A Method of Distribution Network Fault Line Selection Based on Correlation Analysis of Zero-mode Current Wavelet Coefficients
A technology of wavelet coefficient and zero-mode current, applied in the direction of the fault location, etc., can solve the problems of extended power outage time, line power outage, damaged circuit breaker, etc., to avoid the influence of compensation and overcome the effect of being susceptible to noise interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
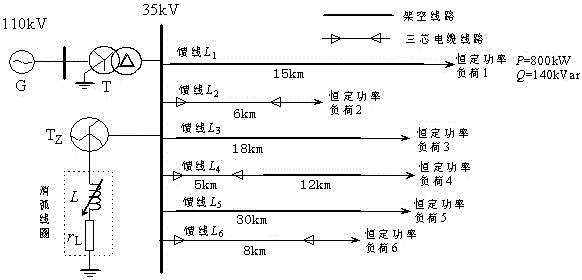
[0038] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 As shown in the distribution network structure, set the feeder L 1 An AG fault occurs 5 kilometers away from the beginning, the transition resistance is 20Ω, and the initial phase angle of the fault is 90°.
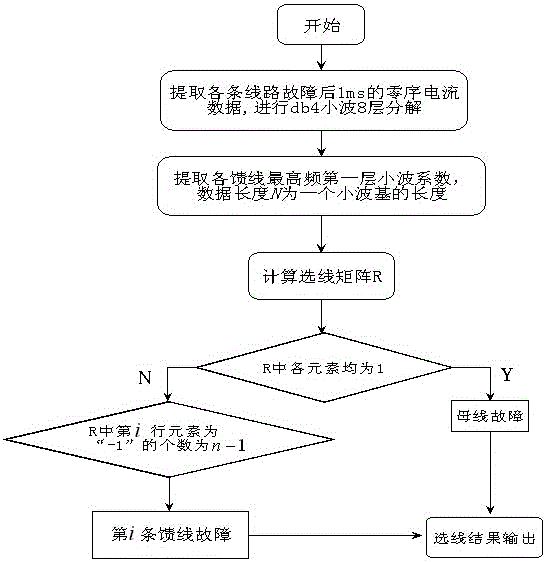
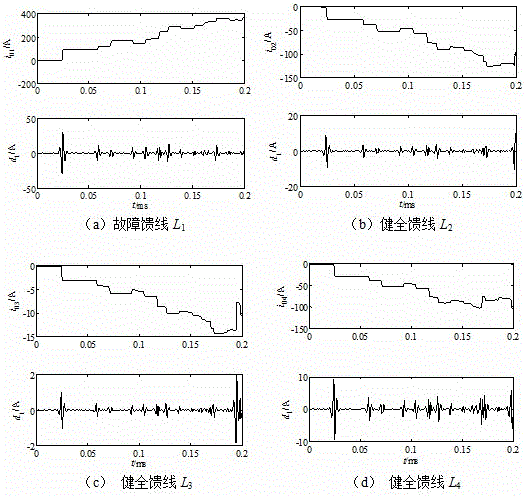
[0039] (1) The sampling rate is 1MHz, and the wavelet decomposition is carried out by extracting the zero-mode current traveling wave in the 0.2ms short-time window of each line. Here, the db4 wavelet base is used as an example to illustrate, and the high-frequency first-scale wavelet coefficient is selected as the research object ,Such as image 3 shown;
[0040] (2) Calculate the relative polarity of the high-frequency first-scale wavelet coefficients of each feeder line whose total number of lines is 6 according to formula (1);
[0041] (3) Calculate according to formula (2) to form the distribution network fault line selection matrix R.
[0042] R = 1 ...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Embodiment 2: as figure 1 As shown in the distribution network structure, set the feeder L 2 An AG fault occurs 4 kilometers away from the beginning, the transition resistance is 10Ω, and the initial phase angle of the fault is 90°.
[0045] (1) The sampling rate is 1MHz, and the wavelet decomposition is carried out by extracting the zero-mode current traveling wave in the 0.2ms short-time window of each line. Here, the db4 wavelet base is used as an example to illustrate, and the high-frequency first-scale wavelet coefficient is selected as the research object ;
[0046] (2) Calculate the relative polarity of the high-frequency first-scale wavelet coefficients of each feeder line whose total number of lines is 6 according to formula (1);
[0047](3) Calculate according to formula (2) to form the distribution network fault line selection matrix R.
[0048] R = 1 - ...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Embodiment 3: as figure 1 In the distribution network structure shown, set the AG fault on the bus, the transition resistance is 10Ω, and the initial phase angle of the fault is 90°.
[0051] (1) The sampling rate is 1MHz, and the wavelet decomposition is carried out by extracting the zero-mode current traveling wave in the 0.2ms short-time window of each line. Here, the db4 wavelet base is used as an example to illustrate, and the high-frequency first-scale wavelet coefficient is selected as the research object ;
[0052] (2) Calculate the relative polarity of the high-frequency first-scale wavelet coefficients of each feeder line whose total number of lines is 6 according to formula (1);
[0053] (3) Calculate according to formula (2) to form the distribution network fault line selection matrix R.
[0054] R = 1 1 1 1 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com