A low-nickel austenitic stainless steel
An austenitic stainless steel, mass percentage technology, applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve the problems of more effective utilization of unfavorable resources, low strength, high nickel content, reduce intergranular corrosion sensitivity, improve tensile strength at room temperature, and improve resistance to corrosion. The effect of pitting performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
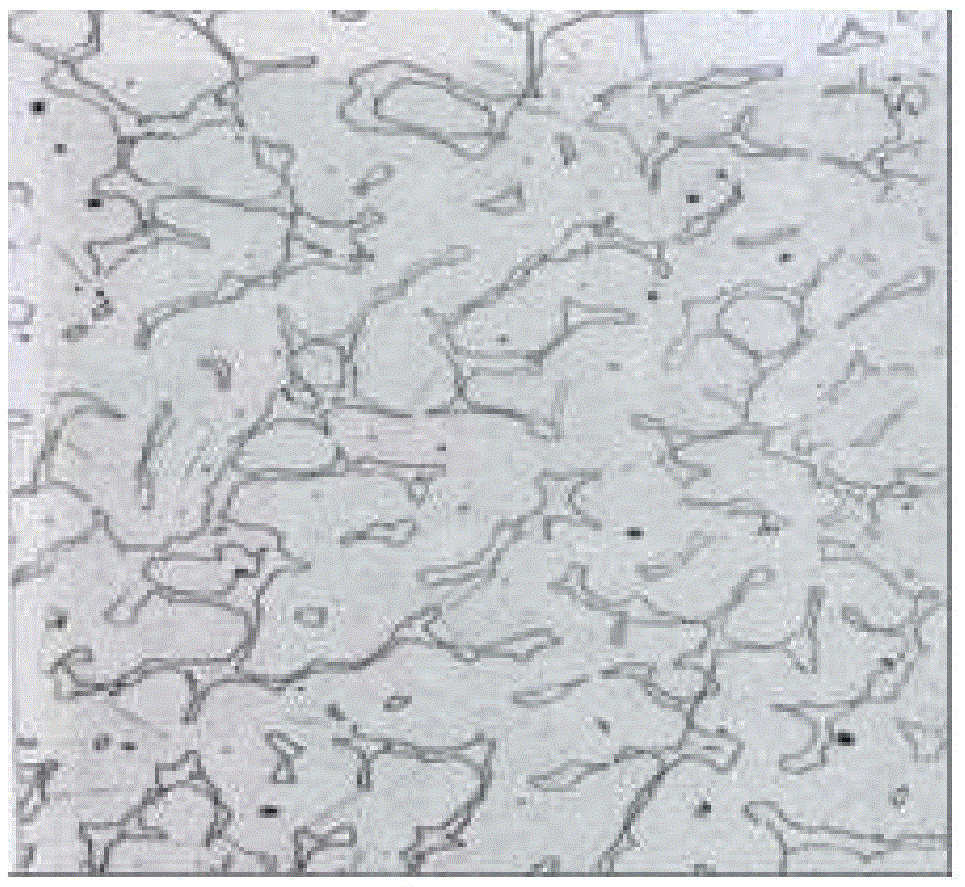
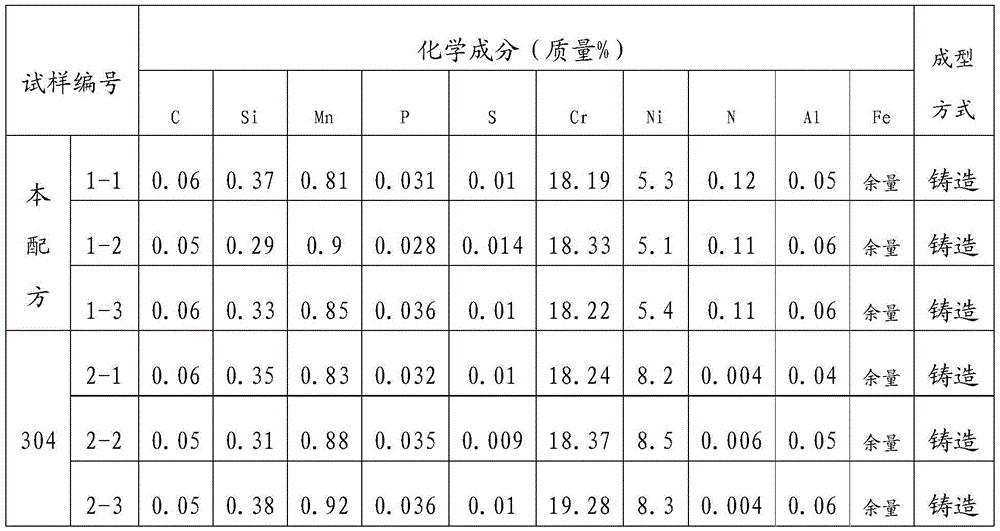
[0040] The low-nickel austenitic stainless steel having the chemical composition shown in 1-1 in Table 1 was melted in an electric furnace, and formed by hot forging and hot rolling. Then, heat treatment was carried out by heating to 1200° C., followed by water cooling, and then a steel plate with a thickness of 20 mm, a width of 50 mm, and a length of 100 mm was produced by machining.
[0041] In addition, 1-1 in Table 1 is the steel whose chemical composition falls within the range prescribed|regulated by this invention.
[0042] On the other hand, 2-1 is the conventional 304 stainless steel of the comparative example outside the conditions prescribed|regulated by this invention.
Embodiment 2
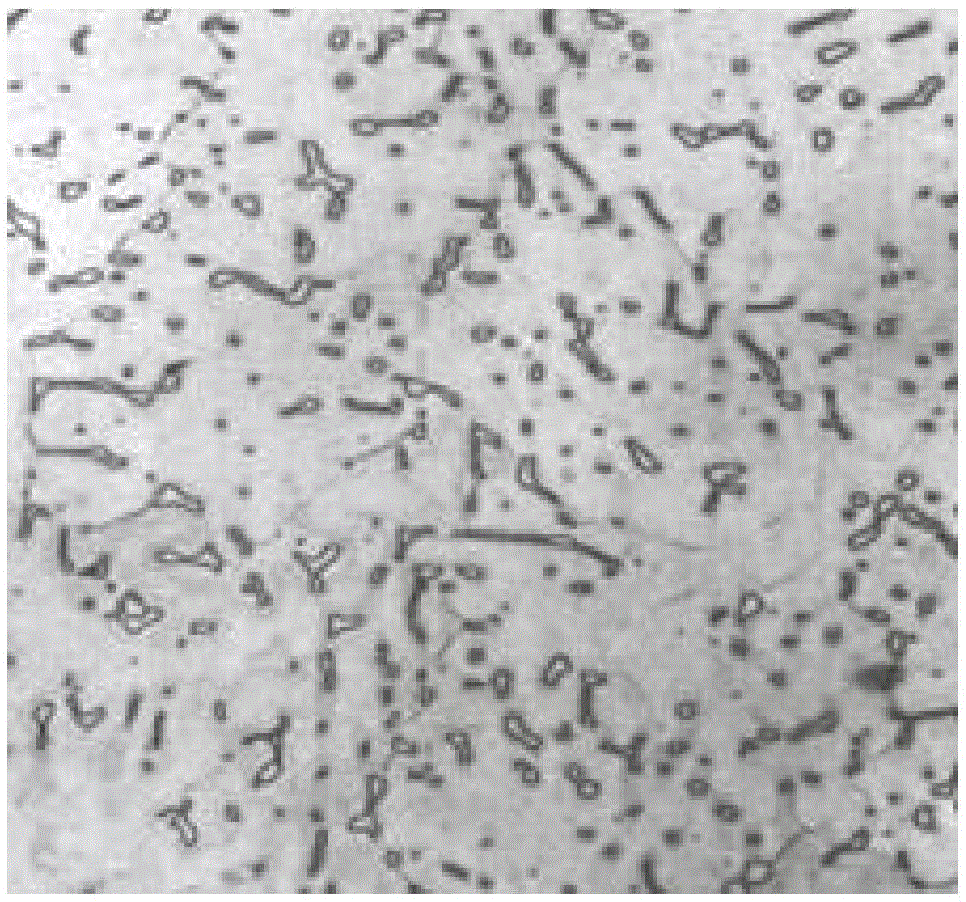
[0046] The low-nickel austenitic stainless steel with the chemical composition shown in 1-2 in Table 1 was melted in an electric furnace, and formed by hot forging and hot rolling. Then, heat treatment was carried out by heating to 1200° C., followed by water cooling, and then a steel plate with a thickness of 20 mm, a width of 50 mm, and a length of 100 mm was produced by machining.
[0047] In addition, 1-2 in Table 1 is the steel whose chemical composition falls within the range prescribed|regulated by this invention.
[0048] On the other hand, 2-2 is the conventional 304 stainless steel of the comparative example outside the conditions prescribed|regulated by this invention.
Embodiment 3
[0052] The low-nickel austenitic stainless steel with the chemical composition shown in 1-3 in Table 1 was melted in an electric furnace, and formed by hot forging and hot rolling. Then, heat treatment was carried out by heating to 1200° C., followed by water cooling, and then a steel plate with a thickness of 20 mm, a width of 50 mm, and a length of 100 mm was produced by machining.
[0053] In addition, 1-3 in Table 1 is the steel whose chemical composition falls within the range prescribed|regulated by this invention.
[0054] On the other hand, 2-3 is the conventional 304 stainless steel of the comparative example outside the conditions prescribed|regulated by this invention.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com