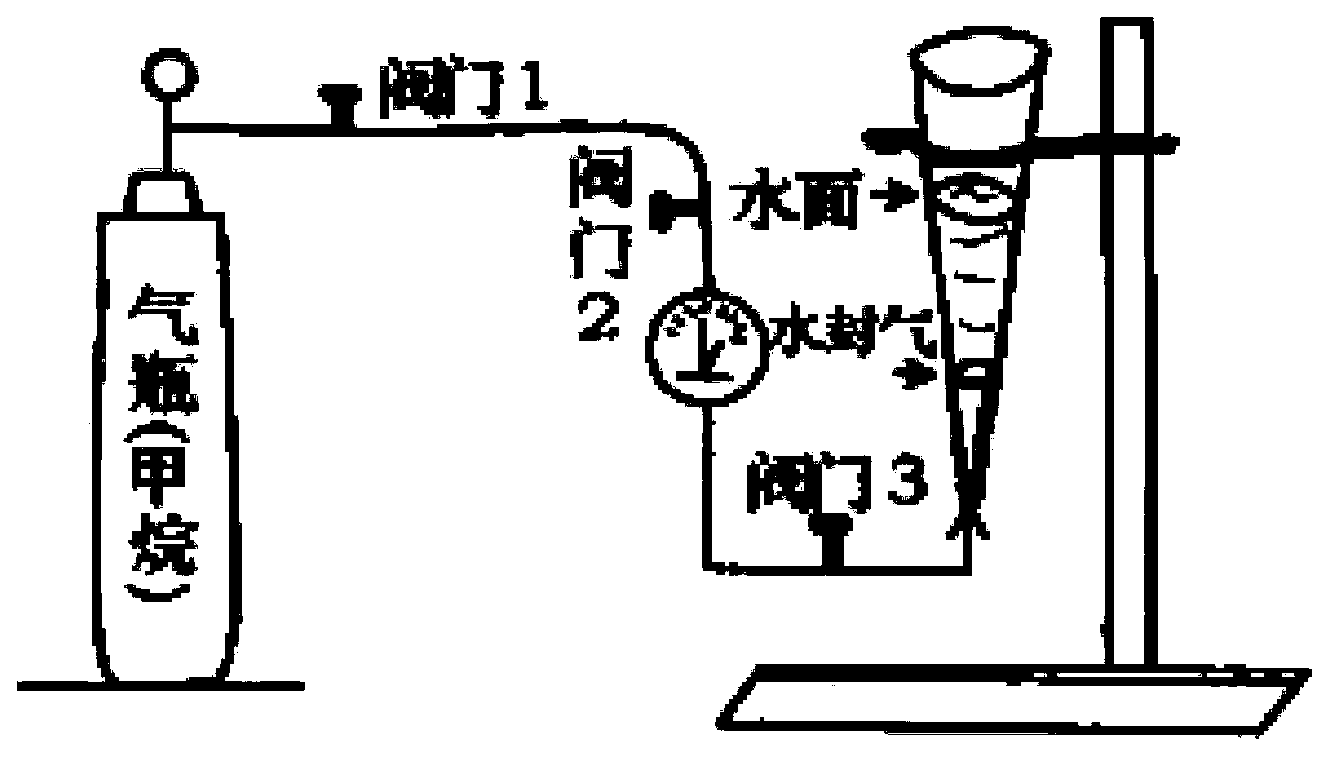
[0053] Design and manufacture a physical simulation experiment device for determining the lower limit of buoyancy and dynamic balance (attached Figure 4 ), the device includes: tight sandstone reservoir pore throat simulation unit, air inflation and pressure measurement unit, formation water simulation unit;
[0054] Among them, the tight sandstone reservoir pore-throat simulation unit includes a "funnel-shaped" simulated pore-throat (1), which is in the middle of a cube-shaped quartz glass carrier (2);
[0055] Among them, the simulated pore throat (1) is made of quartz glass, with a height of 50cm, and the diameter of the pore throat gradually increases from 0.2mm to 30mm from bottom to top;
[0056] Among them, the inflation and pressure measurement unit includes an inflatable steel pipe (3), a methane cylinder (4), a pressure gauge (5), and the two...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com