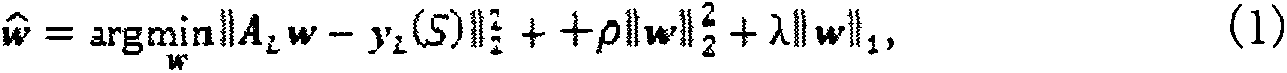Method for registering stereoscopic medical image rapidly, accurately and non-linearly based on sparse representation
A non-linear registration and sparse representation technology, applied in image analysis, image data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of increased calculation cost and affecting interpolation accuracy, so as to improve registration speed, improve accuracy, and accelerate registration The effect of the process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
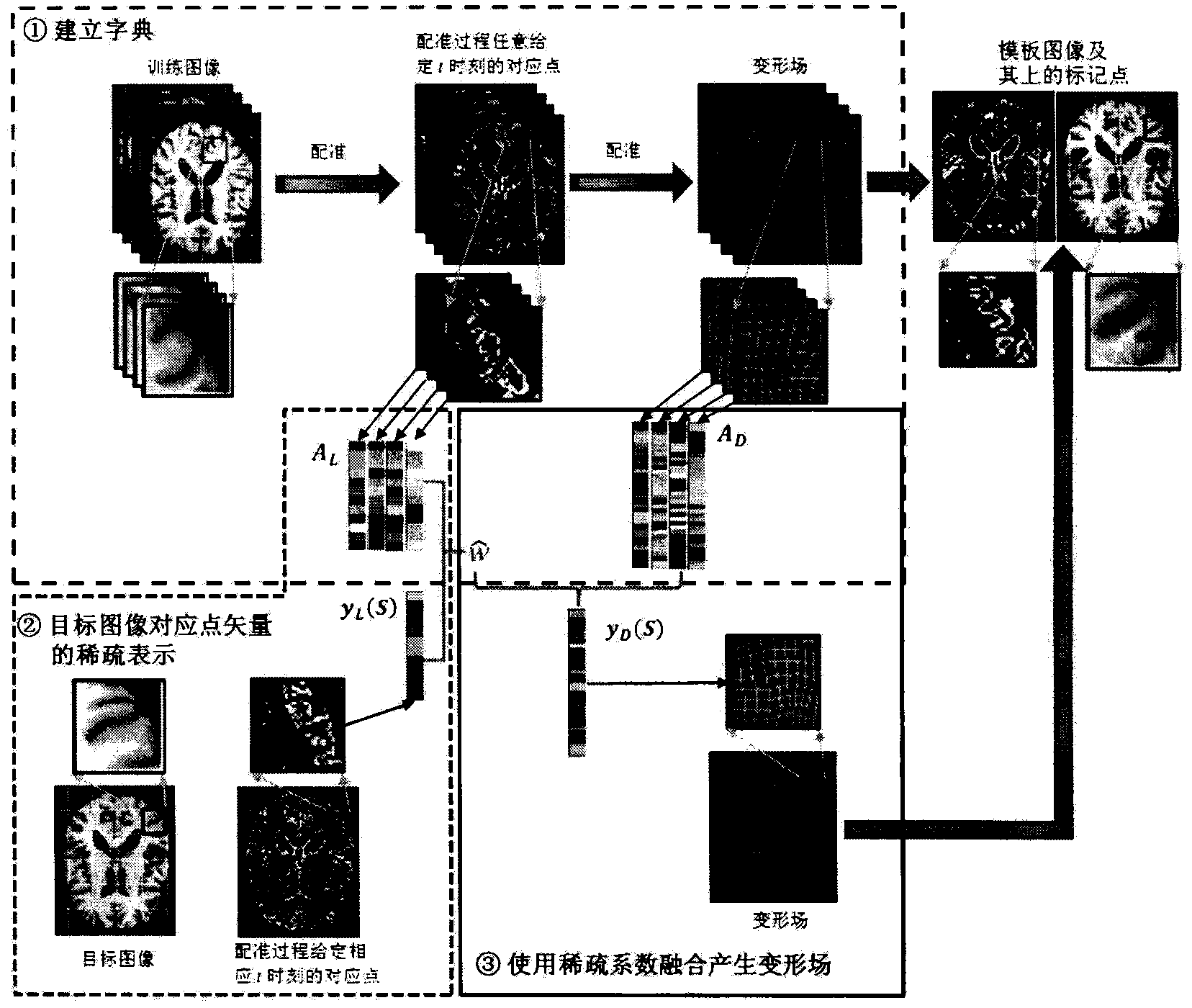
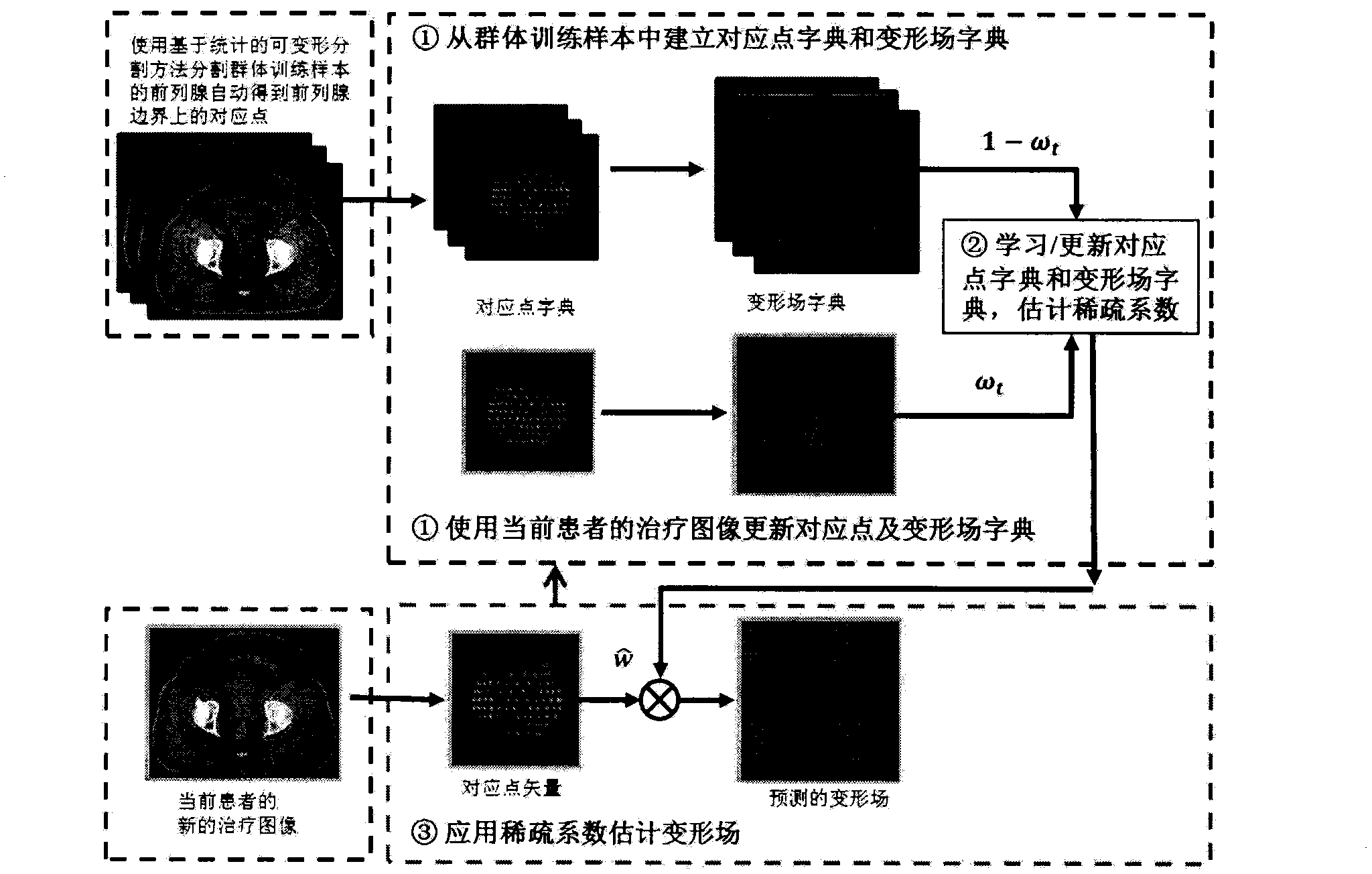
[0034] The goal of deformable-based registration is to register the target image S to the template image T. In many applications, a small number of P marker points or key points on the template image are usually first determined by manual labeling or an automatic marker point detector. The coordinates of these P template marker points can be stored in a long vector x, where Finally, in order to register the target image to the template image, it is necessary to estimate the corresponding points of the target image (stored in the vector y) from the marker points of the template image (stored in the vector x) L (S)) estimates its deformation field y D (S), here, the corresponding points and deformation fields defined by the present invention are all stored in the vector, and the present invention proposes a method based on machine learning to estimate the dense deformation field from discrete corresponding point vectors, that is, it is effective by means of sparse representation...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com