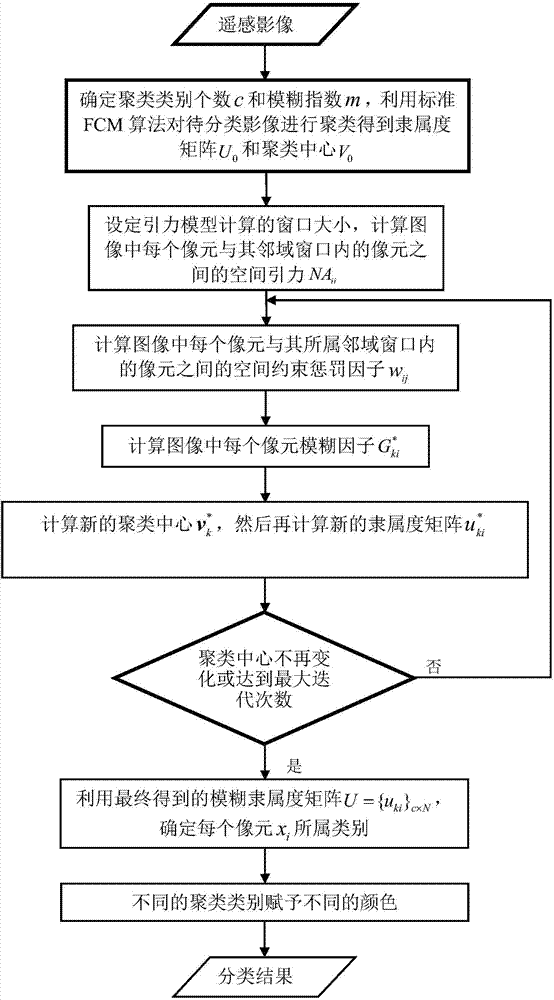
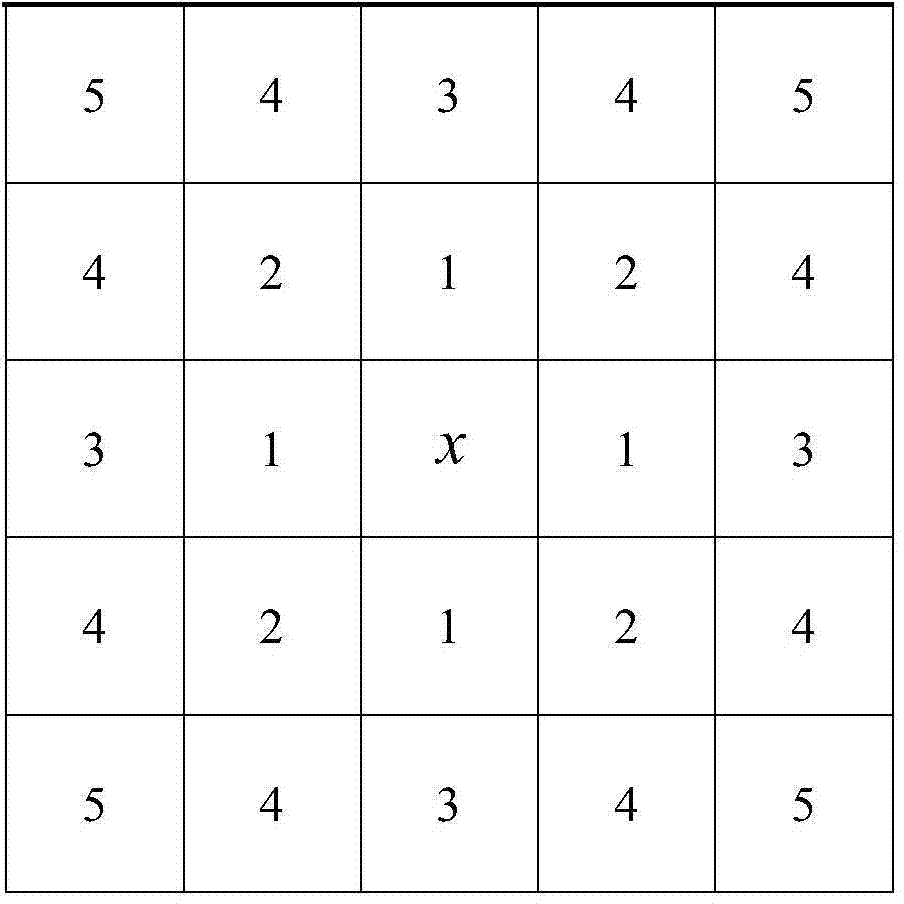
Spatial gravity model based fuzzy c-means remote sensing image automatic classification method
A remote sensing image and gravitational model technology, which is applied in image analysis, image data processing, character and pattern recognition, etc., can solve the problem of not considering the membership degree value of the central pixel, the edge of the region is too smooth, and the fuzzy factor calculation method has no physical meaning, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
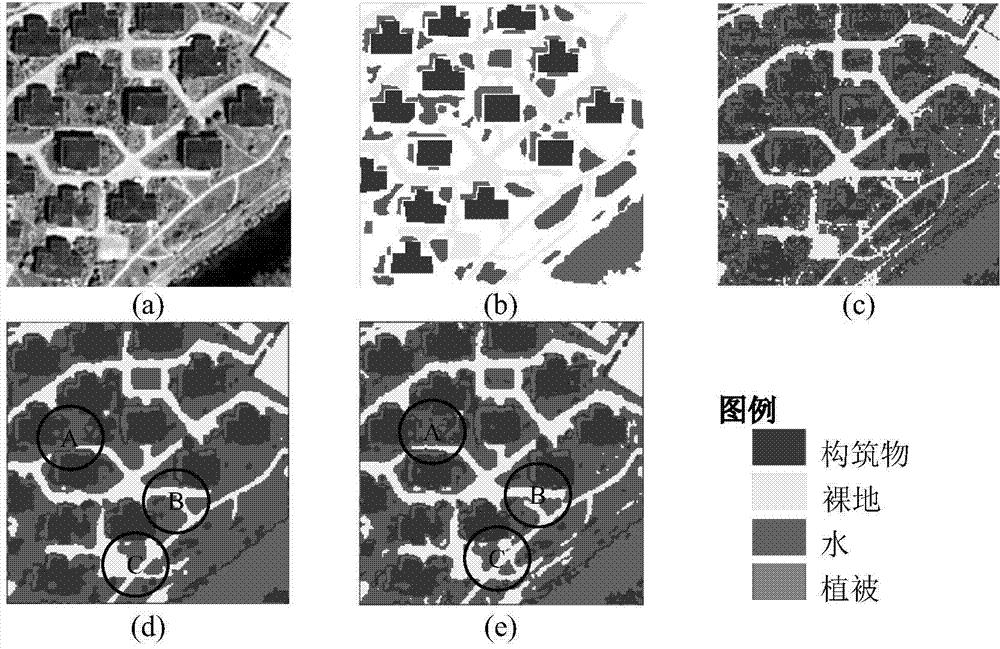
[0043] Embodiment 1. The QuickBird remote sensing image with a resolution of 0.61 meters and a size of 200×200 pixels including red, green and blue bands is used. This data is located in the urban area of Xuzhou City, Jiangsu Province, China, and the acquisition time is 2005 August, if image 3 (a) and (b) are the original classification image and the reference data image respectively. The images are divided into 4 categories: structures, bare land, water and vegetation, and the fuzzy index is 2.
[0044] image 3 (c)-(e) represent the classification results of FCM, FLICM and FLNAICM, respectively, image 3 In (c), due to the similarity of the spectrum and the existence of image noise, FCM only uses the spectral characteristics of the image without considering the spatial context information, resulting in many "salt and pepper" phenomena in the classification results. From image 3 (d) and image 3 (e) It can be seen that the classification effect of FLICM and FLNAICM is...
Embodiment 2
[0048] In Example 2, a QuickBird remote sensing image with a size of 200×200 pixels and a resolution of 0.61 meters including red, green and blue bands was used. This data is located in the suburban area of Xuzhou City, Jiangsu Province, China. The acquisition time for August 2005, as Figure 4 (a) and Figure 4 (b) are the original classification image and the reference data image respectively. The image is divided into 4 categories: road, bare land, water and vegetation, and the fuzzy index is 2.
[0049] Figure 4 (c)-(e) are the classification results of FCM, FLICM and FLNAICM respectively, Figure 4 In (c), due to the similarity of the spectrum and the existence of image noise, the FCM classification method only uses the spectral characteristics of the image without considering the spatial context information, and a large number of "salt and pepper" phenomena appear in the classification results. From Figure 4 (d) and Figure 4(e) It can be seen that the classific...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com