Universal method for preparing polymeric vesicles with sensitive response
A technology of polymers and vesicles, applied in capsule delivery, microcapsules, nanocapsules, etc., can solve problems such as changes in physical and chemical properties, a large amount of stimulation time, and difficulty in penetrating small organic molecules
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0043] The technical solution of the present invention will be described in further detail below. It should be noted that the various embodiments of the present invention can be combined in any way as desired.
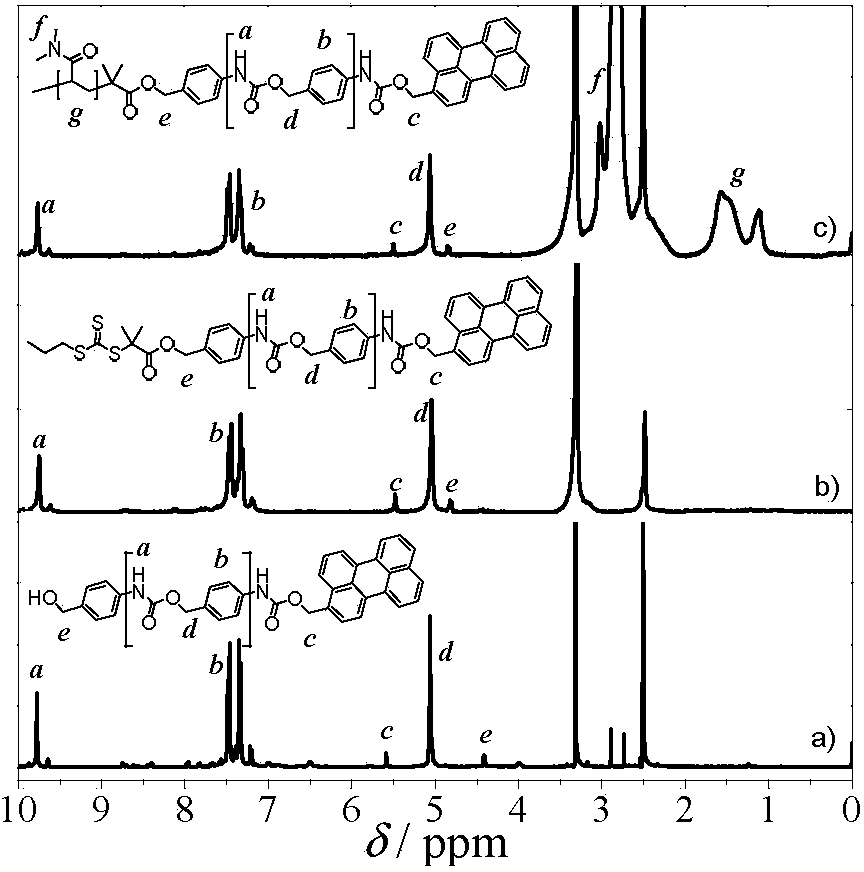
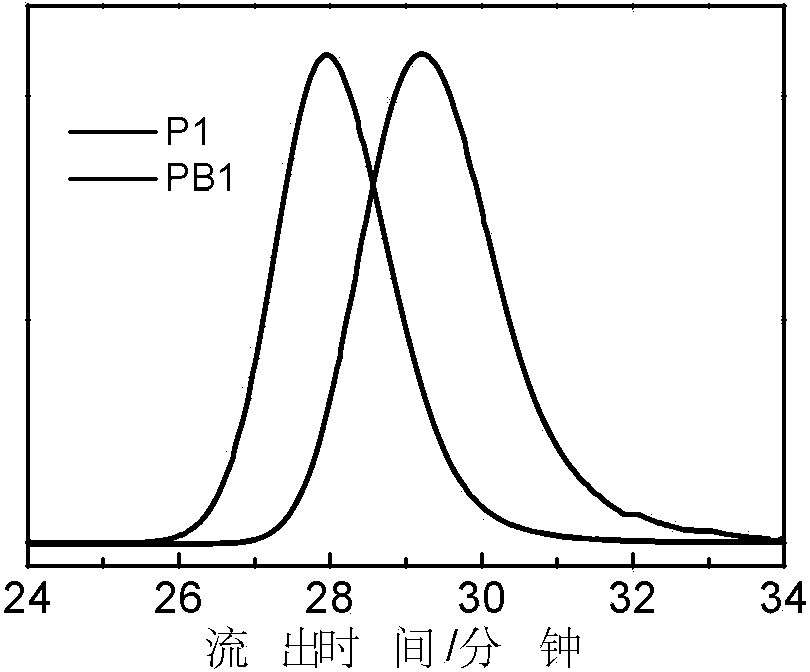
[0044] Polymeric vesicles are usually self-assembled from amphiphilic block polymers and contain a hydrophilic inner cavity surrounded by a hydrophobic bilayer membrane. Therefore, hydrophilic and hydrophobic substances, such as drugs, enzyme substrates, (bio)catalysts, etc., can be simultaneously loaded in polymersomes. However, the hydrophobic barrier properties of the vesicle bilayer membrane hinder the penetration of hydrophilic substances and also bring difficulties to the controllable loading / release of hydrophobic substances. This poses serious challenges to the practical application of vesicles in drug delivery vehicles, nanoreactors, and artificial organelles / cells. To solve this problem, block copolymers containing nucleating blocks capable of changing solu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap