Competition and cooperation clustering method based on maximum clearance segmentation of dynamic bounding box
A technology of maximum gap and clustering method, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems that affect the use effect and practical value of CCL clustering algorithm, initial seed points are sensitive and difficult to determine, etc. , to avoid clustering fragmentation, improve stability, and speed up clustering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0060] The present invention will be described in further detail in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
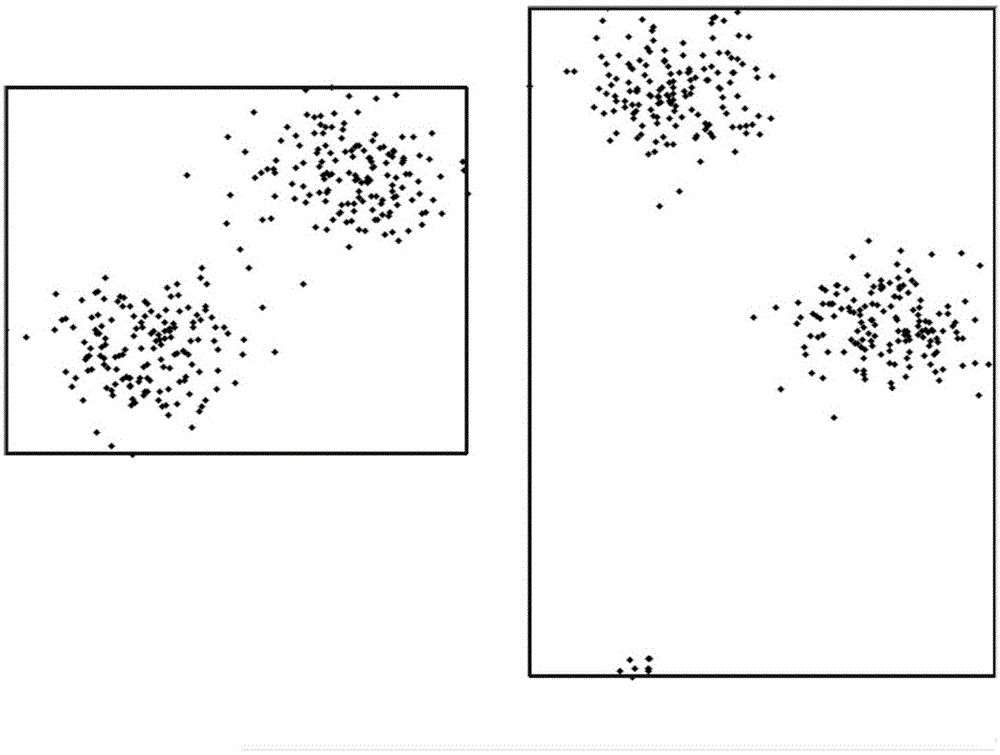
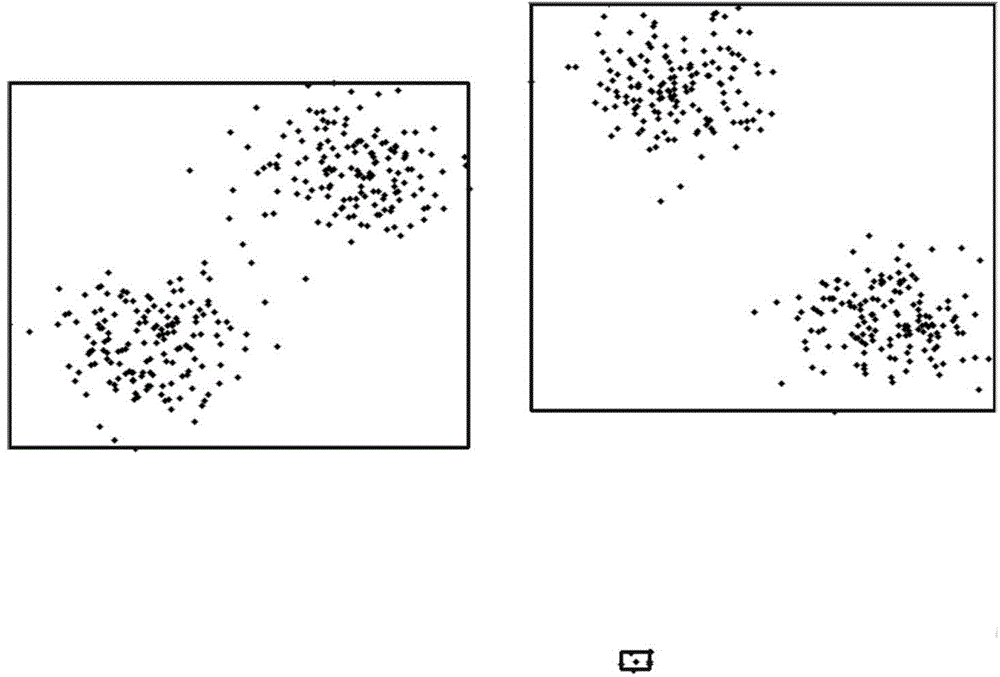
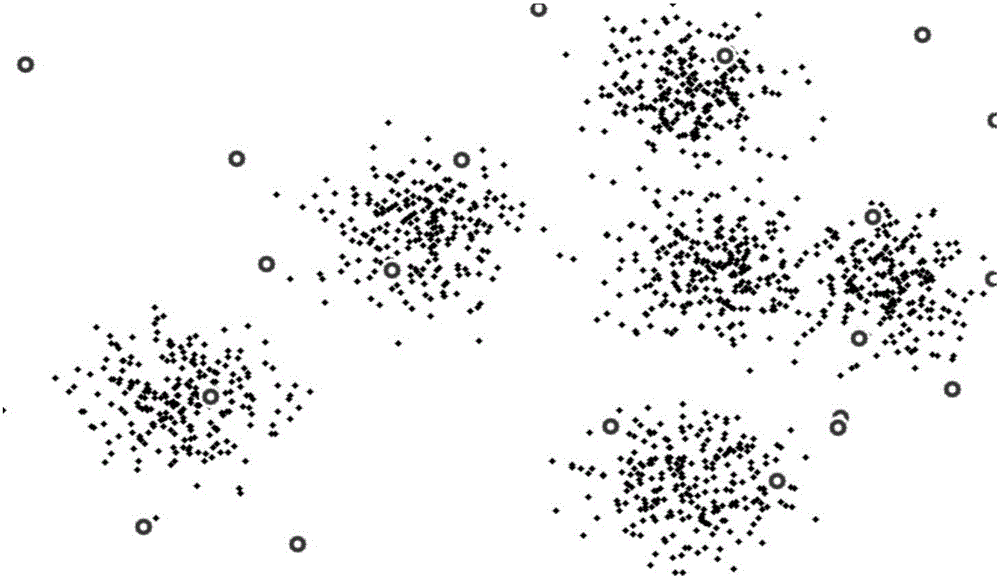
[0061] The present invention discovers its deficiencies through experiments and analysis of the original CCL clustering algorithm, and makes targeted improvements. Concepts and symbols involved in the present invention are defined as follows:
[0062] Input sample: the input data, each input data is a multidimensional vector, denoted as x i , i represents the i-th input data;
[0063] Seed point: also called clustering center in the present invention, a vector with the same dimension as the input data, denoted as c i , i represents the i-th seed point;
[0064] Winner: For the current input data x i , distance x i The closest seed point is called the winner, denoted as c w , the distance measure here adopts Euclidean distance;
[0065] Cooperation group: for the current input data x i , with the winner c w as the center, ||c w -x ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com