Saturation correction method for temperature measurement of pure rotational Raman lidar
A Raman laser and temperature measurement technology, applied in the measurement field, can solve the problems of reducing the occurrence rate of saturation phenomenon, difficult to obtain accurately, and large error in the measurement of atmospheric temperature near the ground.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
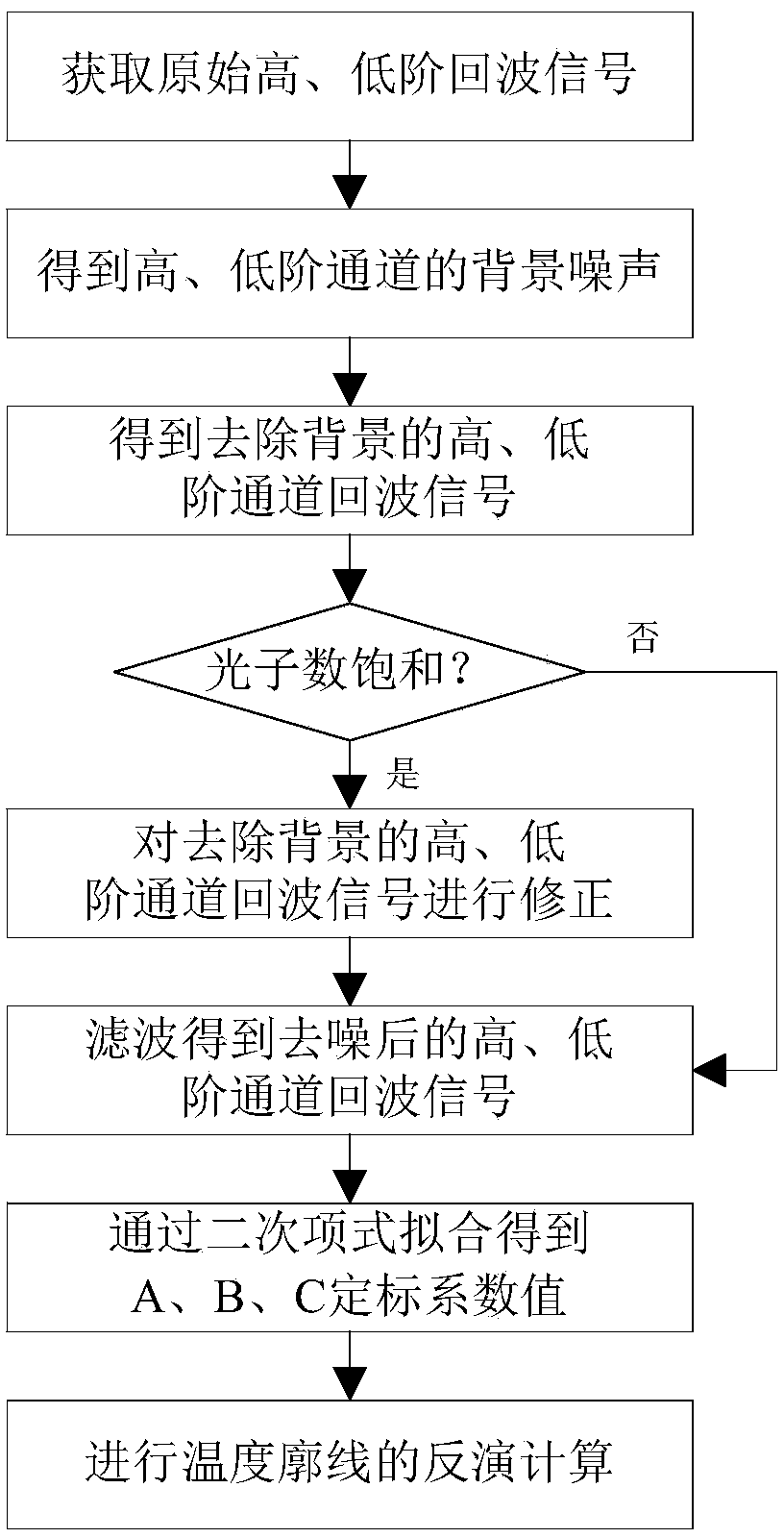
[0039] In order to illustrate the technical solution of the present invention more clearly, a more complete description of the technical solution of the present invention will be given below in conjunction with a specific embodiment and accompanying drawings.
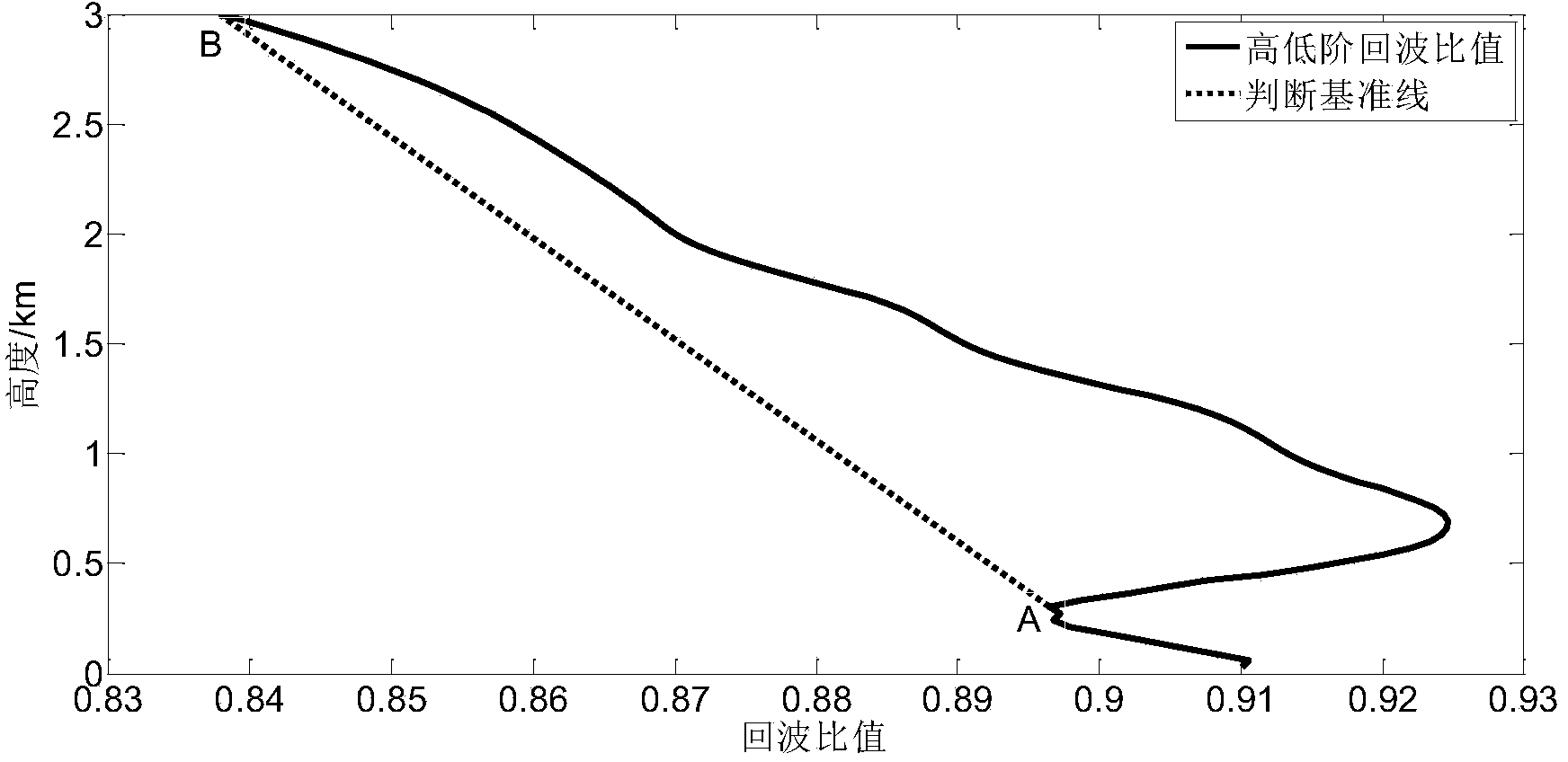
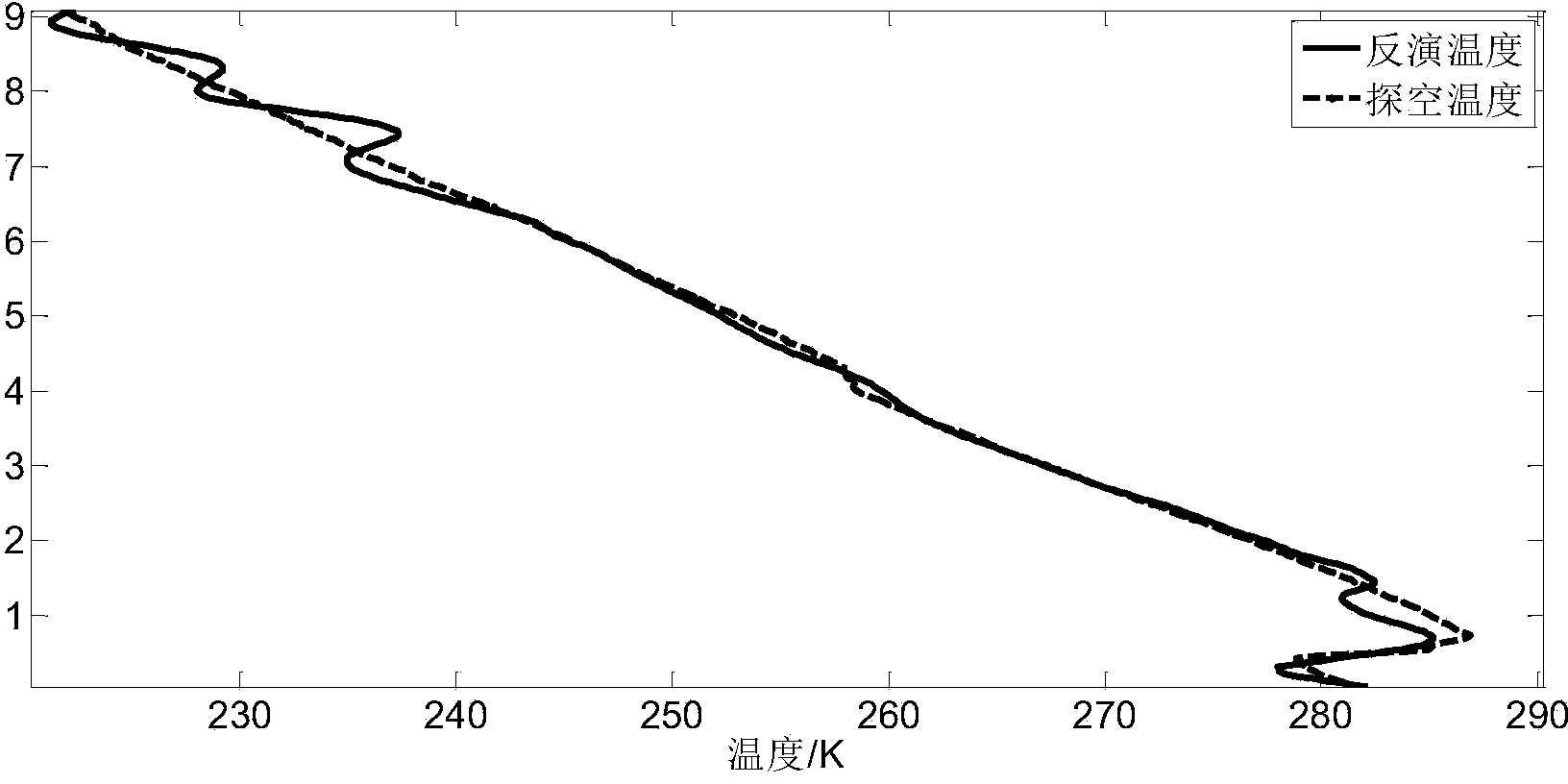
[0040] In this embodiment, the pure rotational Raman lidar data measured at 19:21-21:44 in the evening of 2012.04.06 is corrected by using a saturation correction method for pure rotational Raman lidar temperature measurement proposed by the present invention. Operation process such as figure 1 As shown, the specific operation steps are:
[0041] Step 1: Obtain the original high-order echo signal P of pure rotational Raman lidar 1 and the original low-order echo signal P 2 ;
[0042] Step 2: The original high-order echo signal P obtained by pure rotational Raman lidar 1 The average value of the echo signal of the last 5 km is used as the background noise of the high-order channel P 01 ; The original low-order echo ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com